Abstract
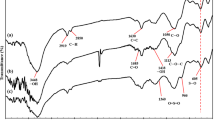
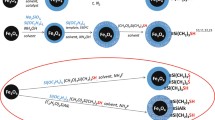
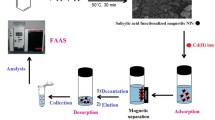
For effective removal of cadmium (II) (Cd(II)) from polluted water, a magnetic adsorbent of Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell microspheres modified with methyl-protected thiol groups (Fe3O4@SiO2-SH-Protected) was synthesized and characterized by scanning electron, transmission electron, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopies, as well as X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and magnetic measurements. Characterization results showed that thiol groups on the surface of Fe3O4@SiO2 material were protected to avoid disulfide formation. Batch adsorption experiments were conducted by varying the contact time, initial pH, solid-liquid ratio, temperature, Cd(II) concentrations, and interfering cations. Fe3O4@SiO2-SH-Protected material exhibited much higher adsorption capacity than Unprotected forms and other adsorbents due to methyl group protection. The maximum adsorption capacity calculated from the Langmuir fitting was 27.5 mg·g−1 (pH 7, 25 °C), and the adsorption kinetics followed a pseudo-second-order model, and adsorption mainly dominated by film diffusion processes. Thermodynamic parameters indicated that the adsorption process was a spontaneous, endothermic, and positive entropic process. Cd(II)-loaded on the adsorbent was easily desorbed with 0.1 M HCl and the adsorbent stable in 0.1 M HCl for long times, showing good reusability and stability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah N, Yusof N, Lau WJ, Jaafar J, Ismail AF (2019) Recent trends of heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by membrane technologies. J Ind Eng Chem 76:17–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.03.029
Asuquo E, Martin A, Nzerem P, Siperstein F, Fan XL (2017) Adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions using mesoporous activated carbon adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetics and characterisation studies. J Environ Chem Eng 5:679–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.043
Bo YS, Eom Y, Tai GL (2011) Removal and recovery of mercury from aqueous solution using magnetic silica nanocomposites nanocomposites. Appl Surf Sci 257:4754–4759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.12.156
Burakov AE, Galunin EV, Burakova IV, Kucherova AE, Agarwal S, Tkachev AG, Gupta VK (2018) Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:702–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.034
Candan N, Tuzmen N, Andac M, Andac CA, Say R, Denizli A (2009) Cadmium removal out of human plasma using ion-imprinted beads in a magnetic column. MAT SCI ENG C-BIO S 29:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2008.06.002
Champagne PO, Westwick H, Bouthillier A, Sawan M (2018) Colloidal stability of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the central nervous system: a review. Nanomedicine 13:1385–1400. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2018-0021
Chen K, He J, Li Y, Cai X, Zhang K, Liu T, Hu Y, Lin D, Kong L, Liu J (2017a) Removal of cadmium and lead ions from water by sulfonated magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 494:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.082
Chen K, He J, Li Y, Cai X, Zhang K, Liu T, Hu Y, Lin D, Kong L, Liu J (2017b) Removal of cadmium and lead ions from water by sulfonated magnetic nanoparticle adsorbents. J Colloid Interface Sci 494:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.082
Chen XT, Yu LS, Zou SH, Xiao LP, Fan J (2020) Zeolite cotton in tube: a simple robust household water treatment filter for heavy metal removal. Sci Rep 10:9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61776-8
Clemens S, Aarts MG, Thomine S, Verbruggen N (2013) Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci 18:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.08.003
Deng H, Li X, Peng Q, Wang X, Chen J, Li Y (2005) Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:2782–2785. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200462551
Dolores E et al (2017) Thiol-ethylene bridged PMO: a high capacity regenerable mercury adsorbent via intrapore mercury thiolate crystal formation. J Hazard Mater 339:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.051
Ghasemi E, Heydari A, Sillanpaa M (2017) Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@EDTA nanoparticles as an efficient adsorbent for simultaneous removal of Ag(I), Hg(II), Mn(II), Zn(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) from water and soil environmental samples. Microchem J 131:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.11.011
Goethals F, Frank D, Prez FED (2016) Protected thiol strategies in macromolecular design. Prog Polym Sci 64:76–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2016.09.003
Gu SQ, Kang XN, Wang L, Lichtfouse E, Wang CY (2019) Clay mineral adsorbents for heavy metal removal from wastewater: a review. Environ Chem Lett 17:629–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0813-9
Jarup L, Akesson A (2009) Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.04.020
Kalapathy U, Proctor A, Shultz J (2000) A simple method for production of pure silica from rice hull ash. Bioresour Technol 73:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(99)00127-3
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Elst LV, Muller RN (2010) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 110:2574–2574. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900197g
Lin S, Xu M, Zhang W, Hua XF, Lin KF (2017) Quantitative effects of amination degree on the magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MIONPs) using as adsorbents to remove aqueous heavy metal ions. J Hazard Mater 335:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.016
Liu JF, Zhao ZS, Jiang GB (2008) Coating Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles with humic acid for high efficient removal of heavy metals in water. Environ Sci Technol 42:6949–6954. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800924c
Liu LH, Liu S, Zhao L, Su G, Liu X, Peng H, Xue J, Tang A (2020) Fabrication of novel magnetic core-shell chelating adsorbent for rapid and highly efficient adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 313:15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113593
Melnyk IV, Pogorilyi RP, Zub YL, Vaclavikova M, Gdula K, Dąbrowski A, Seisenbaeva GA, Kessler VG (2018) Protection of thiol groups on the surface of magnetic adsorbents and their application for wastewater treatment. Sci Rep 8:8592. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-26767-w
Ming H, Zhang S, Pan B, Zhang W, Lu L, Zhang Q (2012) Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. J Hazard Mater 211-212:317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.016
Misra RK, Jain SK, Khatri PK (2011) Iminodiacetic acid functionalized cation exchange resin for adsorptive removal of Cr(VI), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) from their aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 185:1508–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.077
Niu Y, Qu R, Chen H, Mu L, Liu X, Wang T, Zhang Y, Sun C (2014) Synthesis of silica gel supported salicylaldehyde modified PAMAM dendrimers for the effective removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 278:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.012
Pearson G (1969) Hard and soft acids and bases. Surv Prog Chem 5:1–52. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00905a001
Reddy LH, Arias JL, Nicolas J, Couvreur P (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles: design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem Rev 112:5818–5878. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr300068p
Rehman AU, Nazir S, Irshad R, Tahir K, Rehman KU, Ul Islam R, Wahab Z (2021) Toxicity of heavy metals in plants and animals and their uptake by magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 321:33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114455
Ren Y, Abbood HA, He FB, Peng H, Huang KX (2013) Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chem Eng J 226:300–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.059
Roto R, Yusran Y, Kuncaka A (2016) Magnetic adsorbent of Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles modified with thiol group for chloroauric ion adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 377:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.099
Ru J, Wang XM, Wang FB, Cui XL, Du XZ, Lu XQ (2021) UiO series of metal-organic frameworks composites as advanced sorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions: Synthesis, applications and adsorption mechanism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111577
Singh S, Barick KC, Bahadur D (2011) Surface engineered magnetic nanoparticles for removal of toxic metal ions and bacterial pathogens. J Hazard Mater 192:1539–1547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.074
Singh D, Gautam RK, Kumar R, Shukla BK, Shankar V, Krishna V (2014) Citric acid coated magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and application in removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. J WATER PROCESS ENG 4:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.10.005
Sud D, Mahajan G, Kaur MP (2008) Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions-a review. Bioresour Technol 99:6017–6027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.064
Tomina VV, Melnyk IV, Zub YL, Kareiva A, Vaclavikova M, Seisenbaeva GA, Kessler VG (2017) Tailoring bifunctional hybrid organic-inorganic nanoadsorbents by the choice of functional layer composition probed by adsorption of Cu2+ ions. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 8:334–347. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.8.36
Tsai TH, Chou HW, Wu YF (2020) Removal of nickel from chemical plating waste solution through precipitation and production of microsized nickel hydroxide particles. Sep Purif Technol 251:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117315
Vimonses V, Lei SM, Jin B, Chowd CWK, Saint C (2009) Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo Red adsorption by clay materials. Chem Eng J 148:354–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.09.009
Vitali L, Laranjeira MC, Goncalves NS, Favere VT (2008) Spray-dried chitosan microspheres containing 8-hydroxyquinoline -5 sulphonic acid as a new adsorbent for Cd(II) and Zn(II) ions. Int J Biol Macromol 42:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2007.10.020
Wang S, Zhu ZH (2006) Characterisation and environmental application of an Australian natural zeolite for basic dye removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 136:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.038
Xiong T, Yuan XZ, Cao XY, Wang H, Jiang LB, Wu ZB, Liu Y (2020) Mechanistic insights into heavy metals affinity in magnetic MnO2@Fe3O4/poly(m-phenylenediamine) core-shell adsorbent. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 192:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110326
Ya V, Martin N, Chou YH, Chen YM, Choo KH, Chen SS, Li CW (2018) Electrochemical treatment for simultaneous removal of heavy metals and organics from surface finishing wastewater using sacrificial iron anode. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 83:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.12.004
Yanagisawa H, Matsumoto Y, Machida M (2010) Adsorption of Zn(II) and Cd(II) ions onto magnesium and activated carbon composite in aqueous solution. Appl Surf Sci 256:1619–1623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.10.010
Zeng Q, Hu L, Zhong H, He ZG, Sun W, Xiong DL (2021) Efficient removal of Hg2+ from aqueous solution by a novel composite of nano humboldtine decorated almandine (NHDA): Ion exchange, reducing-oxidation and adsorption. J Hazard Mater 404:14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124035
Zhang GY, Qu RJ, Sun CM, Ji CN, Chen H, Wang CH, Niu YZ (2008) Adsorption for metal ions of chitosan coated cotton fiber. J Appl Polym Sci 110:2321–2327. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.27515
Zhang SX, Zhang Y, Liu J, Xu Q, Xiao H, Wang X, Xu H, Zhou J (2013) Thiol modified Fe3O4@SiO2 as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for mercury removal. Chem Eng J 226:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.060
Zhao W, Gu J, Zhang L, Chen H, Shi J (2005) Fabrication of uniform magnetic nanocomposite spheres with a magnetic core/mesoporous silica shell structure. J Am Chem Soc 127:8916–8917. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja051113r
Zhao Y, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang S, Huang Y, Wu X, Wang X (2014a) Synthesis of amidoxime-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell magnetic microspheres for highly efficient sorption of U(VI). Chem Eng J 235:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.034
Zhao YG, Li JX, Zhao LP, Zhang SW, Huang YS, Wu XL, Wang XK (2014b) Synthesis of amidoxime-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell magnetic microspheres for highly efficient sorption of U(VI). Chem Eng J 235:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.034
Zhao JJ, Niu YZ, Ren B, Chen H, Zhang SX, Jin J, Zhang Y (2018) Synthesis of Schiff base functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4 composites for effective removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 347:574–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.151
Zheng CF, Wu QZ, Hu XB, Wang YJ, Chen Y, Zhang SX, Zheng HL (2021) Adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions on a polymer-immobilized amphoteric biosorbent: surface interaction assessment. J Hazard Mater 403:12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123801
Zirino A, Yamamoto S (1972) A pH-dependent model for the chemical speciation of copper, zinc, cadmium, and lead in seawater. Limnol Oceanogr 17:661–671. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1972.17.5.0661
Zubair M, Ihsanullah I, Aziz HA, Ahmad MA, Al-Harthi MA (2021) Sustainable wastewater treatment by biochar/layered double hydroxide composites: progress, challenges, and outlook. Bioresour Technol 319:13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124128
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos:41772255 and 41521001), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (No.CUGGC07), and Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2018Zx07110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.L. conducted experiments, collected and analyzed experimental data, and wrote the manuscript. X. X. designed the study and revised the manuscript. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No animals or human subjects were used in the above research.
Consent for publication
Our manuscript does not contain any individual data in any form.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Xie, X. Thiol-methyl-modified magnetic microspheres for effective cadmium (II) removal from polluted water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 42750–42762 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13773-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13773-1