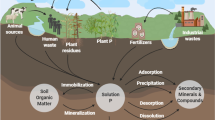
Abstract
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics in soil can cause serious antibiotic pollution. Adsorption is the main factor that influences their destination and transport of antibiotics. Therefore, research on the behaviour of antibiotics once they reach the soil environment is meaningful to design appropriate measures to reduce their potential risks. This research took levofloxacin (LVFX) as the research object and used a static adsorption experiment to study the adsorption behaviour of the vadose zone of silty clay on the North China Plain. The results showed that LVFX had high retention in silty clay, with an average adsorption ratio of more than 90%. Adsorption of LVFX on silty clay reached equilibrium in 24 h with an adsorption amount of 93.5 mg/kg at an initial LVFX concentration of 10 mg/L. Acidity, cations and soil organic matter could affect the adsorption of LVFX, with adsorption variation ratio of 3.3%, 3.4% and 0.6%, respectively. In addition, numerical simulation with Hydrus-1D was utilized, and the results show that LVFX may infiltrate into underground water through silty clay after 28 days and completely penetrate in 100 days.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Beltrán JL, Medeiros J, Prat MD et al (2014) Sorption of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in agricultural soils: effect of organic matter. Adsorpt Sci Technol
Boy-Roura M, Mas-Pla J, Petrovic M et al (2017) Towards the understanding of antibiotic occurrence and transport in groundwater: findings from the Baix Fluvià alluvial aquifer (NE Catalonia, Spain). Sci Total Environ 612:1387–1406
Carter MC, Kilduff JE, Weber WJ (1995) Site energy distribution analysis of preloaded adsorbents. Environ Sci Technol 29(7):1773–1780
Chen QL, An XL, Zheng BX, Ma YB, Su JQ (2018) Long—term organic fertilization increased antibiotic resistome in phyllosphere of maize. Sci Total Environ 645:1230–1237
Chen C, Zhao P, Li Z, Tong Z (2016) Adsorption behaviour of chromium (VI) on activated carbon from eucalyptus sawdust prepared by microwave-assisted activation with ZnCl2. Desalin Water Treat 57(27):12572–12584
Freundlich H (1907) Z Phys Chem 57:385
Gao LH, Shi YL, Li WH et al (2015) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in urban soil in Beijing and Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(15):11360–11371
Gibbs JW (1878) In on the equilibrium of heterogeneous substances. Am J Sci s3-16(96):441–458
Guo T, Lou C, Zhai W, Tang X, Hashmi MZ, Murtaza R, Li Y, Liu X, Xu J (2018) Increased occurrence of heavy metals, antibiotics and resistance genes in surface soil after long-term application of manure. Sci Total Environ 635:995–1003
Halsey G, Taylor HS (1947) The adsorption of hydrogen on tungsten powders. Chem Phys 15:624
Han QF, Zhao S et al (2020) Distribution, combined pollution and risk assessment of antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding the Yellow Sea, North China. Environ Int 138:105551
Hanamoto S, Ogawa F (2019) Predicting the sorption of azithromycin and levofloxacin to sediments from mineral and organic components. Environ Pollut 255(1)
Ho YS (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136(3):681–689
Huang CY, Xu JM (1983) Pedology, 3rd edn. China Agriculture Press, Bei Jing, pp 12–11 (in Chinese)
Jia A, Wan Y, Xiao Y, Hu J (2012) Occurrence and fate of quinolone and fluoroquinolone antibiotics in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Res 46(2):387–394
Kivits, Tano, Broers et al (2018) Presence and fate of veterinary antibiotics in age-dated groundwater in areas with intensive livestock farming. Environ Pollut
Klein EY, Vanboeckel TP, Martinze EM et al (2018) Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(15):3463–3470. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717295115
Ling WC, Fan YM, Fang YY et al (2018) Antibiotics pollution of livestock and poultry breeding in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J Environ Eng Technol 8(4):390–397
Liu YN, Dong CX, Wei H et al (2015) Adsorption of levofloxacin onto an iron-pillared montmorillonite (clay mineral): kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism. Appl Clay Sci 118:301–307
Marchant J (2018) When antibiotics turn toxic. Nature 555(7697):431–433
Mazzei P, Piccolo A (2017) HRMAS NMR spectroscopy applications in agriculture. Chem Biol Technol Agric 4(1):11
Ohore OE, Addo FG, Zhang S, Han N, Anim-Larbi K (2019) Distribution and relationship between antimicrobial resistance genes and heavy metals in surface sediments of Taihu Lake, China. J Environ Sci 77(03):323–335 (In Chinese)
Organization OECD guidelines for testing chemicals (2013) The OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals and pesticides. China Agricultural Press, Beijing
Pan M, Chu LM (2017) Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in soils from waste water irrigation areas in the Pearl River Delta region, southern China. Sci Total Environ 12:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.008
Picó Y, Andreu V (2007) Fluoroquinolones in soil—risks and challenges. Anal Bioanal Chem 387(4):1287–1299
Qin XP, Du P, Chen J et al (2018) Effects of natural organic matter with different properties on levofloxacin adsorption to goethite: experiments and modeling. Chem Eng J 345:425–431 ISSN 1385-8947
Qin XP, Liu F, Wang GC et al (2014) Modeling of levofloxacin adsorption to goethite and the competition with phosphate. Chemosphere 111:283–290
Richmond EK, Rosi EJ, Walters DM, Fick J, Hamilton SK, Brodin T, Sundelin A, Grace MR (2018) A diverse suite of pharmaceuticals contaminates stream and riparian food webs. Nat Commun 9(1):4491
Rodríguez-Liébana JA, Peña A (2020) Differences in the sorption kinetics of various non-ionisable pesticides in a limited number of agricultural soils from the Mediterranean basin. 276
Saha S, Sarkar P (2012) Arsenic remediation from drinking water by synthesized nano-alumina dispersed in chitosan-grafted polyacrylamide. J Hazard Mater 227-228:68–78
Seiki K et al (2006) Adsorption science [M]. Chemical Industry Press (In Japanese)
Shi JZ, Wei H, Zhou XD, Li KB (2020) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin by acidified red mud: process optimization, adsorption characteristics and mechanism. Environ Eng Manag J (In Press)
Shi J, Wei H, Zhou X, Shi Y, Zheng J (2019) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin by acidified red mud: characteristic, mechanism and process optimization. China Environ Sci 39(11):4689–4696 (in Chinese)
Site AD (2001) Factors affecting sorption of organic compounds in natural sorbent/water systems and sorption coefficients for selected pollutants. A review. J Phys Chem Ref Data 30(1):187–439
Van Doorslaer X, Dewulf J, Van Langenhove H et al (2014) Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: an emerging class of environment micropollutants. Sci Total Environ 500-501:250–269
Vaz S, Lopes WT, Martin-Neto L (2015) Study of molecular interactions between humic acid from Brazilian soil and the antibiotic oxytetracycline. Environ Technol Innov 4:260–267
Wan Y, Bao YY, Zhou QX (2010) Effects of soil organic matter and cadmium on adsorption desorption of chlortetracycline. Environ Sci 031(012):3050–3055 (In Chinese)
Wang C, Li YJ, Zhang Z et al (2018) Adsorption of fluoroquinolones in agricultural purple soil. Soil 050(005):958–964 (In Chinese)
Wang CL, Liu CL, Zhang Y et al (2014) Simulation study on the migration of PTA production wastewater in the vadose zone. China Environ Sci 07(7):1824–1824 (In Chinese)
Wang L, Min Z et al (2017) An insight into the removal of fluoroquinolones in activated sludge process: sorption and biodegradation characteristics. J Environ Sci (In Chinese)
Wang S, Wang H (2015) Adsorption behavior of antibiotic in soil environment: a critical review. Front Environ Sci Eng 9(4):565–574
Wang Z, Xue M, Meng ZH et al (2018) Hydrogel nanoparticles for lysozyme affinity study. Chin J Anal Chem 046(003):317–323 (in Chinese)
Wei MX, Lv DY, Cao LH, Yang HY, Jiang K (2020) Effect of pH value on adsorption of levofloxacin in agricultural silty clay of North China. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 474:022020
Wu H, Lu W, Chen Y et al (2020) Application of Boehm titration for the quantitative measurement of soot oxygen functional groups. Energy Fuel online
Wu M, Ning P, Liu SY (2013) Adsorption characteristics of soil organic matter to norfloxacin. Environ Chem 32(1):112–117 (In Chinese)
Wu XL, Xiang L, Yan QY, Jiang YN, Li YW, Huang XP, Li H, Cai QY, Mo CH (2014) Distribution and risk assessment of quinolone antibiotics in the soils from organic vegetable farms of a subtropical city, Southern China. Sci Total Environ 487(1):399–406
Wu DL, Zhang M, He LX et al (2020) Contamination profile of antibiotic resistance genes in ground water in comparison with surface water. Sci Total Environ 715:136975 ISSN 0048-9697
Xu J, Hou WG (2007) Point of zero charge and intrinsic surface reaction equilibrium constants of meadow brown soil in Northeast of China. Acta Chim Sin 6(13):1191–1196
Zhang JM (1995) China soil. Commercial Press
Zhang YJ, Wei H et al (2019) Salinity as a predominant factor modulating the distribution patterns of antibiotic resistance genes in ocean and river beach soils. Sci Total Environ
Zhao ZG (2005) Application principle of adsorption [M]. Chem Indust Press 6:631–631
Zhao FK, Yang L, Qiao M et al (2017) Environmental behaviour and distribution characteristics of antibiotics in soil. Soil 49(3):428–436 (In Chinese)
Zhou D, Chen B, Wu M et al (2014) Ofloxacin sorption in soils after long-term tillage: the contribution of organic and mineral compositions. Sci Total Environ 497-498(nov.1):665–670
Zhu YE, Miao JR et al (2019) Residual characteristics and risk assessment of quinolones in agricultural soil along the Fenhe River. Acta Sci Circumstantiae
Zou WQ, Shu Q, Xu BQ (2019) Adsorption characteristics of spirulina to rare earth erbium ions. China Environ Sci 39(02):674–683 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to my advisors, Dr.Lv and Prof.Cao, for assistance with the experiments and valuable discussion. We also thank Key Laboratory of Groundwater Sciences and Engineering, Ministry of Natural Resources for Economic support.
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 41602273), Geological Survey Project “Zhengzhou Urban Geological Survey of China Geological Survey (Grant no. DD20189262) the Geological Survey Project of China Geological Survey (Grant no. DD20211309) and Key Laboratory of Groundwater Sciences and Engineering, Ministry of Natural Resources.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation was performed by K J (resources). Data collection and analysis, first draft of the manuscript and investigation were finished by MX W (investigation and writing—original draft). DY L led financial support for the project (funding acquisition) and provided ideas (conceptualization). LH C and K Z were major contributors in editing the manuscript before submission (writing—review and editing). All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval, consent to participate, and consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philipp Gariguess
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 404 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, M., Lv, D., Cao, L. et al. Adsorption behaviours and transfer simulation of levofloxacin in silty clay. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 46291–46302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13955-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13955-x