Abstract
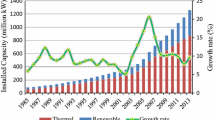
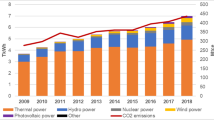
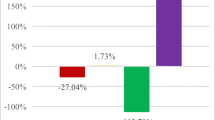
The energy transition from coal and oil to renewable energy, nuclear energy, and natural gas is a fundamental way for emission reduction of China’s power generation sector. Until now, research on the drivers of CO2 emissions from China’s power generation sector has generally evaluated the energy mix as a whole, with a lack of exploration of the decomposition of different types of energy. This paper uses both index decomposition analysis (IDA) and structural decomposition analysis (SDA) to explore the impacts of energy transition on CO2 emissions in the power generation sector during periods of 2002–2007, 2007–2012, and 2012–2017. We find that the results of IDA and SDA are almost consistent, indicating that our results are robust. During the whole study period, CO2 emissions of power generation sector increased by 2447 Mt, of which the fossil fuel structure significantly contributed 642 Mt of incremental emissions (IDA). The thermal power generation efficiency was a dominator for reducing emissions, with a total reduction of 586 Mt (IDA). Simultaneously, the impacts of renewable energy and nuclear energy on emission reduction tend to be strengthening over time, with values changing from 38 Mt and −5 Mt in 2002-2007 to −219 Mt and −83 Mt (IDA) in 2012-2017, respectively. Based on the results, we put forward some suggestions such as promoting coal-to-gas, renewable energy, and nuclear energy in power generation to cut down CO2 emissions of China’s power generation sector.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available in the National Bureau of Statistics of China, China Energy Statistics Yearbook, and China Electricity Statistical Yearbook http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/.
References
Ang BW (2004) Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy. Energy Policy 32:1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-4215(03)00076-4
Ang BW (2015) LMDI decomposition approach: a guide for implementation. Energy Policy 86:233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.07.007
Ang BW, Choi K-H (1997) Decomposition of aggregate energy and gas emission intensities for industry: a refined divisia index method. Energy J 18:59–74. https://doi.org/10.5547/ISSN0195-6574-EJ-Vol18-No3-3
Ang BW, Zhang FQ, Choi K-H (1998) Factorizing changes in energy and environmental indicators through decomposition. Energy 23:489–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(98)00016-4
Bloomberg New Energy Finance (2019) New Energy Outlook. https://about.bnef.com/new-energy-outlook/. Accessed 8 July 2019
Butnar I, Llop M (2011) Structural decomposition analysis and input–output subsystems: changes in CO2 emissions of Spanish service sectors (2000–2005). Ecol Econ 70:2012–2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.05.017
Chen Y, Zhao J, Lai Z, Wang Z, Xia H (2019) Exploring the effects of economic growth, and renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on China’s CO2 emissions: evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew Energy 140:341–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.03.058
Chen G, Hou F, Li J, Chang K (2020) Decoupling analysis between carbon dioxide emissions and the corresponding driving forces by Chinese power industry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:2369–2378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10666-7
China Electric Power Yearbook Editorial Board (2003-2018) China Electric Power Yearbook 2002-2017. China Electric Power Press, Beijing. https://data.cnki.net/yearbook/Single/N2019060101. Accessed 15 June 2019
Chinese Input-Output Association (2017) Chinese input-output table of 42 sector. http://www.stats.gov.cn/ztjc/tjzdgg/trccxh/zlxz/trccb/. Accessed 8 July 2019
Chong CH, Tan WX, Ting ZJ, Liu P, Ma L, Li Z, Ni W (2019) The driving factors of energy-related CO2 emission growth in Malaysia: the LMDI decomposition method based on energy allocation analysis. Renew Sust Energ Rev 115:109356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109356
Cui G, Yu Y, Zhou L, Zhang H (2020) Driving forces for carbon emissions changes in Beijing and the role of green power. Sci Total Environ 728:138688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138688
Dai L, Wang M (2020) Study on the influence of carbon emission constraints on the performance of thermal power enterprises. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:30875–30884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09604-4
De Oliveira-De Jesus PM (2019) Effect of generation capacity factors on carbon emission intensity of electricity of Latin America & the Caribbean, a temporal IDA-LMDI analysis. Renew Sust Energ Rev 101:516–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.11.030
De Oliveira-De Jesus PM, Galvis JJ, Rojas-Lozano D, Yusta JM (2020) Multitemporal LMDI index decomposition analysis to explain the changes of aci by the power sector in Latin America and the Caribbean between 1990–2017. Energies 13:2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092328
Deng M, Li W, Hu Y (2016) Decomposing industrial energy-related CO2 emissions in Yunnan Province, China: switching to low-carbon economic growth. Energies 9:23. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9010023
Dietzenbacher E, Los B (1998) Structural decomposition techniques: sense and sensitivity. Econ Syst Res 10:307–324. https://doi.org/10.1080/09535319800000023
Dietzenbacher E, Los B (2000) Structural decomposition analyses with dependent determinants. Econ Syst Res 12:497–514. https://doi.org/10.1080/09535310020003793
Feng C, Zheng C-J, Shan M-L (2020) The clarification for the features, temporal variations, and potential factors of global carbon dioxide emissions. J Clean Prod 255:120250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120250
Goh T, Ang BW, Su B, Wang H (2018) Drivers of stagnating global carbon intensity of electricity and the way forward. Energy Policy 113:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.10.058
Hastuti SH, Hartono D, Putranti TM, Imansyah MH (2020) The drivers of energy-related CO2 emission changes in Indonesia: structural decomposition analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11414-7
Hoekstra R, van den Bergh JCJM (2003) Comparing structural decomposition analysis and index. Energy Econ 25:39–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-9883(02)00059-2
Huang J-B, Luo Y-M, Feng C (2019) An overview of carbon dioxide emissions from China’s ferrous metal industry: 1991-2030. Resources Pol 62:541–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2018.10.010
IEA (2002-2017) Generation of various energy sources in China. International Energy Agency, Paris. https://www.iea.org. Accessed 25 June 2019
IPCC (2006) 2006 IPCC Guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. intergovernmental panel on climate change. http://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/vol2.html. Accessed 6 June 2019
IPCC (2018) Global warming of 1.5 °C: special report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5 °C. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Switzerland. https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/. Accessed 6 June 2019
Jiang T, Yang J, Huang S (2020) Evolution and driving factors of CO2 emissions structure in China’s heating and power industries: the supply-side and demand-side dual perspectives. J Clean Prod 264:121507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121507
Kim H, Kim M, Kim H, Park S (2020) Decomposition analysis of CO2 emission from electricity generation: comparison of OECD countries before and after the financial crisis. Energies 13:3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13143522
Kung C-C, McCarl BA (2020) The potential role of renewable electricity generation in Taiwan. Energy Policy 138:111227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111227
Li X, Liao H, Du Y-F, Wang C, Wang J-W, Liu Y (2018) Carbon dioxide emissions from the electricity sector in major countries: a decomposition analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:6814–6825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1013-z
Li J, Li S, Wu F (2020) Research on carbon emission reduction benefit of wind power project based on life cycle assessment theory. Renew Energy 155:456–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.03.133
Liao C, Wang S, Zhang Y, Song D, Zhang C (2019) Driving forces and clustering analysis of provincial-level CO2 emissions from the power sector in China from 2005 to 2015. J Clean Prod 240:118026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118026
Lin B, Li Z (2020) Is more use of electricity leading to less carbon emission growth? An analysis with a panel threshold model. Energy Policy 137:111121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111121
Lindner S, Legault J, Guan D (2013) Disaggregating the electricity sector of China’s input–output table for improved environmental life-cycle assessment. Econ Syst Res 25:300–320. https://doi.org/10.1080/09535314.2012.746646
Liu Y, Feng C (2020) Decouple transport CO2 emissions from China’s economic expansion: a temporal-spatial analysis. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 79:102225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2020.102225
Liu Y, Wang M, Feng C (2020) Inequalities of China’s regional low-carbon development. J Environ Manag 274:111042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111042
Luo F, Guo Y, Yao M, Cai W, Wang M, Wei W (2020) Carbon emissions and driving forces of China’s power sector: input-output model based on the disaggregated power sector. J Clean Prod 268:121925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121925
Lykidi M, Gourdel P (2017) Optimal management of flexible nuclear power plants in a decarbonising competitive electricity market: The French case. Energy 132:171–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.05.065
Ma J-J, Du G, Xie B-C (2019) CO2 emission changes of China’s power generation system: input-output subsystem analysis. Energy Policy 124:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.09.030
Mai L, Ran Q, Wu H (2020) A LMDI decomposition analysis of carbon dioxide emissions from the electric power sector in Northwest China. Nat Res Model 33:e12284. https://doi.org/10.1111/nrm.12284
Mi Z, Meng J, Guan D, Shan Y, Song M, Wei YM, Liu Z, Hubacek K (2017) Chinese CO2 emission flows have reversed since the global financial crisis. Nat Commun 8:1712. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01820-w
Mohlin K, Camuzeaux JR, Muller A, Schneider M, Wagner G (2018) Factoring in the forgotten role of renewables in CO2 emission trends using decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 116:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.02.006
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBS) (2003a-2018a) China Energy Statistical Yearbook 2002-2017. China Statistics Press, Beijing. https://data.cnki.net/area/Yearbook/Single/N2008070077?z=D20. Accessed 7 June 2019
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBS) (2003b-2018b) China Statistics Yearbook 2002-2017. China Statistics Press, Beijing. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ Accessed 7 June 2019
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBS) (2020) Input-output table of the People’s Republic of China. China Statistics Press, Beijing. https://data.stats.gov.cn/ifnormal.htm?u=/files/html/quickSearch/trcc/trcc01.html&h=740. Accessed 8 June 2020
Nguyen KH, Kakinaka M (2019) Renewable energy consumption, carbon emissions, and development stages: some evidence from panel cointegration analysis. Renew Energy 132:1049–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.069
Ozcan M (2019) Factors influencing the electricity generation preferences of Turkish citizens: citizens’ attitudes and policy recommendations in the context of climate change and environmental impact. Renew Energy 132:381–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.08.006
Peng X, Tao X, Feng K, Hubacek K (2020) Drivers toward a low-carbon electricity system in China’s provinces. Environ Sci Technol 54:5774–5782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00536
Rauner S, Bauer N, Dirnaichner A, Dingenen RV, Mutel C, Luderer G (2020) Coal-exit health and environmental damage reductions outweigh economic impacts. Nat Clim Chang 10:308–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-020-0728-x
Raza MY, Lin B (2020) Decoupling and mitigation potential analysis of CO2 emissions from Pakistan’s transport sector. Sci Total Environ 730:139000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139000
Roelfsema M, van Soest H, Drouet L, Emmerling JA, Reis L (2020) Taking stock of national climate policies to evaluate implementation of the Paris Agreement. Nat Commun 11:2096. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15414-6
Shan Y, Guan D, Zheng H, Ou J, Li Y, Meng J, Mi Z, Liu Z, Zhang Q (2018) China CO2 emission accounts 1997-2015. Sci Data 5:170201. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.201
Su B, Ang BW (2012) Structural decomposition analysis applied to energy and emissions: some methodological developments. Energy Econ 34:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2011.10.009
Su B, Ang BW (2016) Multi-region comparisons of emission performance: the structural decomposition analysis approach. Ecol Indic 67:78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.02.020
Su B, Ang BW, Li Y (2017) Input-output and structural decomposition analysis of Singapore’s carbon emissions. Energy Policy 105:484–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.03.027
Wang M, Feng C (2020) The impacts of technological gap and scale economy on the low-carbon development of China’s industries: an extended decomposition analysis. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 157:120050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120050
Wang Y, Li J (2019) Spatial spillover effect of non-fossil fuel power generation on carbon dioxide emissions across China’s provinces. Renew Energy 136:317–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.012
Wang H, Ang BW, Su B (2017) Assessing drivers of economy-wide energy use and emissions: IDA versus SDA. Energy Policy 107:585–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.05.034
Wang J, Rodrigues JFD, Hu M, Behrens P, Tukker A (2019a) The evolution of Chinese industrial CO2 emissions 2000–2050: a review and meta-analysis of historical drivers, projections and policy goals. Renew Sust Energ Rev 116:109433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109433
Wang Y, Su X, Qi L, Shang P, Xu Y (2019b) Feasibility of peaking carbon emissions of the power sector in China’s eight regions: decomposition, decoupling, and prediction analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:29212–29233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05909-1
Wang S, Zhu X, Song D, Wen Z, Chen B, Feng K (2019c) Drivers of CO2 emissions from power generation in China based on modified structural decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 220:1143–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.199
Wang Z, Meng J, Guan D (2020a) Dynamic driving forces of India’s emissions from production and consumption perspectives. Earth’s Future 8:e2020EF001485. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020ef001485
Wang P-T, Wei Y-M, Yang B, Li J-Q, Kang J-N, Liu L-C, Yu B-Y, Hou Y-B, Zhang X (2020b) Carbon capture and storage in China’s power sector: optimal planning under the 2 °C constraint. Appl Energy 263:114694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114694
Wen L, Li Z (2020) Provincial-level industrial CO2 emission drivers and emission reduction strategies in China: combining two-layer LMDI method with spectral clustering. Sci Total Environ 700:134374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134374
Xu Y, Yang K, Yuan J (2020) China’s power transition under the global 1.5 degrees C target: preliminary feasibility study and prospect. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:15113–15129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08085-9
Yang J, Cai W, Ma M, Li L, Liu C, Ma X, Li L, Chen X (2020) Driving forces of China’s CO2 emissions from energy consumption based on Kaya-LMDI methods. Sci Total Environ 711:134569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134569
Yuan R, Zhao T (2016) Changes in CO2 emissions from China’s energy-intensive industries: a subsystem input–output decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 117:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.081
Yuan J, Na C, Lei Q, Xiong M, Guo J, Hu Z (2018) Coal use for power generation in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.03.021
Zhang C, Zhang M, Zhang N (2017) CO2 Emissions from the power industry in the China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region: decomposition and policy analysis. Pol J Environ Stud 26:903–916. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/66718
Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wu S (2019) Chapter 1 - Review and outlook of world energy development. In: Zhang Y et al (eds) Non-fossil energy development in China. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 1–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813106-0.00001-5
Zhang P, Cai W, Yao M, Wang Z, Yang L, Wei W (2020) Urban carbon emissions associated with electricity consumption in Beijing and the driving factors. Appl Energy 275:115425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115425
Zhao Y, Cao Y, Shi X, Li H, Shi Q, Zhang Z (2020) How China’s electricity generation sector can achieve its carbon intensity reduction targets? Sci Total Environ 706:135689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135689
Acknowledgements
We thank the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was funded by the Major Program of Social Science Foundation of Tianjin Municipal Education Commission (No. 2016JWZD04) and the Ministry of Education of Humanities and Social Science Research Fund Plan (No. 15YJA790091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW did the data collection and decomposition analysis and writing the original draft. TZ came up with this research idea and financially supported this work. JW analyzed existing literatures and provided a lot of work for the revision of the paper. XZ was responsible for the preliminary investigation and data collection. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Eyup Dogan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix. Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 224 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Zhao, T., Wang, J. et al. Exploring the impact of transition in energy mix on the CO2 emissions from China’s power generation sector based on IDA and SDA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 30858–30872 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12599-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12599-1