Abstract
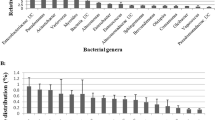
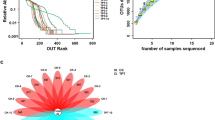
The insect egg surface can serve as a vehicle for vertical symbiont transmission from the maternal parent to its offspring. Hypochlorite and formaldehyde are two common disinfectants used for insect egg surface sterilization. Here, we explored the intestinal microecology and immune response profile of the silkworm Bombyx mori strain Dazao after disinfectant exposure by using high-throughput sequencing technology and real-time PCR analysis. After egg surface sterilization, no significant difference (P > 0.05) in overall body weight was observed among the control, sodium hypochlorite, and formaldehyde groups. 16S rRNA metagenomic sequencing revealed that the main abundant intestinal bacteria were Enterococcus, Burkholderia, Phenylobacterium, Ralstonia, Chitinophaga, Bradyrhizobium, Herbaspirillum, and two unclassified Bacteroidetes species. Egg surface sterilization evidently altered the composition and abundance of intestinal microbiota but did not significantly change its alpha diversity. The dysbiosis of intestinal microbiota resulted in the perturbation of the immune response profile of the silkworm intestine. Our findings reveal that hypochlorite has a blocking effect on the symbiont transmission compared with formaldehyde. More importantly, egg surface sterilization exerts substantial effects on the ecophysiological traits of insects. The present study contributes to the scientific and reasonable application of disinfectants for insect egg surface sterilization during industrial silk production and laboratory-scale insect rearing.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aydin ZU, Akpinar KE, Hepokur C, Erdönmez D (2018) Assessment of toxicity and oxidative DNA damage of sodium hypochlorite, chitosan and propolis on fibroblast cells. Braz Oral Res 32:e119
Beall JR, Ulsamer AG (1984) Formaldehyde and hepatotoxicity: a review. J Toxicol Environ Health 14:1–21
Bicalho MLS, Machado VS, Higgins CH, Lima FS, Bicalho RC (2017) Genetic and functional analysis of the bovine uterine microbiota. Part I: metritis versus healthy cows. J Dairy Sci 100:3850–3862
Banskar S, Mourya DT, Shouche YS (2016) Bacterial diversity indicates dietary overlap among bats of different feeding habits. Microbiol Res 182:99–108
Barko PC, McMichael MA, Swanson KS, Williams DA (2018) The gastrointestinal microbiome: a review. J Vet Intern Med 32:9–25
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stomabaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Cappellozza S, Saviane A, Tettamanti G, Squadrin M, Vendramin E, Paolucci P, Franzetti E, Squartini A (2011) Identification of Enterococcus mundtii as a pathogenic agent involved in the “flacherie” disease in Bombyx mori L. larvae reared on artificial diet. J Invertebr Pathol 106:386–393
Chen L, Zhou W, Zhou Y, Tan TT, Feng LC (2019) Analysis of the effects of nanosilver on bacterial community in the intestinal fluid of silkworms using high-throughput sequencing. Bull Entomol Res 27:1–13
Chen Y, Tian W, Shao Y, Li YJ, Lin LA, Zhang YJ, Han H, Chen ZJ (2020) Miscanthus cultivation shapes rhizosphere microbial community structure and function as assessed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing combined with PICRUSt and FUNGUIld analyses. Arch Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01830-1
Dhital R, Paudel A, Bohra N, Shin AK (2020) Herbaspirillum Infection in Humans: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Case Rep Infect Dis 19(2020):9545243. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9545243
Dornelles LV, Procianoy RS, Roesch LFW, Corso AL, Priscila TD, Mai V, Silveira RC (2020) Meconium microbiota predicts clinical early-onset neonatal sepsis in preterm neonates. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767058.2020.1774870
Duong A, Steinmaus C, McHale CM, Vaughan CP, Zhang LP (2011) Reproductive and developmental toxicity of formaldehyde: a systematic review. Mutat Res 728:118–138
Engel P, Moran NA (2013) The gut microbiota of insects – diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:699–735
Ferrari J, Vavre F (2011) Bacterial symbionts in insects or the story of communities affecting communities. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 366:1389–1400
Ge J, Yang HL, Lu XX, Wang SQ, Zhao Y, Huang JW, Xi ZG, Zhang LP, Li R (2020) Combined exposure to formaldehyde and PM2.5: hematopoietic toxicity and molecular mechanism in mice. Environ Int 144:106050
Grau T, Vilcinskas A, Joop G (2017) Probiotic Enterococcus mundtii isolate protects the model insect Tribolium castaneum against Bacillus thuringiensis. Front Microbiol 8:1261
Gulati A, Sood S, Rahi P, Thakur R, Chauhan S, Chawla I (2011) Diversity analysis of diazotrophic bacteria associated with the roots of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:545–555
Hirsch AM, Fujishige NA (2008) Commensalisms. Encyclopedia Ecol 679–683
Imler JL, Bulet P (2020) Antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila: structures, activities and gene regulation. Chem Immunol Allergy 86:1–21
Kaiwa N, Hosokawa T, Kikuchi Y, Nikoh N, Meng XY, Kimura N, Ito M, Fukatsu T (2010) Primary gut symbiont and secondary, sodalis-allied Symbiont of the scutellerid stinkbug Cantao ocellatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3486–3494
Karamipour N, Fathipour Y, Mehrabadi M (2017) Gammaproteobacteria as essential primary symbionts in the striped shield bug, Graphosoma Lineatum (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Sci Rep 7:40271
Kwon YM, Kim HJ, Kim YI, Kang YJ, Lee IH, Jin BR, Han YS, Cheon HM, Ha NG, Seo SJ (2008) Comparative analysis of two attacin genes from Hyphantria cunea. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 151:213–220
Li GN, Xia XJ, Tang WC, Zhu Y (2016) Intestinal microecology associated with fluoride resistance capability of the silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:6715–6724
Li GN, Xia XJ, Zhao S, Shi M, Liu FD, Zhu Y (2020a) The physiological and toxicological effects of antibiotics on an interspecies insect model. Chemosphere 248:126019
Li GN, Zheng X, Zhu Y, Long YH, Xia XJ (2022) Bacillus symbiont drives alterations in intestinal microbiota and circulating metabolites of lepidopteran host. Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15934
Li MX, Li FC, Lu ZT, Fang YL, Qu JW, Mao TT, Wang H, Chen J, Li B (2020b) Effects of TiO2 nanoparticles on intestinal microbial composition of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Sci Total Environ 704:135273
Liu W, Wang Y, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Wang D, Jiang Y, Shi S, Qin L (2019) Peptidoglycan recognition proteins regulate immune response of Antheraea pernyi in different ways. J Invertebr Pathol 166:107204
Macêdo LPR, Dornelas ASP, Vieira MM, Ferreira JSDJ, Sarmento RJ, Cavallini GS (2019) Comparative ecotoxicological evaluation of peracetic acid and the active chlorine of calcium hypochlorite: use of Dugesia tigrina as a bioindicator of environmental pollution. Chemosphere 233:273–281
McLean AHC, van Asch M, Ferrari J, Godfray HCJ (2011) Effects of bacterial secondary symbionts on host plant use in pea aphids. Proc R Soc B 278:760–766
Miao Z, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Liu J, Wang G (2019) Single-cell analysis reveals the effects of glutaraldehyde and formaldehyde on individual Nosema bombycis spores. Analyst 144:3136–3143
Nakajima H, Matsumoto Y, Sekimizu K (2018) Establishment of a gnotobiotic silkworm model. Drug Discov Ther 12:291–294
Plain KM, Marsh IB, Waldron AM, Galea F, Whittington AM, Saunders VF, Begg DJ, de Silva K, Purdie AC, Whittington RJ (2014) High-throughput direct fecal PCR assay for detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in sheep and cattle. J Clin Microbiol 52:745–757
Rai MM, Gore DG, Rathod MK, Khurad AM (2013) Evidence of transovarial transmission of Bacillus subtilis in the silkworm, Bombyx mori L. J Pharm Res 7:318–323
Remenant B, de Cambiaire JC, Cellier G, Jacobs JM, Mangenot S, Barbe V, Lajus A, Vallenet D, Medigue C, Fegan M, Allen C, Prior P (2011) Ralstonia syzygii, the blood disease bacterium and some Asian R. solanacearum strains form a single genomic species despite divergent lifestyles. PLoS One 6:e24356
Rhodes KA, Schweizer HP (2016) Antibiotic resistance in Burkholderia species. Drug Resist Updat 28:82–90
Salem H, Florez L, Gerardo N, Kaltenpoth M (2015) An out-of-body experience: the extracellular dimension for the transmission of mutualistic bacteria in insects. Proc Biol Sci 282:20142957
Slaughter RJ, Watts M, Vale JA, Grieve JR, Schep LS (2019) The clinical toxicology of sodium hypochlorite. Clin Toxicol 57:303–311
Sudha R, Murthy GN, Awasthi AK, Ponnuvel K (2015) Attacin gene sequence variations in different ecoraces of Tasar silkworm Antheraea mylitta. Bioinformation 11:481–485
Sun ZL, Lu YH, Zhang H, Kumar D, Liu B, Gong YC, Zhu M, Zhu LY, Liang Z, Kuang SL, Chen F, Hu XL, Cao GL, Xue RY, Gong CL (2016) Effects of BmCPV infection on silkworm Bombyx mori intestinal bacteria. PLoS One 11:30146313
Taylor S, Wakem M, Dijkman G, Alsarraj M, Nguyen M (2010) A practical approach to RT-qPCR-publishing data that conform to the MIQE guidelines. Methods 50:S1-5
Voirol LRP, Frago E, Kaltenpoth M, Fatouros NE (2018) Bacterial symbionts in Lepidoptera: their diversity, transmission, and impact on the host. Front Microbiol 9:556
Wang M, Zheng KW, Lin JL, Huang MH, Ma Y, Li S, Luo XC, Wang JF (2008) Rapid and efficient production of cecropin A antibacterial peptide in Escherichia coli by fusion with a self-aggregating protein. BMC Biotechnol 18:62
Watson E, MacNeil LT, Ritter AD, Yilmaz LS, Rosebrock AP, Caudy AA, Walhout AJM (2014) Interspecies systems biology uncovers metabolites affecting C. elegans gene expression and life history traits. Cell 156:759–770
Wexler HM (2007) Bacteroides: the good, the bad, and the nitty-gritty. Clin Microbiol Rev 20:593–621
Willing BP, Russell SL, Finlay BB (2011) Shifting the balance: antibiotic effects on host-microbiota mutualism. Nat Rev Microbioal 9:233e243
Yuval B (2017) Symbiosis: gut bacteria manipulate host behaviour. Curr Biol 27:R746–R747
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to everyone who provided the means for us to access the free software used and cited in this article.
Funding
This research was supported by the Chongqing Special Grant for Postdoctoral Researchers (Grant No. Xm2017177), the Guizhou Medical University cultivation Plan for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 19NSP065), the Guizhou Provincial Natural Science Foundation [2020]1Y139, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32160816).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guannan Li wrote the main manuscript text; Yong Zhu and Yaohang Long performed the study conception and design; Guannan Li, Miao Cai, Xi Zheng, and Xiaofan Xie performed the experiments. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript, and all authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the standards of the Animal Management Committee of Southwest University, China.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Giovanni Benelli.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Cai, M., Zheng, X. et al. Impact of disinfectants on the intestinal bacterial symbionts and immunity of silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 79545–79554 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21442-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21442-0