Abstract
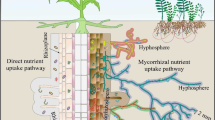
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (AMF) is generally colonized in plant roots and influences the migration of mineral elements such as nitrogen (N) in soils. However, its effect on N leaching loss in red soils is limited. In the present study, red soils were collected from wasteland, farmland, and slopeland in the Yunnan Plateau. Maize, as a host plant, was cultured in a dual-compartment cultivation system. There were mycorrhizal and hyphal compartments for the AMF inoculation treatment and root and soil compartments for the non-inoculation treatment. The N concentration and uptake in maize, N concentration in pore water within two depth (0–20 and 20–40 cm), and N leaching losses from soil under simulated heavy rainfall (40 and 80 mm/h) were analyzed. Results showed that AMF inoculation significantly enhanced the biomass and N uptake in maize. Compared with the root and soil compartments, the N concentrations in pore water and their leaching losses from the mycorrhizal and hyphal compartments were decreased by 48–77% and 51–74%, respectively. Moreover, significant or extremely significantly positive correlations were observed between the N concentrations in pore water with the N leaching losses from soil. The three-way ANOVA showed that AMF highly significantly decreased N concentrations in pore water and their leaching losses from wasteland, farmland, and slopeland; rainfall intensity had strong influences on the N concentration in pore water from farmland and N leaching losses from wasteland and farmland, whereas the maize root’s effect was insignificant. The study indicated that the AMF-induced decreases in the N leaching loss from red soils were caused by increased N uptake by maize and decreased N concentrations in pore water. These results have implications for reducing nutrient leaching loss through the management of beneficial microorganisms in soils.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asghari HR, Cavagnaro TR (2011) Arbuscular mycorrhizas enhance plant interception of leached nutrients. Funct Plant Biol 38:219–226
Asghari HR, Cavagnaro TR (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhizas reduce nitrogen loss via leaching. PLoS One 7:e29825
Bao S (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Behie SW, Bidochka MJ (2014) Nutrient transfer in plant–fungal symbioses. Trends Plant Sci 19:734–740
Bender SF, Conen F, Van der Heijden MGA (2015) Mycorrhizal effects on nutrient cycling, nutrient leaching and N2O production in experimental grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 80:283–292
Bouwman AF (1990) Global distribution of the major soils and land cover types. In: Bouwman AF (ed) Soils and the greenhouse effect. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp 33–57
Bowles TM, Jackson LE, Cavagnaro TR (2018) Mycorrhizal fungi enhance plant nutrient acquisition and modulate nitrogen loss with variable water regimes. Glob Chang Biol 24:171–182
Cameron KC, Di HJ, Moir JL (2013) Nitrogen losses from the soil/plant system: a review. Ann Appl Biol 162:145–173
Cavagnaro TR, Jackson LE, Scow KM, Hristova KR (2007) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizas on ammonia oxidizing bacteria in an organic farm soil. Microb Ecol 54:618–626
Cavagnaro TR, Bender SF, Asghari HR, van der Heijden MGA (2015) The role of arbuscular mycorrhizas in reducing soil nutrient loss. Trends Plant Sci 20:283–290
Chen B, Christie P, Li X (2001) A modified glass bead compartment cultivation system for studies on nutrient and trace metal uptake by arbuscular mycorrhiza. Chemosphere 42:185–192
Corkidi L, Merhaut DJ, Allen EB, Downer J, Bohn J, Evans M (2011) Effects of mycorrhizal colonization on nitrogen and phosphorus leaching from nursery containers. HortScience 46:1472–1479
Daniels BA, Skipper HD (1982) Methods for the recovery and quantitative estimation of propagules from soil, Methods and Principles of Mycorrhizal Research. American Phytopathologic Society, St. Paul, pp 29–35
Drew EA, Murray RS, Smith SE, Jakobsen I (2003) Beyond the rhizosphere: growth and function of arbuscular mycorrhizal external hyphae in sands of varying pore sizes. Plant Soil 251:105–114
Fang F, Wang C, Wu F, Tang M, Doughty R (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi mitigate nitrogen leaching under poplar seedlings. Forests 11:325
Ghestem M, Stokes A, Slide R (2011) The influence of plant root systems on subsurface flow: implications for slope stability. BioScience 61:869–879
He YM, Fan XM, Zhang GQ, Li B, Li MR, Zu YQ, Zhan FD (2019) Influences of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and dark septate endophytes on the growth, nutrition, photosynthesis and antioxidant physiology of maize. Int J Agric Biol 22:1071–1078
He YM, Yang R, Lei G, Li B, Jiang M, Yan K, Zu YQ, Zhan FD, Li Y (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduce cadmium leaching from polluted soils under simulated heavy rainfall. Environ Pollut 263:114406
Huang J, Xu C, Ridoutt BG, Wang X, Ren P (2017) Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J Clean Prod 159:171–179
Jiang XJ, Liu W, Chen C, Liu J, Yuan ZQ, Jin B, Yu X (2018) Effects of three morphometric features of roots on soil water flow behavior in three sites in China. Geoderma 320:161–171
Köhl L, van der Heijden MGA (2016) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal species differ in their effect on nutrient leaching. Soil Biol Biochem 94:191–199
Lu Y, Hu W, Lei B, Duan Z, Liu H, Zhai L (2012) The monitoring of nitrogen and phosphorus loss by surface runoff in sloping red soil fields of Yunnan Province, China. J Agro–Environ Sci 31:1544–1553
Lu S, Wang S, Chen Y (2015) Palaeopedogenesis of red palaeosols in Yunnan Plateau, southwestern China: pedogenical, geochemical and mineralogical evidences and palaeoenvironmental implication. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl 420:35–48
Ma X, Li Y, Li B, Han W, Liu D, Gan X (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus losses by runoff erosion: field data monitored under natural rainfall in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 147:797–808
Mardhiah U, Caruso T, Gurnell A, Rillig MC (2016) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal hyphae reduce soil erosion by surface water flow in a greenhouse experiment. Appl Soil Ecol 99:137–140
Martínez-García LB, De Deyn GB, Pugnaire FI, Kothamasi D, van der Heijden MGA (2017) Symbiotic soil fungi enhance ecosystem resilience to climate change. Glob Chang Biol 23:5228–5236
McGonigle TP, Miller MH, Evans DG, Fairchild GL, Swan JA (1990) A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 115:495–501
Mohan JE, Cowden CC, Baas P, Dawadi A, Frankson PT, Helmick K, Hughes E, Khan S, Lang A, Machmuller M, Taylor M, Witt CA (2014) Mycorrhizal fungi mediation of terrestrial ecosystem responses to global change: mini–review. Fungal Ecol 10:3–19
Morales VL, Parlange JY, Steenhuis TS (2010) Are preferential flow paths perpetuated by microbial activity in the soil matrix? A review. J Hydrol 393:29–36
Morris E, Morris D, Vogt S, Gleber SC, Bigalke M, Wilcke W, Rillig M (2019) Visualizing the DYNAMICS of soil aggregation as affected by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. ISME J 13:1639–1646
Morrison E, Lagos L, Al-Agely A, Glaab H, Johnson W, Jorquera MA, Ogram A (2017) Mycorrhizal inoculation increases genes associated with nitrification and improved nutrient retention in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 53:275–279
Olsson PA, Thingstrup I, Jakobsen I, Bååth E (1999) Estimation of the biomass of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a linseed field. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1879–1887
Peng E, Wang S, Hao L, Yu Y, Yu J (2009) Approaches to basic farmland and plowland protection in Yunnan province. Resourc Indu 11:59–63
Rillig MC, Mummey DL (2006) Mycorrhizas and soil structure. New Phytol 171:41–53
Saia S, Aissa E, Luziatelli F, Ruzzi M, Colla G, Ficca AG, Cardarelli M, Rouphael Y (2020) Growth-promoting bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi differentially benefit tomato and corn depending upon the supplied form of phosphorus. Mycorrhiza 30:133–147
Smith SE, Read DJ (2010) Mycorrhizal symbiosis Academic Press. Elsevier Ltd, Oxford
Smith SE, Smith FA (2011) Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant nutrition and growth: new paradigms from cellular to ecosystem scales. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:227–250
Tanaka Y, Yano K (2005) Nitrogen delivery to maize via mycorrhizal hyphae depends on the form of N supplied. Plant Cell Environ 28:1247–1254
Treseder KK, Cross A (2006) Global distributions of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecosystems 9:305–316
van der Heijden MGA (2010) Mycorrhizal fungi reduce nutrient loss from model grassland ecosystems. Ecology 91:1163–1171
van der Heijden MGA, Martin FM, Selosse MA, Sanders IR (2015) Mycorrhizal ecology and evolution: the past, the present, and the future. New Phytol 205:1406–1423
Veresoglou SD, Shaw LJ, Hooker JE, Sen R (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhizal modulation of diazotrophic and denitrifying microbial communities in the (mycor)rhizosphere of Plantago lanceolata. Soil Biol Biochem 53:78–81
Wang T, Zhu B (2011) Nitrate loss via overland flow and interflow from a sloped farmland in the hilly area of purple soil, China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 90:309–319
Wei F, Qi W, Sun Z, Huang Y, Shen Y (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method (4th Edition) China Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Zhang N, Yu Y, Hong B, Chen J, Zhang Y (2004) Factors influencing runoff P losses from farmlands of the Dianchi Lake Watershed in Yunnan, China. Pedosphere 14:259–262
Zhang S, Wang L, Ma F, Zhang X, Fu D (2016) Reducing nitrogen runoff from paddy fields with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under different fertilizer regimes. J Environ Sci 46:92–100
Zhang S, You Z, Guo X, Yun W, Xia Y, Rillig MC (2020) Suitability of mycorrhiza-defective rice and its progenitor for studies on the control of nitrogen loss in paddy fields via arbuscular mycorrhiza. Front Microbiol 11:186
Zhao QG, Huang GQ, Ma YQ (2013) The problems in red soil ecosystem in southern of China and its countermeasures. Acta Ecol Sin 2013(33):7615–7622
Zheng HJ, Hu JM, Huang PF, Wang LY, Wan JL (2014) Comparative study of nitrogen and phosphorus through surface–flow and interflow on red soil farmland. J Soil Water Conserv 28:41–45
Zhong X, Zhang L, Zhang N, Nian F, Jia G, Yue X, Xia Y (2018) Soil N and P loss in slope farmland of Dianchi watershed. J Soil Water Conserv 32:42–47
Zou L, Liu Y, Wang Y, Hu X (2020) Assessment and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution loads in China: 1978-2017. J Environ Manag 263:110400
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key Research Development Project of Yunnan Province (No. 2019BC001-04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41661056), and the Reserve Talents Fund for Young and Middle-Aged Academic and Technological Leaders in Yunnan Province (Nos. 2018HB043 and 202005AC160038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yongmei He: conceptualization, writing (original draft), funding acquisition
Bo Li: methodology, investigation, writing (original draft), data curation
Kai Yan: methodology, formal analysis
Rui Yang: methodology, investigation
Gang Lei: methodology, writing (original draft preparation), investigation
Mingrui Li: software, formal analysis
Yuan Li: funding acquisition, project administration, supervision
Fangdong Zhan: conceptualization, funding acquisition, data curation, writing (review and editing), project administration, supervision
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Li, B., Yan, K. et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus-induced decrease in nitrogen concentration in pore water and nitrogen leaching loss from red soil under simulated heavy rainfall. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 17457–17467 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12131-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12131-x