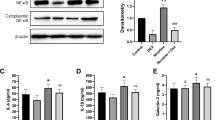
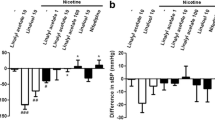
Abstract
The present study was carried out to investigate the ameliorative effects of melatonin against nicotine-induced heart and lung toxicity. For this purpose, 75 mature male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats weighing 150–170 g were randomly divided into five groups (15 rats each): control group (rats were I/P injected with 1% ethanol in saline), nicotine group (rats were I/P injected with 0.6 mg/kg body weight), and combined nicotine and melatonin groups (rats received nicotine as in the previous group and melatonin at a dose of 1, 5, or 10 mg/kg body weight, respectively); all treatments were continued for 21 days. Fasting blood samples were collected from each rat at the 11th day and one day after the end of the last injection (22nd day) for complete blood count (CBC) determination, while sera were collected for the determination of lipid profiles. Malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and reduced glutathione (GSH) as well as DNA fragmentation percentage were assessed in cardiac tissue. Heart and lung samples were collected for estimation of caspase-3 expression and histopathological examination. The results revealed that nicotine increased the number of RBCs, Hb concentration, total cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein (LDL) and decreased high density lipoprotein (HDL). In addition, it decreased SOD activity and GSH concentration with increased MDA concentration, and DNA fragmentation in the heart, as well as caspase-3 expression in both heart and lungs. It also induced histopathological changes in the heart and lung tissues. Melatonin could ameliorate the deleterious effect of nicotine on the previous parameters either partially or completely, where melatonin restored complete blood count, improved lipid profile, mended lipid peroxidation and antioxidant parameters in the cardiac tissue, rectified caspase-3 expression in the heart and lungs, ameliorated DNA fragmentation percentage in the heart, and protected both heart and lung tissue against the harmful effect of nicotine. It is concluded that melatonin has a protective effect on the heart and lungs against the harmful effect of nicotine.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
30 January 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32104-8
References
Abou Fard MG, Madi MN, El-Saka HM (2013) Effect of melatonin on obesity and lipid profile in high fat–fed rats. J Ameri Sci 9(10)
Adedayo AD, Tijani AA, Musa AA, Adeniyi DT (2011) Histological studies of smoke extract of Tobacco nicotiana on the heart, liver, lungs, kidney, and testes of male Sprague-Dawley rats. Niger Med J 52(4):217–222. https://doi.org/10.4103/0300-1652.93791
Agil A, Navarro-Alarcon M, Ruiz R, Abuhamadah S, El-Mir MY, Vázquez FG (2011) Beneficial effects of melatonin on obesity and lipid profile in young Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Pineal Res 50:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600079X.2010.00830.x
Ahmadi Z, Ashrafizadeh M, Forouzan M (2019) Apoptotic and autophagic modulation by nicotine. Int J Adv Biol Biomed Res 7(3):263–273. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.14592.
Ahmed H, Essawy SG, Salem AH, el Abd daim AM (2011) Effect of melatonin on some hematological parameters and immune status of broiler chicks. Proj plant growth regulator. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v3n2p243
Bancroft JD, Gamble M (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 6th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier, China
Benowitz N (2009) Pharmacology of nicotine: addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:57–71. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094742
Borjigin J, Zhang SL, Calinescu AA (2012) Circadian regulation of pineal gland rhythmicity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 349(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2011.07.009
Centner MA, Bhide GP, Salazar G (2020) Nicotine in senescence and atherosclerosis. Cells. 9(4):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041035
DeMarini DM (2004) Genotoxicity of tobacco smoke and tobacco smoke. Mutat Res 567:447–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2004.02.001
Deutsch V, Lerner-Geva L, Reches A, Boyko V, Limor R, Grisaru D (2007) Sustained leukocyte count during rising cortisol level. Acta Haematol 118(2):73–76. https://doi.org/10.1159/000103216
Dhouib H, Jallouli M, Draief M, El-Fazaa S, Bouraoui S (2014) The effect of nicotine and its interaction with ethanol on biochemical parameters, oxidative damage and histological changes in the rat’s liver. J Environ Sci Toxicol And Food Technol 8(1):72–82. https://doi.org/10.9790/2402-08157282
Du J, Song Y, Chen M, Du Q (2018) Protective effects of melatonin on lung and liver injuries in a rat model of acute sepsis. Int J Clin Exp Med 11(11):11720–11731
Ellefson RD and Caraway WT (1976) Fundamentals of clinical chemistry Ed Tietz NW; p506.
El-Zayadi A (2006) Heavy smoking and liver. World J Gastroenterol 12(38):6098–6101. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6098
Forrest G (2009) Meat free rat and mouse diet. Specialty feeds.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502
Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2013) On the free radical scavenging activities of melatonin’s metabolites, AFMK and AMK. J Pineal Res 54(3):245–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12010
Galano A, Medina ME, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2015) Melatoninand its metabolites as copper chelating agents and their role in inhibiting oxidative stress: a physicochemical analysis. J Pineal Res 58(1):107–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12196
Galano A, Tan D, Reiter R (2018) Melatonin: a versatile protector against oxidative DNA damage. Molecules 23(3):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030530
Gumustekin K, Taysi S, Alp HH (2010) Vitamin E and Hippophea rhamnoides L. extract reduce nicotine-induced oxidative stress in rat heart cell. Biochem Func 28:329–333. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.1663
Gürses I, Özeren M, Serin M, Yücel N, Erkal SH (2014) Histopathological evaluation of melatonin as a protective agent in heart injury induced by radiation in a rat model. Pathol Res Pract 210(12):863–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2014.08.006
Hacisevki A and Baba B (2018) An overview of melatonin as an antioxidant molecule: a biochemical approach. Chapter In book: Melatonin - molecular biology, clinical and pharmaceutical approaches. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.79421.
Hamza ZR, El-Shenawy SN (2017) Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant role of resveratrol on nicotine-induced lung changes in male rats. Toxicol Rep 17(4):399–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.07.003
Haragopal R, Aruna BMK (2016) Effects of tobacco chewing on serum lipid profile in south Indian population. Inter J of Scie Study 4(4). https://doi.org/10.17354/ijss/2016/363
Hassan EE, Gabra MH, Abdalla AZ, Ali EA (2013) Effect of cigarette smoking on lipid profile in male at collage of police and low Khartoum. Sudan Asian J Biomed and Pharma Scie 3(26):28–31
Hermoso D, Shimada L, Gilglioni E, Constantin J, Mito M, Hermoso A, Salgueiro-Pagadigorria C, Iwamoto E (2016) Melatonin protects female rats against steatosis and liver oxidative stress induced by estrogen deficiency. Life Sci 157:178–186
Higuchi T, Omata F, Tsuchihashi K, Higashioka K, Koyamada R (2016) Current cigarette smoking is a reversible cause of elevated white blood cell count: cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Prev Med Rep 4:417–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2016.08.009
Hikim SI, Friedman CT, Falz M, Chalfant V (2016) Nicotine plus a high-fat diet triggers cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Article in Cell and Tissue Research 368(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2536-1
Hofstra WA, Weerd A (2008) How to assess circadian rhythm in humans: a review of literature. Epilepsy Behav 13(3):438–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2008.06.002
Hussein MR, Ahmed OG, Hassan AF, Ahmed MA (2007) Intake of melatonin is associated with ameliorationof physiological changes, both metabolic and morphological pathologies associated with obesity: ananimal model. Int J Exp Pathol 88:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2613.2006.00512.x
Jockers R, Maurice P, Boutin JA, Delagrange P (2008) Melatonin receptors, heterodimerization, signal transduction and binding sites: what’s new? Br. Aust J Pharm 154(6):1182–1195. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjp.2008.184
Khan S, Fell P, James P (2014) Smoking-related chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Divers and Equality in Health and Care 11:267–271
Kilany OE, Abdelrazek HM, Aldayel TS, Abdo S, Mahmoud MM (2020) Anti-obesity potential of Moringa olifera seed extract and lycopene on high fat diet induced obesity in male Sprage Dawley rats. Sau J Bio Sci 27(10):2733–2746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.06.026
Leger D, Laudon M, Zisapel N (2004) Nocturnal 6-sulphatoxymelatoninexcretion in insomnia patients and its relationship to their response to melatonin replacement therapy. Am J Med 116:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.07.017
Leifert JA (2008) Anemia and cigarette smoking. Int J Lab Hematol 30:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-553X.2008.01067.x
Loloei S, Sepidarkish M, Heydarian A, Tahvilian N, Khazdouz M, Heshmati J, Pouraram H (2019) The effect of melatonin supplementation on lipid profile and anthropometric indices: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Dia & Meta Synd: Clinical Research & Reviews 13(3):1901–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2019.04.043
Longanbach SA, Chapman DH, Waldron KB, Miers MK (2007) Automated cell counting instrumentation and point of care testing. In: Rodak BF, Fritsma GA, Doig K (eds) Hematology: clinical principles and applications, 3rd edn, Missouri, pp 540–547
Lopes V (1977) Cholesterol determination in HDL separated by three different methods. Clin Chem 23:882–886
Lu L, Ma J, Sun M, Wan X (2020) Melatonin ameliorates mi-induced cardiac remodeling and apoptosis through a jnk/p53-dependent mechanism in diabetes mellitus. Article in Oxidmedand cell Long:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1535201
Masana MI, Doolen S, Ersahin C, Al-Ghoul WM, Duckles SP, Dubocovich ML, Krause DN (2002) MT2 melatonin receptors are present and functional in rat caudal artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302(3):1295–1302. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.302.3.1295
Mercan S, Eren B (2012) Protective role of melatonin supplementation against nicotine-induced liver damage in mouse. Toxicol Ind Health 29(10):888–896. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233712446725
Milad A, Zahra A (2019) A mechanistic review of nicotine toxicity with recent updates. Int J Biochem & Physio 4(2). https://doi.org/10.23880/ijbp-16000155
Nadia MM, Shams-eldein HA, Sara AS (2015) Effects of cigarette and shisha smoking on hematological parameters: an analytic case-control study. Int Multispecial J Health 1(10):44–51
Nduhirabandi F, Huisamen B, Strijdom H, Blackhurst D, Lochner A (2014) Short-term melatonin consumption protects the heart of obese rats independent of body weight change and visceral adiposity. J Pineal Res 57:317–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12171
Nishikimi M, Rao NA, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulphate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys 46:849–864
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:35l–358l
Ozdinc S, Oz G, Ozdemir C, Kilic I, Karakaya Z, Bal A, Koken T, Solak O (2016) Melatonin: is it an effective antioxidant for pulmonary contusion? J Surg Res 204(2):445–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.05.020
Papathanasiou G, Mamali A, Papafloratos S, Zerva E (2014) Effects of smoking on cardiovascular function: the role of nicotine and carbon monoxide. Health Sci J 8(2)
Perandones CE, Illera AV, Peckham D, Stunz LL, Ashman RF (1993) Regulation of apoptosis in vitro in mature murine spleen T cell. J Immunol 151:3521–3529
Plaimee P, Weerapreeyakul N, Thumanu K, Tanthanuch W, Barusrux S (2014) Melatonin induces apoptosis through biomolecular changes, in SK-LU-1 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Prolif 47:564–577. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12140
Prastyanto S, Sitaresmi MN, Julia M (2014) Lipid profiles in smoking and non-smoking male adolescents. Article in Paediatrica Indonesiana 54(4):232. https://doi.org/10.14238/pi54.4.2014.232-5
Rahman I, Kode A, Biswas S (2006) Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat Protoc 1:3159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.378
Ramalingam A, Santhanathas T, Ali S, Zainalabidin S (2019) Resveratrol supplementation protects against nicotine-induced kidney injury. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:4445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224445
Rodriguez C, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Antol I, Herrera F, Mart V, Reiter RJ (2004) Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: a significant role for melatonin. J Pineal Res 36(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1600-079X.2003.00092.x
Sakhatskyy P, Miranda AGG, Newton J, Lee GC, Choudhary G, Vang A, Rounds S, Lu Q (2014) Cigarette smoke-induced lung endothelial apoptosis and emphysema is associated with impairment of FAK and eIF2α. Microvasc Res 94:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2014.05.003
Sener S, Toklu ZH, Cetinel S (2007) β-Glucan protects against chronic nicotine-induced oxidative damage in rat kidney and bladder. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2006.06.003
Sharif S, Farasat T, Fatima N, Farooq SA, Naz S (2014) Effect of nicotine on hematology, lipid profile and liver enzymes in adult male mice (Mus musculus). Advances in Ani and Vet Sci 2(4):222–225. https://doi.org/10.14737/journal.aavs/2014/2.4.222.225
She M, Deng X, Guo Z, Laudon M, Hu Z, Liao D, Hu X, Luo Y, Shen Q, Su Z, Yin W (2009) NEU-P11, a novel melatonin agonist, inhibits weight gain and improves insulin sensitivity in high-fat/high-sucrosefed rats. Pharmacol Res 59:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2009.01.005
Sherke AB, Vadapalli K, Bhargava VD, Sherke RA, Gopireddy MRM (2016) Effect of number of cigarettes smoked per day on red blood cell, lecocyte and platelet count in adult Indian male smokers – a case control study. Int J MedRes & Health Sci 5(2):13–17 Available online at: www.ijmrhs.com. Accessed 23 Nov 2020
Sherwin MA, Gastwirth CM (1990) Detrimental effects of cigarette smoking on lower extremity wound healing. J Foot Surg 29(1):84–87
Slanar O, Pelisek V, Vanecek J (2000) Melatonin inhibitspituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating polypeptide induced increase of cyclic AMP accumulationand [Ca2+] in cultured cells of neonatal rat pituitary. Neurochem Int 36(3):213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-0186(99)00120-5
Stein EA (1987) Lipids, lipoproteins. In: Tietz NW (ed) Fundamentals of clinical chemistry, 3rd edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 448–481
Suzuki J, Bayna E, Molle DE, Lew YWW (2003) Nicotine inhibits cardiac apoptosis induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. J the Ame Coll Cardiol:41(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(02)02820-6
Szczepanik M (2008) Melatonin and its influence on immune system. J Physiol Pharmacol 58:115–124
Tengattini S, Reiter JR, Tan DX, Terron PM, Rodella FL, Rezzani R (2008) Cardiovascular diseases: protective effects of melatonin. J Pineal Res 44:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00518.x.
Tordjman S, Chokron S, Delorme R, Charrier A, Bellissant E, Jaafari N, Fougerou C (2017) Melatonin: pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr Neuropharmacol 15(3):434–443. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X14666161228122115
Unlu M, Fidan F, Sezer M, Tetik L, Sahin O, Esme H, Koken T, Serteser M (2006) Effects of melatonin on the oxidant/antioxidant status and lung histopathology in rabbits exposed to cigarette smoke. Respirology 11(4):422–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.00865.x
Warren WG, Singh KA (2013) Nicotine and lung cancer. J Carcinog 12:1. https://doi.org/10.4103/1477-3163.106680
Wu J, Gorman A, Zhou X, Sandra C, Chen E (2002) Involvement of caspase-3 in photoreceptor cell apoptosis induced by in vivo blue light exposure. Invest Ophthalmol& Visual Sci 43:10
Zeidler R, Albermann K, Lang S (2007) Nicotine and apoptosis. Springer 12:1927–1943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0102-8
Zhong J, Liu Y (2018) Melatonin and age-related cardiovascular diseases. Aging Med 1:197–203. https://doi.org/10.1002/agm2.12036
Zhou X, Sheng Y, Yang R, Kong X (2010) Nicotine promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis via oxidative stress and altered apoptosis-related gene expression. Cardiol. 115:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1159/000301278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aya Khalil Hendawy: the corresponding author, writing the original draft, application of statistical analysis of data; Nahed El Sayed El-Toukhey: oversight and leadership responsibility for the research activity planning and execution “Supervision”; Sahar Samir Abd El-Rahman: histopathological examination; Hodallah Hatem Ahmed: ideas; formulation or evolution of overarching research goals and aims “Conceptualization,” development or design of methodology “Methodology,” oversight and leadership responsibility for the research activity planning and execution “Supervision,” and revision paper before submission for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval and consent to participate are already stated in “Materials and methods” as the following: The experimental protocol and procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University (VET. CU. IACUC, (Egypt) with approval number (Vet CU/23012020104).
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32104-8
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(JPG 273 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hendawy, A.K., El-Toukhey, N.E.S., AbdEl-Rahman, S.S. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Ameliorating effect of melatonin against nicotine induced lung and heart toxicity in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 35628–35641 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12949-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12949-z