Abstract
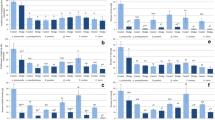
Mine tailings are one of main causes of diffused heavy metal pollution since the heavy metals in there may acquire mobility. The current knowledge of the processes at work in long-term phytoremediation by woody species remains insufficient. Through a 4-year field study, we evaluated the phytoextraction efficiency of Populus deltoides CL. ‘Xianglin 90’ grown on a mine tailing co-polluted by Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn. The concentrations of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the rhizospheric soil were reduced by amounts ranging from 12.86 to 42.19% during the study period. Bioconcentration factors and translocation factors showed that the accumulation of Cd and Zn occurring in the shoots was the most effective. Combined with the considerable biomass produced by poplar, the extracted amounts of Cd and Zn could reach 0.61 g and 10.66 g plant−1, respectively, in which the shoots account for 77.3% (Cd) and 89.0% (Zn) of the overall extraction amounts. Acid-soluble Cd and Zn increased by 5.49% and 4.29%, respectively, in the rhizosphere compared to the bulk soil, indicating that poplar enhanced the mobility of Cd and Zn in the rhizosphere, which explained its ability for bioaccumulation and root–shoot translocation. Moreover, calculated time required to address the issue of Cd and Zn pollution was theoretically shortened by more than half from 2015 to 2019. This study brings new insights into the long-term effects of phytoextraction on the concentration, fractionation, and transportation of heavy metals and confirms the potential of poplar as a Cd and Zn remediation species.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author (X. Zhang).
References
Afonso TF, Demarco CF, Pieniz S, Quadro MS, Camargo FAO, Andreazza R (2020) Bioprospection of indigenous flora grown in copper mining tailing area for phytoremediation of metals. J Environ Manag 256:109953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109953
Antoniadis V, Shaheen SM, Boersch J, Frohne T, Du Laing G, Rinklebe J (2017) Bioavailability and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in garden edible vegetables and soils around a highly contaminated former mining area in Germany. J Environ Manag 186:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.04.036
Ariani A, Di Baccio D, Romeo S, Lombardi L, Andreucci A, Lux A, Stephen Horner D, Sebastiani L (2015) RNA sequencing of Populus x canadensis roots identifies key molecular mechanisms underlying physiological adaption to excess zinc. PLoS One 10(2):e0117571
Baldantoni D, Cicatelli A, Bellino A, Castiglione S (2014) Different behaviours in phytoremediation capacity of two heavy metal tolerant poplar clones in relation to iron and other trace elements. J Environ Manag 146:94–99
Benyó D, Horváth E, Németh E, Leviczky T, Takács K, Lehotai N, Gallé Á (2016) Physiological and molecular responses to heavy metal stresses suggest different detoxification mechanism of Populus deltoides and P. x canadensis. J Plant Physiol 201:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2016.05.025
Cai J (2010) Studies on the productivity and carbon storage of poplar plantations in Dongting Lake area. Dissertation, Central South University of Forestry and Technology (In Chinese)
Castiglione S, Todeschini V, Franchin C, Torrigiani P, Gastaldi D, Cicatelli A, Lingua G (2009) Clonal differences in survival capacity, copper and zinc accumulation, and correlation with leaf polyamine levels in poplar: a large-scale field trial on heavily polluted soil. Environ Pollut 157(7):2108–2117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.02.011
Chaturvedi R, Favas PJC, Pratas J, Varun M, Paul MS (2019) Metal(loid) induced toxicity and defense mechanisms in Spinacia oleracea L.: ecological hazard and prospects for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109570
Chenzhou Water Conservancy Bureau (2020) Chenzhou water resources. http://slj.czs.gov.cn/zwgk/slgk/content_533602.html
Cuong DT, Obbard JP (2006) Metal speciation in coastal marine sediments from Singapore using a modified BCR-sequential extraction procedure. Appl Geochem 21:1335–1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.05.001
Dai HP, Shan CJ, Jia GL, Yang TX, Wei AZ, Zhao H, Cao XY (2013) Responses to cadmium tolerance, accumulation and translocation in Populus × canescens. Water Air Soil Pollut 224(4):1504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1504-6
De Oliveira VH, Tibbett M (2018) Tolerance, toxicity and transport of Cd and Zn in Populus trichocarpa. Environ Exp Bot 155:281–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.07.011
Di Baccio D, Castagna A, Tognetti R, Ranieri A, Sebastiani L (2014) Early responses to cadmium of two poplar clones that differ in stress tolerance. J Plant Physiol 171(18):1693–1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2014.08.007
Duan X, Zhang G, Rong L, Fang H, He D, Feng D (2015) Spatial distribution and environmental factors of catchment-scale soil heavy metal contamination in the dry-hot valley of Upper Red River in southwestern China. CATENA 135:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.07.006
Dubey S, Shri M, Gupta A, Rani V, Chakrabarty D (2018) Toxicity and detoxification of heavy metals during plant growth and metabolism. Environ Chem Lett 16(4):1169–1192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0741-8
Durand A, Maillard F, Alvarez-Lopez V, Guinchard S, Bertheau C, Valot B, Chalot M (2018) Bacterial diversity associated with poplar trees grown on a Hg-contaminated site: community characterization and isolation of Hg-resistant plant growth-promoting bacteria. Sci Total Environ 622-623:1165–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.069
Ent A, Baker A, Reeves R, Pollard A, Schat H (2012) Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements: Facts and fiction. Plant Soil 362:319–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1287-3
Foulon J, Zappelini C, Durand A, Valot B, Girardclos O, Blaudez D, Chalot M (2016) Environmental metabarcoding reveals contrasting microbial communities at two poplar phytomanagement sites. Sci Total Environ 571:1230–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.151
Gamalero E, Cesaro P, Cicatelli A, Todeschini V, Musso C, Castiglione S, Lingua G (2012) Poplar clones of different sizes, grown on a heavy metal polluted site, are associated with microbial populations of varying composition. Sci Total Environ 425:262–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.03.012
GB15618-2018 (2018) Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (grade II), Chinese Environmental Quality Standard for Soil (GB15618-2018), In: China, Beijing
Jakovljević T, Bubalo MC, Orlović S, Sedak M, Bilandžić N, Brozinčević I, Redovniković IR (2014) Adaptive response of poplar (Populus nigra L.) after prolonged Cd exposure period. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(5):3792–3802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2292-7
Jukić M, Ćurković L, Šabarić J, Kerolli Mustafa M (2017) Fractionation of heavy metals in fly ash from wood biomass using the BCR sequential extraction procedure. B. Environ Contam Toxicol 99:524–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2160-0
Kaste JM, Friedland AJ, Miller EK (2005) Potentially mobile lead fractions in montane organic-rich soil horizons. Water Air Soil Pollut 167(1):139–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-8861-8
Lebrun M, De Zio E, Miard F, Scippa GS, Renzone G, Scaloni A, Bourgerie S, Morabito D, Trupiano D (2020) Amending an As/Pb contaminated soil with biochar, compost and iron grit: effect on Salix viminalis growth, root proteome profiles and metal(loid) accumulation indexes. Chemosphere 244:125397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125397
Lettens S, Vandecasteele B, De Vos B, Vansteenkiste D, Verschelde P (2011) Intra- and inter-annual variation of Cd, Zn, Mn and Cu in foliage of poplars on contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 409(11):2306–2316
Li YZ, Chen XS, Xie YH, Li X, Li F, Hou ZY (2014) Effects of young poplar plantations on understory plant diversity in the Dongting Lake wetlands, China. Sci Rep 4:6339. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06339
Liu HK, Xu F, Xie YL, Wang C, Zhang AK, Li LL, Xu H (2018a) Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 645:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.115
Liu LW, Li W, Song WP, Guo MX (2018b) Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: principles and applicability. Sci Total Environ 633:206–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.161
Liu S, Ali S, Yang R, Tao J, Ren B (2019) A newly discovered Cd-hyperaccumulator Lantana camara L. J Hazard Mater 371:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.016
Liu BH, Wang SX, Wang J, Zhang XZ, Shen ZG, Shi L, Chen YH (2020) The great potential for phytoremediation of abandoned tailings pond using ectomycorrhizal Pinus sylvestris. Sci Total Environ 719:137475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137475
Luo J, Qi SH, Gu XWS, Wang JJ, Xie XM (2016) Evaluation of the phytoremediation effect and environmental risk in remediation processes under different cultivation systems. J Clean Prod 119:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.01.043
Luo J, Cai LM, Qi SH, Wu J, Sophie Gu XW (2017) A multi-technique phytoremediation approach to purify metals contaminated soil from e-waste recycling site. J Environ Manag 204:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.08.029
Madejón P, Domínguez MT, Gil Martínez M, Navarro Fernández CM, Montiel Rozas MM, Madejón E, Murillo JM, Cabrera F, Marañón T (2018) Evaluation of amendment addition and tree planting as measures to remediate contaminated soils: the Guadiamar case study (SW Spain). Catena 166:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.03.016
Marschner P, Solaiman Z, Rengel Z (2006) Rhizosphere properties of Poaceae genotypes under P-limiting conditions. Plant Soil 283:11–24 https://www.jstor.org/stable/24129050
Massaccesi L, Benucci GMN, Gigliotti G, Cocco S, Corti G, Agnelli A (2015) Rhizosphere effect of three plant species of environment under periglacial conditions (Majella Massif, central Italy). Soil Biol Biochem 89:184–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.07.010
Mihucz VG, Csog Á, Fodor F, Tatár E, Szoboszlai N, Silaghi-Dumitrescu L, Záray G (2012) Impact of two iron(III) chelators on the iron, cadmium, lead and nickel accumulation in poplar grown under heavy metal stress in hydroponics. J Plant Physiol 169:561–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.12.012
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China (1990) Background concentration of soil elements in China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Miyadate H, Adachi S, Hiraizumi A, Tezuka K, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Katou K, Kodama I, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Satoh-Nagasawa N, Watanabe A, Fujimura T, Akagi H (2011) Osheavy metalA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol 189(1):190–199. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03459
Mohanty M, Kumar Patra H (2020) Phytoassessment of in situ weed diversity for their chromium distribution pattern and accumulation indices of abundant weeds at South Kaliapani chromite mining area with their phytoremediation prospective. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 194:110399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110399
Nareshkumar A, Nagamallaiah GV, Pandurangaiah M, Kiranmai K, Amaranathareddy V, Lokesh U, Venkatesh B, Sudhakar C (2015) Pb-stress induced oxidative stress caused alterations in antioxidant efficacy in two groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars. Agric Sci 6(10):1283–1297. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2015.610123
Pietrini F, Zacchini M, Iori V, Pietrosanti L, Bianconi D, Massacci A (2010) Screening of poplar clones for cadmium phytoremediation using photosynthesis, biomass and cadmium content analyses. Int J Phytoremediat 12(1):105–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510902767163
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E (2011) Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 213:113–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_4
Qasim B, Motelica Heino M, Bourgerie S, Gauthier A, Morabito D (2016) Rhizosphere effects of Populus euramericana dorskamp on the mobility of Zn, Pb and Cd in contaminated technosols. J Soils Sediments 16:811–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1270-8
Rafael RBA, Fernández-Marcos ML, Cocco S, Ruello ML, Fornasier F, Corti G (2019) Benefits of biochar and NPK fertilizers for soil quality and growth of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) in an acid Arenosol. Pedosphere 29:311–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(19)60805-2
Richter DD, Oh N-H, Fimmen R, Jackson J (2007) The Rhizosphere and Soil Formation. In: Cardon ZG, Whitbeck JL (eds) The rhizosphere – an ecological perspective. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012088775-0/50010-0
Robinson BH, Mills TM, Petit D, Fung LE, Green SR, Clothier BE (2000) Natural and induced cadmium-accumulation in poplar and willow: implications for phytoremediation. Plant Soil 227(1):301–306. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026515007319
Saxena G, Purchase D, Mulla SI, Saratale GD, Bharagava RN (2020) Phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated sites: eco-environmental concerns, field studies, sustainability issues, and future prospects. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 249:71–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2019_24
Shi K, Dai X, Fan X, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Wang G (2020) Simultaneous removal of chromate and arsenite by the immobilized Enterobacter bacterium in combination with chemical reagents. Chemosphere 259:127428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127428
Siemianowski O, Barabasz A, Kendziorek M, Ruszczyńska A, Bulska E, Williams LE, Antosiewicz DM (2014) AtHMA4 expression in tobacco reduces Cd accumulation due to the induction of the apoplastic barrier. J Exp Bot 65(4):1125–1139. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert471
Sun WH, Xiong Z, Chu L, Li W, Soares MA, White JF Jr, Li H (2019) Bacterial communities of three plant species from Pb-Zn contaminated sites and plant-growth promotional benefits of endophytic Microbacterium sp. (strain BXGe71). J Hazard Mater 370:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.003
Sut Lohmann M, Jonczak J, Raab T (2020) Phytofiltration of chosen metals by aquarium liverwort (Monosoleum tenerum). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 188:109844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109844
Tang WP, Wang YR, Zheng LY (2004) Study on biomass and productivity from plantation for southern type of poplar. HuBei For Sci Technol:1004–3020 (In Chinese)
Todeschini V, Lingua G, D’Agostino G, Carniato F, Roccotiello E, Berta G (2011) Effects of high zinc concentration on poplar leaves: a morphological and biochemical study. Environ Exp Bot 71(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.10.018
Vocciante M, Caretta A, Bua L, Bagatin R, Franchi E, Petruzzelli G, Ferro S (2019) Enhancements in phytoremediation technology: environmental assessment including different options of biomass disposal and comparison with a consolidated approach. J Environ Manag 237:560–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.104
Wang LW, Hou DY, Shen ZT, Zhu J, Jia XY, Ok YS, Tack FMG, Rinklebe J (2019) Field trials of phytomining and phytoremediation: a critical review of influencing factors and effects of additives. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 1705724:2724–2774. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1705724
Xu S, Li B, Li P, He XY, Chen W, Yan K, Li Y, Wang YJ (2019) Soil high Cd exacerbates the adverse impact of elevated O3 on Populus alba ‘Berolinensis’ L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.057
Yang Y, Han X, Liang Y, Ghosh A, Chen J, Tang M (2015) The combined effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and lead (Pb) stress on Pb accumulation, plant growth parameters, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzymes in Robinia pseudoacacia L. PLoS One 10:e0145726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145726
Yang X, Liu JJ, McGrouther K, Huang HG, Lu KP, Guo X, He LZ, Lin XM, Che L, Ye ZQ, Wang HL (2016) Effect of biochar on the extractability of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and enzyme activity in soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:974–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4233-0
Ye YX, Dong W, Luo Y, Fan T, Xiong XY, Sun L, Hu XX (2020) Cultivar diversity and organ differences of cadmium accumulation in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) allow the potential for Cd-safe staple food production on contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 711:134534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134534
Zeng W, Duo H, Lei X, Chen X, Wang X, Pu Y, Zou W (2017) Individual tree biomass equations and growth models sensitive to climate variables for Larix spp. in China. Eur J For Res 136(2):233–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-017-1024-9
Zhang X, Xia H, Li Z, Zhuang P, Gao B (2010) Potential of four forage grasses in remediation of Cd and Zn contaminated soils. Bioresour Technol 101(6):2063–2066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.065
Zhang X, Yang HH, Cui ZJ (2018) Evaluation and analysis of soil migration and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in iron tailings. J Clean Prod 172:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.2
Funding
Financial supports were from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51808216, 51776188, 21805244, 51709285), Hunan Science and Technology Planning Project, China (2018RS3109), Science and Technology International Cooperation Project of Changsha City (kq1907082), Training Program for Excellent Young Innovators of Changsha (kq1802010, kq1802040), Hunan Forestry Science and Technology Project (XLK201801, XLK201908), and the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Hunan Province 2018NK2051. The Hunan Ecology and Environment Department provided financial support on mine dump’s phytoremediation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. YGS created the research idea and wrote the manuscript. NT collected and analyzed the samples and analyzed the statistics. HL supervised the research results and provided financial support. GC led and organized the research activity and supervised the research results. LJJ performed informatics analyses and designed the methodology. ZLH and ZGZ analyzed the statistics and experiments data. JH provided research instruments. ZJW and CLF participated in laboratory experiments. XZ led and organized the research activity, analyzed the statistics, and revised the manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Zhejiang University of Science and Technology. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The participant has consented to the submission of the research paper to the journal.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 190 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suo, Y., Tang, N., Li, H. et al. Long-term effects of phytoextraction by a poplar clone on the concentration, fractionation, and transportation of heavy metals in mine tailings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 47528–47539 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13864-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13864-z