Abstract
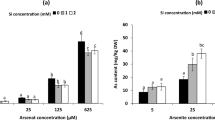
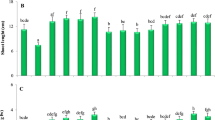
Arsenic (As) is known to be one of the most toxic metalloids for humans and plants; however, little is known about the use of silicon (Si) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles (NPs) in reducing As toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). The experiment was conducted to examine the effects of Si-NPs (50 and 100 mg/L), TiO2-NPs (25 and 50 mg/L) and As (50 µM) on growth, photosynthetic pigments, antioxidant defense system, glyoxalase system, expression of Si/As transporters, and genes involved in As sequestration in rice under hydroponic conditions. The results revealed that Si- and TiO2-NPs by upregulating the activity of antioxidant enzymes and glyoxalase cycle reduced hydrogen peroxide, methylglyoxal, malondialdehyde, and electrolyte leakage, and thus protected the photosynthetic apparatus and improved plant growth under As stress. By increasing the expression of GSH1, PCS, and ABC1 genes, Si- and TiO2-NPs increased leaf and root accumulation of glutathione and phytochelatins and sequestered As in vacuoles, which protected plant cells from As toxicity. Si-NPs diminished As uptake and increased Si uptake in As-exposed rice plants by modulating the expression of Si/As transporters (Lsi1, Lsi2, and Lsi6). The results depicted that 100 mg/L Si-NPs treatment had the highest positive effect on plant growth and tolerance under As stress compared to other treatments. In general, Si- and TiO2-NPs augmented the growth of rice under As stress through different strategies, which can be used to design effective fertilizers to enhance the crop growth and yield in areas contaminated with toxic metals.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in Vitro. Method Enzymol 105:121–126
Asgari F, Majd A, Jonoubi P, Najafi F (2018) Effects of silicon nanoparticles on molecular, chemical, structural and ultrastructural characteristics of oat (Avena sativa L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 127:152–160
Bidi H, Fallah H, Niknejad Y, Barari Tari D (2021) Iron oxide nanoparticles alleviate arsenic phytotoxicity in rice by improving iron uptake, oxidative stress tolerance and diminishing arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiol Biochem 163:348–357
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen R, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Liu Z (2018) Foliar application with nano-silicon reduced cadmium accumulation in grains by inhibiting cadmium translocation in rice plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:2361–2368
De Vos RCH, Vonk MJ, Vooijs R, Schat H (1992) Glutathione depletion due to copper-induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol 98l:853–858
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Gerami M, Ghorbani A, Karimi S (2018) Role of salicylic acid pretreatment in alleviating cadmium-induced toxicity in Salvia officinalis L. Iran J Plant Biol 10(1):81–95
Ghasemi-Omran VO, Ghorbani A, Sajjadi-Otaghsara SA (2021) Melatonin alleviates NaCl-induced damage by regulating ionic homeostasis, antioxidant system, redox homeostasis, and expression of steviol glycosides-related biosynthetic genes in in vitro cultured Steviarebaudiana Bertoni. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 57:319–331
Ghorbani A, Ghasemi Omran VO, Razavi SM, Pirdashti H, Ranjbar M (2019) Piriformospora indica confers salinity tolerance on tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) through amelioration of nutrient accumulation, K+/Na+ homeostasis and water status. Plant Cell Rep 38:1151–1163
Ghorbani A, Pishkar L, Roodbari N, Pehlivan N, Wu C (2021) Nitric oxide could allay arsenic phytotoxicity in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by modulating photosynthetic pigments, phytochelatin metabolism, molecular redox status and arsenic sequestration. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:337–348
Ghorbani A, Razavi SM, Ghasemi Omran VO, Pirdashti H (2018a) Piriformospora indica alleviates salinity by boosting redox poise and antioxidative potential of tomato. Russ J Plant Physiol 65:898–907
Ghorbani A, Razavi SM, Ghasemi Omran VO, Pirdashti H (2018b) Piriformospora indica inoculation alleviates the adverse effect of NaCl stress on growth, gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Biol 20:729–736
Ghorbani A, Tafteh M, Roudbari N, Pishkar L, Zhang W, Wu C (2020) Piriformosporaindica augments arsenic tolerance in rice (Oryzasativa) by immobilizing arsenic in roots and improving iron translocation to shoots. Ecotoxicol Environmen Saf 209:111793
Ghorbani A, Zarinkamar F, Fallah A (2009) The effect of cold stress on the morphologic and physiologic characters of tow rice varieties in seedling stage. J Crop Breed 1:50–66
Ghorbani A, Zarinkamar F, Fallah A (2011) Effect of cold stress on the anatomy and morphology of the tolerant and sensitive cultivars of rice during germination. J Cell Tissue 2(3):235–244
Giannopolitis CN, Reis SK (1977) Super oxide dismutase. I Occurrence in Higher Plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gohari G, Mohammadi A, Akbari A, Panahirad S, Dadpour MR, Fotopoulos V, Kimura S (2020) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) promote growth and ameliorate salinity stress effects on essential oil profile and biochemical attributes of Dracocephalum moldavica. Sci Rep 10:912
Guo J, Dai X, Xu W, Ma M (2008) Overexpressing GSH1 and AsPCS1 simultaneously increases the tolerance and accumulation of cadmium and arsenic in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chemosphere 72(7):1020–1026
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hoagland D, Arnon D (1941) Physiological aspects of availability of nutrients for plant growth. Soil Sci 51:431–444
Hossain MA, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2010) Up-regulation of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems by exogenous glycinebetaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:259–272
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SA, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Hussain A, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Ali S (2019) Seed priming with silicon nanoparticles increased biomass and yield while reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat grains. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(8):7579–7588
Ivanova LA, Ronzhina DA, Ivanov LA, Stroukova LV, Peuke AD, Rennenberg H (2011) Over-expression of gsh1 in the cytosol affects the photosynthetic apparatus and improves the performance of transgenic poplars on heavy metal-contaminated soil. Plant Biol 13(4):649–659
Khan ZS, Rizwan M, Hafeez M, Ali S, Adrees M, Qayyum MF, Khalid S, Ur Rehman MZ, Sarwar MA (2020) Effects of silicon nanoparticles on growth and physiology of wheat in cadmium contaminated soil under different soil moisture levels. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(5):4958–4968
Khan E, Gupta M (2018) Arsenic–silicon priming of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds influence mineral nutrient uptake and biochemical responses through modulation of Lsi-1, Lsi-2, Lsi-6 and nutrient transporter genes. Sci Rep 8:10301
Kim EH, Yoon NJ, Kim SU, Kwon TK, Sohn S, Choi KS (2008) Arsenic trioxide sensitizes human glioma cells, but not normal astrocytes, to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein dependent DR5 up-regulation. Cancer Res 68:266–275
Kong X, Liu T, Yu Z, Chen Z, Lei D, Wang Z, Zhang H, Li Q, Zhang S (2018) Heavy metal bioaccumulation in rice from a high geological background area in Guizhou Province, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(10):2281
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using Realtime quantitative PCR and the 2–ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lukačová Z, Švubová R, Kohanová J, Lux A (2013) Silicon mitigates the Cd toxicity in maize in relation to cadmium translocation, cell distribution, antioxidant enzymes stimulation and enhanced endodermal apoplasmic barrier development. Plant Growth Regul 70:89–103
Ma JF, Mitani N, Nagao S, Konishi S, Tamai K, Iwashita T, Yano M (2004) Characterization of the silicon uptake system and molecular mapping of the silicon transporter gene in rice. Plant Physiol 136(2):3284–3289
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Tamai K, Mitani N (2007) Genotypic difference in silicon uptake and expression of silicon transporter genes in rice. Plant Physiol 145(3):919–924
Mohamed AK, Qayyum MF, Abdel-Hadi AM, Rehman RA, Ali S, Rizwan M (2017) Interactive effect of salinity and silver nanoparticles on photosynthetic and biochemical parameters of wheat. Arch Agron Soil Sci 63:1736–1747
Mousavi SR, Niknejad Y, Fallah H, Barari-Tari D (2020) Methyl jasmonate alleviates arsenic toxicity in rice. Plant Cell Rep 39:1041–1060
Munir T, Rizwan M, Kashif M, Shahzad A, Ali S, Amin N, Zahid R, Alam MF, Imran M (2018) effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the growth and Zn uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by seed priming method. Digest J Nanomater Biostr 13:315–323
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Principato GB, Rosi G, Talesa V, Govannini E, Uolila L (1987) Purification and characterization of two forms of glyoxalase II from rat liver and brain of Wistar rats. Biochem Biophys Acta 911:349–355
Rafique R, Zahra Z, Virk N, Shahid M, Pinelli E, Park TJ, Kallerhoff J, Arshad M (2018) Dose-dependent physiological responses of Triticum aestivum L. to soil applied TiO2 nanoparticles: alterations in chlorophyll content, H2O2 production, and genotoxicity. Agri Ecosyst Environ 255:95–101
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM, Miah MAM, Tasmin A (2008) Straight head disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.) induced by arsenic toxicity. Environ Exp Bot 62:54–59
Ramezani M, Enayati M, Ramezani M, Ghorbani A (2021) A study of different strategical views into heavy metal (oid) removal in the environment. Arab J Geosci 14:2225
Rizwan M, Ali S, ur Rehman MZ, Malik S, Adrees M, Qayyum MF, Alamri SA, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019) Effect of foliar applications of silicon and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on growth, oxidative stress, and cadmium accumulation by rice (Oryzasativa). Acta Physiol Plant 41:35
Schaedle M, Bassham JA (1977) Chloroplast glutathione reductase. Plant Physiol 59:1011–1022
Sharma DK, Andersen SB, Ottosen CO, Rosenqvist E (2012) Phenotyping of wheat cultivars for heat tolerance using chlorophyll a fluorescence. Funct Plant Biol 39(11):936–947
Shen SW, Li XF, Cullen WR, Weinfeld M, Le XC (2013) Arsenic binding to proteins. Chem Rev 113:7769–7792
Singh J, Lee BK (2016) Influence of nano-TiO2 particles on the bioaccumulation of Cd in soybean plants (Glycine max): a possible mechanism for the removal of Cd from the contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 170:88–96
Sinha S, Saxena R, Singh S (2005) Chromium induced lipid peroxidation in the plants of Pistia stratiotes L.: role of antioxidants and antioxidant enzymes. Chemosphere 58:595–604
Sun GX, Van de Wiele T, Alava P, Tack F, Du Laing G (2012) Arsenic in cooked rice: effect of chemical, enzymatic and microbial processes on bioaccessibility and speciation in the human gastrointestinal tract. Environ Pollut 162:241–246
Tripathi DK, Singh S, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (2016) Silicon nanoparticles more efficiently alleviate arsenate toxicity than silicon in maize cultiver and hybrid differing in arsenate tolerance. Front Environ Sci 4:46
Tripathi P, Tripathi RD, Singh RP, Dwivedi S, Goutam D, Shri M, Trivedi PK, Chakrabarty D (2013) Silicon mediates arsenic tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) through lowering of arsenic uptake and improved antioxidant defence system. Ecol Eng 52:96–103
Yamaji N, Mitatni N, Ma JF (2008) A transporter regulating silicon distribution in rice shoots. Plant Cell 20(5):1381–1389
Yu CW, Murphy TM, Lin CH (2003) Hydrogen peroxide-induced chilling tolerance in mung beans mediated through ABA-independent glutathione accumulation. Funct Plant Biol 30(9):955–963
Zhang W, Long J, Geng J, Li J, Wei Z (2020) Impact of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on Cd phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(9):2979
Zhao FJ, Ma JF, Meharg AA, McGrath SP (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181:777–794
Zhu YG, Sun GX, Lei M, Teng M, Liu YX, Chen NC, Wang LH, Carey AM, Deacon C, Raab A, Meharg AA, Williams PN (2008) High percentage inorganic arsenic content of mining impacted and nonimpacted Chinese rice. Environ Sci Technol 42:5008–5013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology, T.K., L.P.; Validation and Investigation, L.P., N.S.; Analysis, T.K., G.B.; Resources, L.P., A.I.; Writing original, T.K.; Review and editing, L.P.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiany, T., Pishkar, L., Sartipnia, N. et al. Effects of silicon and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on arsenic accumulation, phytochelatin metabolism, and antioxidant system by rice under arsenic toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 34725–34737 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17927-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17927-z