Abstract
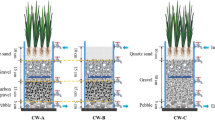
Four subsurface flow constructed wetlands (SFCWs) filled with different substrates including ceramsite, ceramsite+pyrite, ceramsite+ferrous sulfide, and ceramsite+pyrite+ferrous sulfide (labeled as SFCW-S1, SFCW-S2, SFCW-S3, and SFCW-S4) were constructed, and the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus by these SFCWs coupled with intermittent aeration in the front section was discussed. The key findings from different substrate analyses, including nitrification and denitrification rate, enzyme activity, microbial community structure, and the X-ray diffraction, revealed the nitrogen and phosphorus removal mechanism. The results showed that the nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency for SFCW-S1 always remained the lowest, and the phosphorus removal efficiency for SFCW-S4 was recorded as the highest one. However, after controlling the dissolved oxygen by intermittent aeration in the front section of SFCWs, the nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiencies of SFCWs-S2 and S4 became higher than those of SFCW-S1, and SFCW-S3. It was noticed that the pollutants were removed mainly in the front section of the SFCWs. Both precipitation and adsorption on the substrate were the main mechanisms for phosphorus removal. A minute difference of nitrification rate and ammonia monooxygenase activity was observed in the SFCWs’ aeration zone. The denitrification rates, nitrate reductase, nitrite reductase, and electron transport system activity for SFCW-S2 and SFCW-S4 were higher than those detected for SFCW-S1 and SFCW-S3 in the non-aerated zone. Proteobacteria was the largest phyla found in the SFCWs. Moreover, Thiobacillus occupied a large proportion found in SFCW-S2, and SFCW-S4, and it played a crucial role in pyrite-driven autotrophic denitrification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Kandil A, Shibli A, Azaizeh H, Wolff D, Wick A, Jadoun J (2021) Fate and removal of bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in horizontal subsurface constructed wetlands: effect of mixed vegetation and substrate type. Sci Total Environ 759:144193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144193
Adyasari D, Hassenrück C, Oehler T, Sabdaningsih A, Moosdorf N (2019) Microbial community structure associated with submarine groundwater discharge in northern Java (Indonesia). Sci Total Environ 689:590–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.193
Anjali G, Sabumon PC (2015) Development of enhanced SNAD process in a down-flow packed bed reactor for removal of higher concentrations of NH4–N and COD. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.02.022
Bae H, Chung YC, Jung JY (2010) Microbial community structure and occurrence of diverse autotrophic ammonium oxidizing microorganisms in the anammox process. Water Sci Technol 61:2723–2732. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.075
Baldovi AA, de Barros Aguiar AR, Benassi RF, Vymazal J, de Jesus TA (2021) Phosphorus removal in a pilot scale free water surface constructed wetland: hydraulic retention time, seasonality and standing stock evaluation. Chemosphere 266:128939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128939
Bernat K, Kulikowska D, Zielińska M, Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A, Wojnowska-BarylA I (2011) Nitrogen removal from wastewater with a low COD/N ratio at a low oxygen concentration. Bioresour Technol 102:4913–4916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.116
Bosch J, Lee KY, Jordan G, Kim KW, Meckenstock RU (2011) Anaerobic, nitrate-dependent oxidation of pyrite nanoparticles by thiobacillus denitrificans. Environ Sci Technol 46:2095–2101. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2022329
Buelna G, Dubé R, Turgeon N (2008) Pig manure treatment by organic bed biofiltration. Desalination 231:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.11.049
Chakraborty A, Picardal F (2013) Induction of nitrate-dependent Fe(II) oxidation by Fe(II) in Dechloromonas sp. strain UWNR4 and Acidovorax sp. strain 2AN. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:748–752. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02709-12
Chiu YC, Chung M-S (2003) Determination of optimal COD/nitrate ratio for biological denitrification. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 51:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(02)00074-4
Dong X, Reddy GB (2012) Ammonia-oxidizing bacterial community and nitrification rates in constructed wetlands treating swine wastewater. Ecol Eng 40:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.12.022
Dong L, Qi Z, Li M, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Qi Y, Wu H (2021) Organics and nutrient removal from swine wastewater by constructed wetlands using ceramsite and magnetite as substrates. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104739
Du S, Tao Y, Zhang M, Zhu M, Wang X (2020) Distinct microbial communities and their networks in an anammox coupled with sulfur autotrophic/mixotrophic denitrification system. Environ Pollut 262:114190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114190
Ge Z, Wei D, Zhang J, Hu J, Liu Z, Li R (2019) Natural pyrite to enhance simultaneous long-term nitrogen and phosphorus removal in constructed wetland: Three years of pilot study. Water Res 148:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.037
Ge X, Cao X, Song X, Wang Y, Si Z, Zhao Y, Wang W, Tesfahunegn AA (2020) Bioenergy generation and simultaneous nitrate and phosphorus removal in a pyrite-based constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 296:122350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122350
Guan W, Yin M, He T, Xie S (2015) Influence of substrate type on microbial community structure in vertical-flow constructed wetland treating polluted river water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16202–16209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5160-9
Higgins D, Curtin T, Pawlett M, Courtney R (2016) The potential for constructed wetlands to treat alkaline bauxite-residue leachate: Phragmites australis growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:24305–24315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7702-1
Hussein A, Scholz M (2018) Treatment of artificial wastewater containing two azo textile dyes by vertical-flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:6870–6889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0992-0
Ibekwe AM, Ma J, Murinda S, Reddy GB (2016) Bacterial community dynamics in surface flow constructed wetlands for the treatment of swine waste. Sci Total Environ 544:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.139
Ishimoto C, Sugiyama T, Matsumoto T, Uenishi H, Waki M (2020) Full-scale simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox, and denitrification process for treating swine-wastewater. Water Sci Technol 81:456–465. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.120
Juncher Jørgensen C, Jacobsen OS, Elberling B, Aamand J (2009) Microbial oxidation of pyrite coupled to nitrate reduction in anoxic groundwater sediment. Environ Sci Technol 43:4851–4857. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803417s
Kolmonen E, Sivonen K, Rapala J, Haukka K (2004) Diversity of cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria in cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Joutikas, Finland. Aquat Microb Ecol 36:201–211. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame036201
Kong Z, Li L, Feng C, Dong S, Chen N (2016) Comparative investigation on integrated vertical-flow biofilters applying sulfur-based and pyrite-based autotrophic denitrification for domestic wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 211:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.083
Kumar G, Radha V, Jagadeeshwari U, Sasikala C, Venkata Ramana C (2020) Bacterial communities of sponges from the wetland ecosystem of Little Rann of Kutch, India with particular reference to Planctomycetes. 3. Biotech 10:478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02449-1
Lai X, Zhao Y, Pan F, Yang B, Wang H, Wang S, He F (2020) Enhanced optimal removal of nitrogen and organics from intermittently aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands: Relative COD/N ratios and microbial responses. Chemosphere 244:125556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125556
Leang C, Coppi MV, Lovley DR (2003) OmcB, a c-type polyheme cytochrome, involved in Fe(III) reduction in Geobacter sulfurreducens. J Bacteriol 185:2096–2103. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.185.7.2096-2103.2003
Li R, Morrison L, Collins G, Li A, Zhan X (2016) Simultaneous nitrate and phosphate removal from wastewater lacking organic matter through microbial oxidation of pyrrhotite coupled to nitrate reduction. Water Res 96:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.034
Li H, Chi Z, Yan B, Cheng L, Li J (2017) An innovative wood-chip-framework substrate used as slow-release carbon source to treat high-strength nitrogen wastewater. J Environ Sci 51:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.07.008
Li R, Wei D, Wang W, Zhang Y (2020) Pyrrhotite-sulfur autotrophic denitrification for deep and efficient nitrate and phosphate removal: synergistic effects, secondary minerals and microbial community shifts. Bioresour Technol 308:123302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123302
Lin Z, Xu F, Wang Y, Huang W, Zhou J, He Q, Zhou J (2020) Autotrophic nitrogen removal by partial nitrification-anammox process in two-stage sequencing batch constructed wetlands for low-strength ammonium wastewater. J Water Process Eng 38:101625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101625
Miot J, Maclellan K, Benzerara K, Boisset N (2011) Preservation of protein globules and peptidoglycan in the mineralized cell wall of nitrate-reducing, iron(II)-oxidizing bacteria: a cryo-electron microscopy study. Geobiol. 9:459–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4669.2011.00298.x
Nicomrat D, Dick WA, Tuovinen OH (2006) Assessment of the microbial community in a constructed wetland that receives acid coal mine drainage. Microb Ecol 51:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-005-0267-z
Okada N, Nomura N, Nakajima-Kambe T, Uchiyama H (2005) Characterization of the aerobic denitrification in Mesorhizobium sp. strain NH-14 in comparison with that in related rhizobia. Microbes Environ 20:208–215. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.20.208
Omwene PI, Kobya M (2018) Treatment of domestic wastewater phosphate by electrocoagulation using Fe and Al electrodes: a comparative study. Process Saf Environ Prot 116:34–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.01.005
Pan Z, Zhou J, Lin Z, Wang Y, Zhao P, Zhou J, Liu S, He X (2020) Effects of COD/TN ratio on nitrogen removal efficiency, microbial community for high saline wastewater treatment based on heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification process. Bioresour Technol 301:122726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122726
Park M, Kim J, Lee T, Oh YK, Cho S (2020) Correlation of microbial community with salinity and nitrogen removal in an anammox-based denitrification system. Chemosphere 263:128340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128340
Rashidan KK, Bird DF (2001) Role of predatory bacteria in the termination of a cyanobacterial bloom. Microb Ecol 41:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002480000074
Rìos-Montes KA, Casas-Zapata JC, Briones-Gallardo R, Peñuela G (2017) Optimal conditions for chlorothalonil and dissolved organic carbon in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. J Environ Sci Health B 52:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2016.1273005
Rizzo A, Tondera K, Pálfy TG, Dittmer U, Meyer D, Schreiber C, Zacharias N, Ruppelt JP, Esser D, Molle P, Troesch S, Masi F (2020) Constructed wetlands for combined sewer overflow treatment: a state-of-the-art review. Sci Total Environ 727:138618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138618
Rous V, Vymazal J, Hnátková T (2019) Treatment wetlands aeration efficiency: a review. Ecol Eng 136:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.06.006
Sahinkaya E, Dursun N, Kilic A, Demirel S, Uyanik S, Cinar O (2011) Simultaneous heterotrophic and sulfur-oxidizing autotrophic denitrification process for drinking water treatment: control of sulfate production. Water Res 45:6661–6667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.056
Si Z, Song X, Wang Y, Cao X, Zhao Y, Wang B, Chen Y, Arefe A (2018) Intensified heterotrophic denitrification in constructed wetlands using four solid carbon sources: denitrification efficiency and bacterial community structure. Bioresour Technol 267:416–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.029
Si Z, Song X, Wang Y, Cao X, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Ge X (2021) Natural pyrite improves nitrate removal in constructed wetlands and makes wetland a sink for phosphorus in cold climates. J Clean Prod 280:124304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124304
Stefanakis AI (2020) Constructed wetlands for sustainable wastewater treatment in hot and arid climates: opportunities, challenges and case studies in the Middle East. Water 12:1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061665
Sun G, Gray KR, Biddlestone AJ, Allen SJ, Cooper DJ (2004) Effect of effluent recirculation on the performance of a reed bed system treating agricultural wastewater. Process Biochem 39:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00075-X
Tan X, Yang YL, Li X, Zhou ZW, Liu CJ, Liu YW, Yin WC, Fan XY (2020) Intensified nitrogen removal by heterotrophic nitrification aerobic denitrification bacteria in two pilot-scale tidal flow constructed wetlands: influence of influent C/N ratios and tidal strategies. Bioresour Technol 302:122803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122803
Ter Braak CJF, Prentice IC (1988) A theory of gradient analysis. Adv Ecol Res 18:271–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60183-X
Torrentó C, Cama J, Urmeneta J, Otero N, Soler A (2010) Denitrification of groundwater with pyrite and Thiobacillus denitrificans. Chem Geol 278:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.09.003
Vipindas PV, Krishnan KP, Rehitha TV, Jabir T, Dinesh SL (2020) Diversity of sediment associated Planctomycetes and its related phyla with special reference to anammox bacterial community in a high Arctic fjord. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36:107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02886-3
Wan R, Chen Y, Zheng X, Su Y, Li M (2016) Effect of CO2 on microbial denitrification via inhibiting electron transport and consumption. Environ Sci Technol 50:9915–9922. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05850
Wang Y, Lin Z, Wang Y, Huang W, Wang J, Zhou J, He Q (2019) Sulfur and iron cycles promoted nitrogen and phosphorus removal in electrochemically assisted vertical flow constructed wetland treating wastewater treatment plant effluent with high S/N ratio. Water Res 151:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.005
Wang JJ, Huang BC, Li J, Jin RC (2020) Advances and challenges of sulfur-driven autotrophic denitrification (SDAD) for nitrogen removal. Chin Chem Lett 31:2567–2574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.07.036
Wang SS, Cheng HY, Zhang H, Su SG, Sun YL, Wang HC, Han JL, Wang AJ (2021) Sulfur autotrophic denitrification filter and heterotrophic denitrification filter: comparison on denitrification performance, hydrodynamic characteristics and operating cost. Environ Res 197:111029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111029
Wu X, Xi W, Ye W, Yang H (2007) Bacterial community composition of a shallow hypertrophic freshwater lake in China, revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequences. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 61:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00326.x
Wu H, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Hu Z, Liang S, Fan J, Liu H (2015) A review on the sustainability of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: design and operation. Bioresour Technol 175:594–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.068
Wu H, Fan J, Zhang J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Liang S, Lv J, Lu S, Wu W, Wu S (2016) Intensified organics and nitrogen removal in the intermittent-aerated constructed wetland using a novel sludge-ceramsite as substrate. Bioresour Technol 210:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.051
Wu Z, Xu F, Yang C, Su X, Guo F, Xu Q, Peng G, He Q, Chen Y (2018) Highly efficient nitrate removal in a heterotrophic denitrification system amended with redox-active biochar: a molecular and electrochemical mechanism. Bioresour Technol 275:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.058
Xu N, Tan G, Wang H, Gai X (2016) Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur J Soil Biol 74:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.02.004
Xu Z, Dai X, Chai X (2018) Effect of different carbon sources on denitrification performance, microbial community structure and denitrification genes. Sci Total Environ 634:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.348
Xu X, Ma S, Jiang H, Yang F (2021) Start-up of the anaerobic hydrolysis acidification (ANHA)- simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD)/enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) process for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal for domestic sewage treatment. Chemosphere 275:130094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130094
Yang Y, Chen T, Morrison L, Gerrity S, Collins G, Porca E, Li R, Zhan X (2017) Nanostructured pyrrhotite supports autotrophic denitrification for simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal from secondary effluents. Chem Eng J 328:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.061
Yang X, He Q, Guo F, Sun X, Zhang J, Chen M, Vymazal J, Chen Y (2020) Nanoplastics disturb nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: responses of microbes and macrophytes. Environ Sci Technol 54:14007–14016. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c03324
Ye L, Shao MF, Zhang T, Tong AHY, Lok S (2011) Analysis of the bacterial community in a laboratory-scale nitrification reactor and a wastewater treatment plant by 454-pyrosequencing. Water Res 45:4390–4398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.05.028
Yuan C, Zhao F, Zhao X, Zhao Y (2020) Woodchips as sustained-release carbon source to enhance the nitrogen transformation of low C/N wastewater in a baffle subsurface flow constructed wetland. Chem Eng J 392:124840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124840
Zhang X, Song Z, Guo W, Lu Y, Qi L, Wen H, Ngo HH (2017) Behavior of nitrogen removal in an aerobic sponge based moving bed biofilm reactor. Bioresour Technol 245:1282–1285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.106
Zhang Q, Chen X, Zhang Z, Luo W, Wu H, Zhang L, Zhang X, Zhao T (2020) Performance and microbial ecology of a novel moving bed biofilm reactor process inoculated with heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacteria for high ammonia nitrogen wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 315:123813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123813
Zhang C, Guisasola A, Baeza JA (2021) Achieving simultaneous biological COD and phosphorus removal in a continuous anaerobic/aerobic A-stage system. Water Res 190:116703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116703
Zhao S, Su X, Wang Y, Yang X, Bi M, He Q, Chen Y (2020) Copper oxide nanoparticles inhibited denitrifying enzymes and electron transport system activities to influence soil denitrification and N2O emission. Chemosphere 245:125394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125394
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This work was supported by Key Research and Development Project of Anhui Province (202104i07020013), the National Water Pollution Control and Treatment Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX07603-004), the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse (PCRRF19034), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51208163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liya Li: writing—original draft; data curation; validation; visualization. Jingwei Feng: writing—review and editing; visualization. Liu Zhang: conceptualization, supervision. Hao Yin: resources, project administration. Chunli Fan: data curation, validation. Zechun Wang: data curation, validation. Menglei Zhao: data curation, validation. Chengchang Ge: data curation, validation. Hao Song: data curation, validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 288 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Feng, J., Zhang, L. et al. Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal by natural pyrite–based constructed wetland with intermittent aeration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 69012–69028 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15461-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15461-6