Abstract
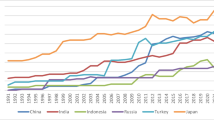
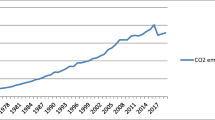
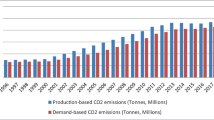
Since the nonlinear ARDL approach is introduced in advanced econometric, some old relationships are getting new empirical attention. Therefore, we examine the asymmetric macroeconomic determinants of carbon dioxide (CO2) emission in China, covering the time from 1971 to 2019 and using a nonlinear ARDL model. The study results show that GDP and industrialization have an asymmetric effect on CO2 emission in long-run in direction and magnitude, while agriculturalization has also an asymmetric effect on environmental pollution in magnitude, but not in the direction. In short, GDP and industrialization have also asymmetric response on CO2 emissions in the short term only in magnitude, but agriculturalization has an asymmetric response in magnitude and direction in short-run. Therefore, this empirical research is more applicable for policymakers in China.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Zhao ZY (2018) Empirics on linkages among industrialization, urbanization, energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth: a heterogeneous panel study of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(30):30617–30632
Ahmad N, Iqbal A, Mahmood H (2013) CO emission, population and industrial growth linkages. World Appl Sci J 21(4):615–622
Ahmad M, Zhao ZY, Li H (2019) Revealing stylized empirical interactions among construction sector, urbanization, energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in China. Sci Total Environ 657:1085–1098
Apergis N, Payne JE (2010) The emissions, energy consumption, and growth nexus: evidence from the commonwealth of independent states. Energy Policy 38:650–655
Asghar N, Anwar A, Ur H, Saba R (2019) Industrial practices and quality of environment: evidence for Asian economies. Environ Dev Sustain
Bahmani-Oskooee M, Shafiullah M, Islam F (2017) The bilateral J-curve in Australia: a nonlinear reappraisal. Aust Econ Pap 56(3):249–269
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Osundina OA (2019) Do agricultural activities induce carbon emissions? The BRICS experience. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(24):25218–25234
Brock W, Dechert W, Scheinkman J (1996) A test for independence based on the correlation dimension. Econ Rev 15:197–235
Caporale, G. M., Claudio-Quiroga, G., & Gil-Alana, L. A. (2019) CO2 Emissions and GDP: evidence from China
Chaudhry SM, Ahmed R, Shafiullah M, Huynh TLD (2020) The impact of carbon emissions on country risk: evidence from the G7 economies. J Environ Manag 265:110533
Chen L, Chen S (2015) The estimation of environmental Kuznets curve in China: nonparametric panel approach. Comput Econ 46(3):405–420
Dogan N (2016) Agriculture and Environmental Kuznets Curves in the case of Turkey: evidence from the ARDL and bounds test. Agric Econ (Zemědělská Ekon) 62(12):566–574
Doğan N (2018) The impact of agriculture on CO2 emissions in China. Panoeconomicus 66(2):257–271
Dong K, Sun R, Jiang H, Zeng X (2018) CO2 emissions, economic growth, and the environmental Kuznets curve in China: what roles can nuclear energy and renewable energy play? J Clean Prod 196:51–63
Fodha M, Zaghdoud O (2010) Economic growth and pollutant emissions in Tunisia: an empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38(2):1150–1156
Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N (2018) Testing the agriculture-induced EKC hypothesis: the case of Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:22829–22841
Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N, Kaakeh M (2019) Agriculture-induced environmental Kuznets curve: the case of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(36):37137–37151
Govindaraju VC, Tang CF (2013a) The dynamic links between CO2 emissions, economic growth and coal consumption in China and India. Appl Energy 104:310–318
Govindaraju VGRC, Tang CF (2013b) The dynamic links between CO2 emissions, economic growth and coal consumption in China and India. Appl Energy 104(C):310–318
Grossman, G. M., & Krueger, A. B. (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement (No. w3914). National Bureau of economic research
Hao Y, Chen H, Wei Y, Li Y (2016) The influence of climate change on CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions: an empirical estimation based on Chinese provincial panel data. J Clean Prod 131:667–677
Huang, Y, and He, Y. (2012) The carbonization of China’s agriculture. United Nations University, World Institute for Development Economic Research Working Paper 74
Jalil A, Feridun M (2011) The impact of growth, energy and financial development on the environment in China: a cointegration analysis. Energy Econ 33:284–291
Jebli MB, Youssef SB (2017) The role of renewable energy and agriculture in reducing CO2 emissions: evidence for North Africa countries. Ecol Indic 74:295–301
Kasperowicz R (2015) Economic growth and CO2 emissions: the ECM analysis. J Int Stud 8(3):91–98
Li K, Lin B (2015) Impacts of urbanization and industrialization on energy consumption/CO2 emissions: does the level of development matter? Renew Sust Energ Rev 52:1107–1122
Li T, Wang Y, Zhao D (2016) Environmental Kuznets curve in China: new evidence from dynamic panel analysis. Energy Policy 91:138–147
Lin FL, Inglesi-Lotz R, Chang T (2018) Revisit coal consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth nexus in China and India using a newly developed bootstrap ARDL bound test. Energy Explor Exploit 36(3):450–463
Liu X, Bae J (2018) Urbanization and industrialization impact of CO2 emissions in China. J Clean Prod 172:178–186
Liu X, Zhang S, Bae J (2017) The impact of renewable energy and agriculture on carbon dioxide emissions: Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve in four selected ASEAN countries. J Clean Prod 164:1239–1247
Luo G, Weng JH, Zhang Q, Hao Y (2017) A reexamination of the existence of environmental Kuznets curve for CO 2 emissions: evidence from G20 countries. Nat Hazards 85(2):1023–1042
Ma H, Du J (2012) Influence of industrialization and urbanisation on China’s energy consumption. Adv Mater Res 524-527:3122–3128
Mahmood H, Alkhateeb TTY, Al-Qahtani MMZ, Allam Z, Ahmad N, Furqan M (2019) Agriculture development and CO2 emissions nexus in Saudi Arabia. PLoS One 14(12):e0225865
Mamun MA, Sohag K, MAH M, Uddin GS, Ozturk I (2014) Regional differences in the dynamic linkage between CO2 emissions, sectoral output and economic growth. Renew Sust Energ Rev 38:1–11
Mensi W, Shafiullah M, Vo XV, Kang SH (2021) Volatility spillovers between strategic commodity futures and stock markets and portfolio implications: evidence from developed and emerging economies. Res Policy 71:102002
Mitić P, Munitlak Ivanović O, Zdravković A (2017) A cointegration analysis of real GDP and CO2 emissions in transitional countries. Sustainability 9(4):568
Narayan PK, Popp S (2012) The energy consumption-real GDP nexus revisited: empirical evidence from 93 countries. Econ Model 29:303–308
Nugraha AT, Osman NH (2018) The environmental study on causality relationship among energy consumption, CO2 emissions, the value added of development sectors and household final consumption expenditure in Indonesia. Ekoloji. 27(106):837–852
Olajide OT, Akinlabi BH, Tijani AA (2012) Agriculture resource and economic growth in Nigeria. Eur Sci J 8(22)
Önder, M., Ceyhan, E., & Kahraman, A. (2011). Effects of agricultural practices on environment. In International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry, Singapore (pp. 28-30)
Pao HT, Tsai CM (2011) Multivariate Granger causality between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, FDI (foreign direct investment) and GDP (gross domestic product): evidence from a panel of BRIC (Brazil, Russian Federation, India, and China) countries. Energy 36(1):685–693
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Qiao H, Zheng F, Jiang H, Dong K (2019) The greenhouse effect of the agriculture-economic growth-renewable energy nexus: evidence from G20 countries. Sci Total Environ 671:722–731
Rafiq S, Salim R, Apergis N (2016) Agriculture , trade openness and emissions: an empirical analysis and policy options. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 60(3):348–365
Riti JS, Song D, Shu Y, Kamah M (2017) Decoupling CO2 emission and economic growth in China: is there consistency in estimation results in analyzing environmental Kuznets curve? J Clean Prod 166:1448–1461
Samreen I, Majeed MT (2020) Spatial econometric model of the spillover effects of financial development on carbon emissions: A global analysis. Pak J Commer Soc Sci 14(2):569–202
Selden TM, Song D (1994) Environmental quality and development: is there a Kuznets curve for air pollution emissions? J Environ Econ Manag 27(2):147–162
Shafiullah M, Selvanathan S, Naranpanawa A (2017) The role of export composition in export-led growth in Australia and its regions. Economic Analysis and Policy 53:62–76
Shafiullah M, Chaudhry SM, Shahbaz M, Reboredo JC (2020a) Quantile causality and dependence between crude oil and precious metal prices. Int J Financ Econ
Shafiullah M, Islam F, Navaratnam R (2020b) The Harberger–Laursen–Metzler effect: evidence from five SAARC countries. Empir Econ 58(4):1749–1777
Shafiullah M, Khalid U, Shahbaz M (2020c) Does meat consumption exacerbate greenhouse gas emissions? Evidence from US data Environmental Science and Pollution Research:1–15
Shahbaz M, Lean HH (2012) Does financial development increase energy consumption? The role of industrialization and urbanization in Tunisia. Energy Policy 40:473–479
Shahbaz M, Shafiullah M, Papavassiliou VG, Hammoudeh S (2017) The CO2–growth nexus revisited: A nonparametric analysis for the G7 economies over nearly two centuries. Energy Econ 65:183–193
Shahbaz M, Shafiullah M, Khalid U, Song M (2020) A nonparametric analysis of energy environmental Kuznets Curve in Chinese Provinces. Energy Econ 89:104814
Shin Y, Yu B, Greenwood-Nimmo M (2014) Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework.Festschrift in honor of Peter Schmidt. Springer, New York, pp 281–314
Stolze, M., Piorr, A., Häring, A. M., & Dabbert, S. (2000) Environmental impacts of organic farming in Europe. Universität Hohenheim, Stuttgart-Hohenheim
Tao S, Zheng T, Lianjun T (2008) An empirical test of the environmental Kuznets curve in China: a panel cointegration approach. China Econ Rev 19(3):381–392
Tiwari AK (2011) A structural VAR analysis of renewable energy consumption, real GDP and CO2 emissions: evidence from India. Econ Bull 31(2):1793–1806
Uddin MMM (2015) Causal relationship between agriculture, industry and services sector for GDP growth in Bangladesh: an econometric investigation. Journal of Poverty, Investment and Development 8
Ullah A, Khan D, Khan I, Zheng S (2018) Does agricultural ecosystem cause environmental pollution in Pakistan? Promise and menace. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(14):13938–13955
Ullah S, Apergis N, Usman A, Chishti MZ (2020a) Asymmetric effects of inflation instability and GDP growth volatility on environmental quality in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–13
Ullah S, Ozturk I, Usman A, Majeed MT, Akhtar P (2020b) On the asymmetric effects of premature deindustrialization on CO2 emissions: evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Van DTB, Bao HHG (2018) The role of globalization on CO2 emission in Vietnam incorporating industrialization, urbanization, GDP per capita and energy use. Int J Energy Econ Policy 8(6):275
Wang Q, Su M, Li R (2018) Toward to economic growth without emission growth: the role of urbanization and industrialization in China and India. J Clean Prod 205:499–511
Xu B, Lin B (2017) Does the high–tech industry consistently reduce CO2 emissions? Results from nonparametric additive regression model. Environ Impact Assess Rev 63:44–58
Xu GY, Song DY (2010) An empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve for China’s carbon emissions—based on provincial panel data [J]. China Industrial Economics 5:37–47
Zamula I, Kireitseva A (2013) Environmental liabilities arising from the transactions with atmospheric air as an accounting object. Econ Soc 6(2):190–200
Zhang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2020) Tourism, economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions in China. Tourism Economics, 1354816620918458
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China with Grant No. 71771129.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This idea was given by Bilal Aslam. Jinsong Hu, Bilal Aslam, Zubaria Andlib, and Muhammad Tariq Majeed analyzed the data and wrote the complete paper. Jinsong Hu and Sana Ullah read and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
I am free to contact any of the people involved in the research to seek further clarification and information.
Consent to publish
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, B., Hu, J., Majeed, M.T. et al. Asymmetric macroeconomic determinants of CO2 emission in China and policy approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 41923–41936 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13743-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13743-7