Abstract
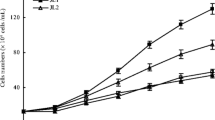
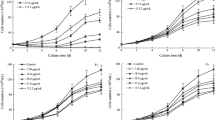
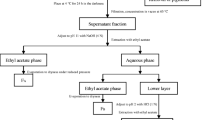
The ethanol extracts of Gracilaria lemaneiformis that have inhibitory effects on Karenia mikimotoi and Skeletonema costatum were separated by liquid-liquid extraction using different polar solvents into five fractions with antialgal activities (petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, and water-soluble fractions). These fractions were chromatographed on silica gel to give, after repeated preparative thin-layer chromatography (PTLC) purification processes, 1-β-d-ribofuranosyluracil (1), 3-hydroxymethyl-pyrrolopiperazine-2,5-dione (2), benzene-1,2-propanoic acid (3), 1-O-palmitoyl-2-O-palmitoleoyl-3-O-β-d-galactopyranosyl glycerol (4), 7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]-heptan-3-ol (5), linoleic acid (6), 3,4-dimethoxy-6-(methoxymethyl)-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2,5-diol (7), and 3,7,11,16-tetramethyl -2-heptadecen-1-ol (8). Five of them, natural products 1, 2, 5, 7, and 8, were isolated from Gracilaria lemaneiformis for the first time, and three natural products (3, 5, and 8) were isolated from marine macroalgae for the first time. Among them, natural products (1, 2, 3, 4, and 6) showed the most obvious inhibition activities to the growth of Karenia mikimotoi and Skeletonema costatum at the concentration of 80 μg/mL. Therefore, antialgal activities of these five natural products against Amphidinium carterae, Heterosigma akashiwo, Karenia mikimotoi, Phaeocystis globosa, Prorocentrum donghaiense, and Skeletonema costatum were further tested at different concentrations (0.4, 2, 10, and 50 μg/mL). This was the first report of antialgal activities of five natural products (1, 2, 3, 4, and 6) to these six red tide microalgae. They showed significantly selective antialgal activities against all tested red tide microalgae. At the concentration of 50 μg/mL, the growth of Amphidinium carterae, Heterosigma akashiwo, Karenia mikimotoi, and Phaeocystis globosa was obviously inhibited; for Karenia mikimotoi, natural products 1, 2, and 6 have significant antialgal activities; the growth inhibition of Skeletonema costatum that was exposed to natural products 1, 3, and 4 was remarkable. Furthermore, by analyzing and comparing EC50–96 h values, it has been determined that natural product 3 (natural product 4) showed the superior application potential than potassium dichromate and some reported natural products (such as gossonorol isolated from Porphyra yezoensis, trehalose purified from Ulva pertusa) as a characteristic antialgal agent against Amphidinium carterae (Phaeocystis globosa). In addition, natural products 1 and 3 also showed good superiority than some reported natural products in inhibiting Skeletonema costatum; however, it was a pity that they were inferior to potassium dichromate in the inhibiting this red tide microalgae. Taken together, it is not hard to conclude that Gracilaria lemaneiformis was a good source of natural products with antialgal activities against some red tide microalgae.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Accoroni S, Percopo I, Cerino F, Romagnoli T, Totti C (2015) Allelopathic interactions between the HAB dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata and macroalgae. Harmful Algae 49:147–155
Alamsjah MA, Hirao S, Ishibashi F, Fujita Y (2005) Isolation and structure determination of algicidal compounds from Ulva fasciata. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69:2186–2192
An Z, Wang ZY, Li FM, Tian ZJ, Hu HY (2008) Allelopathic inhibition on red tide microalgae Skeletonema costatum by five macroalgal extracts. Front Environ Sci Eng China 2(3):297–305 (in Chinese)
Anderson RJ, Monteiro PMS, Levitt GJ (1996) The effect of localised eutrophication on competition between Ulva lactuca (Ulvaceae, Chlorophyta) and a commercial resource of Gracilaria verrucosa (Gracilariaceae, Rhodophyta). Hydrobiologia 326–327(1):291–296
Ben Gharbia H, Kéfi-Daly Yahia O, Cecchi P, Masseret E, Amzil Z, Herve F, Rovillon G, Nouri H, M’Rabet C, Couet D, Triki HZ, Laabir M (2017) New insights on the species-specific allelopathic interactions between macrophytes and marine HAB dinoflagellates. PLoS One 12(11):1–28
Bie CC, Li FM, Li YY, Zhao YH, Wang ZY (2011) Inhibitory effects of 6 macroalgae extracts on Skeletonema costatum and isolation of allelochemicals. Period Ocean Univ China 41(7/8):107–112 (in Chinese)
Cai SY (2016) Effects of the massive cultivation of Gracilaria lemaneiformis on plankton community structure and its inhibition on microalgal bloom. Dissertation, Jinan University (in Chinese)
Chen MZ, Zhang YY, Yu J, Xie XB (2004) Studies on separation and scavenging activities on free radicals of phycobiliproteins from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Food Sci 25(3):159–162 (in Chinese)
Chen MZ, Yu J, Long ZJ, Luo QB (2005) Studies on antimutagenic and the free radical scavenging effect of polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Food Sci 26(7):219–222 (in Chinese)
Chen MZ, Ge AS, Yu J, Yang WJ (2007) Studies of antitumor activity of phycoerythrin from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Chin J Mar Drugs 26(4):27–31 (in Chinese)
Chen MZ, Yu J, Liao ZH, Wang X (2008) Study on the antitumor activity and antioxidation of polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis in sarcoma180 bearing mice. Chin J Mar Drugs 27(2):46–49 (in Chinese)
Cho JY, Jin HJ, Lim HJ, Whyte JNC, Hong YK (1999) Growth activation of the microalga Isochrysis galbana by the aqueous extract of the seaweed Monostroma nitidum. J Appl Phycol 10(6):561–567
Chowdhury MTH, Bangoura I, Kang JY, Cho JY, Joo J, Choi YS, Hwang DS, Hong YK (2014) Comparison of Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis for phlorotannin extraction. J Environ Biol 35:713
Cui F (2014) Studies on allelopathy effects of Ulva prolifera on red tide microalgae and allelochemicals identification. Dissertation, Shanghai Ocean University. (in Chinese)
El Hattab M, Genta-Jouve G, Bouzidi N, Ortalo-Magné A, Hellio C, Maréchal J-P, Piovetti L, Thomas OP, Culioli G (2015) Cystophloroketals A-E, unusual phloroglucinol-meroterpenoid hybrids from the brown alga Cystoseira tamariscifolia. J Nat Prod 78:1663–1670
Fletcher RL (1975) Heteroantagonism observed in mixed algal cultures. Nature 253(5492):534–535
Gao H, Zhou FF, Tang HJ, Shi XY, Su RG (2018) Allelopathy of extracts of Ulva prolifera on green tides in the Yellow Sea and the identification of the allelochemicals. Acta Oceanol Sin 240(12):11–20 (in Chinese)
Gross EM (2003) Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:313–339
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatom. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can J Microbiol 17:309–314
Hirao S, Tara K, Kuwan K, Tanaka J, Ishibashi F (2012) Algicidal activity of glycerolipids from brown alga Ishige sinicola toward red tide microalgae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76(2):372–374
Jeong JH, Jin HJ, Sohn CH, Suh KH, Hong YK (2000) Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J Appl Phycol 12:37–43
Jin Q (2005) Studies on the allelopathic effects of macroalga Ulva pertusa on red tide microalgae and isolation and characterization of its allelochemicals. Dissertation, Ocean University of China. (in Chinese)
Jin HL (2011) Studies on the inhibition activity of Ulva intestinalis on red tide microalgae and the isolation and identification of the algicidal compounds. Dissertation, Ningbo University
Kang K (2006) Isolation and characterization of allelochemicals from Chlorophyta Ulva pertusa. Dissertation, Ocean University of China
Konig GM, Wright AD, Linden A (1999) Plocamium hamatum and its monoterpenes: chemical and biological investigation of the tropical marine red alga. Phytochemistry 52:1047–1053
Lee VC, Olsen S (1985) Eutrophication and management initiatives for the control of nutrient inputs to rhode island Coastal Lagoons. Estuaries 8(2):191
Lei GY, Yang YF, Li X (2010) Inhibitory effects of Gracilaria lemaneiformis on growth of Heterosigma akashiwo and Prorocentrum micans. Mar Environ Sci 29(1):27–31 (in Chinese)
Li B, Cai HJ, Liu CF (2007) Allelopathic effect of sea weed Chondrus ocellatus on algae Karenia mikimotoi and Prorocentrum minimum. J Dalian Ocean Univ 27(1):27–31 (in Chinese)
Li B, Cai HJ, Liu CF (2012) Allelopathic effect of sea weed Chondrus ocellatus on algae Karenia mikimotoi and Prorocentrum minimum. J Dalian Ocean Univ 27(1):27–31 (in Chinese)
Liu TT (2006) Study on inhibitory effects of Gracilaria lemaneiformis on the three red tide microalgae. Master's thesis, Jinan University. (in Chinese)
Lu HM (2011) Chemical constituents of the seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis and their allelopathic effects on Skeletonema costatum. Dissertation, Jinan University. (in Chinese)
Lu JF, Yang WG, Yan WH, Zhou XY (2009) Purification and composition of polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Oceanol ET Limnol Sin 40(4):484–488 (in Chinese)
Lu CY, Deng Y, Mei L, Guo DL (2011a) Studies on chemical constituents of Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 42(6):1069–1071 (in Chinese)
Lu HM, Xie HH, Yang YF, Wei XY (2011b) Chemical constituents from the macroalga Gracilaria lemaneiformis. J Tropic Subtropic Botany 19(2):166–170 (in Chinese)
Luyen HQ, Cho JY, Choi JS, Kang JY, Park NG, Hong YK (2009) Isolation of algal spore lytic C17 fatty acid from the crustose coralline seaweed Lithophyllum yessoense. J Appl Phycol 21:423–427
Macίas FA, Galindo JLG, Garcίa-Dίaz MD, Galindo JCG (2008) Allelopathic agents from aquatic ecosystems: potential biopesticides models. Phytochem Rev 7:155–178
Manilal A, Sujith S, Sabarathnam B, Kiran GS, Selvin J, Shakir C, Lipton AP (2010) Bioactivity of the red algae Asparagopsis taxiformis collected from the southwestern coast of India. Braz J Oceanogr 58:93–100
Marklund S, Marklun G (1974) Involvement of superoxide anion radical in the auto-oxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:169–174
Marshall SM, Orr AP (1949) Further experiments on the fertilization of a sea loch (Loch Craiglin). J Mar Biol Assoc UK 27:360–379
McLachlan J, Craigie JS (1964) Algal inhibition by yellow ultraviolet-absorbing substances from fucus vesiculosus. Can J Bot 42(3):287–292
Mei WL, Dai HF, Xu JT (2006) Composition and cytotoxic activity of the organic acids from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Chin J Mar Drugs 25(2):45–47 (in Chinese)
Oh MY, Lee SB, Jin DH, Hong YK, Jin HJ (2010) Isolation of algicidal compounds from the red alga Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J Appl Phycol 22(4):453–458
Nagayama K, Shibata T, Fujimoto K, Honjo T, Nakamura T (2003) Algicidal effect of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome on red tide microalgae. Aquaculture 218(1–4):601–611
Nan CR, Zhang HZ, Zhao GQ (2004) Allelopathic interactions between the macroalga Ulva pertusa and eight microalgal species. J Sea Res 52:259–268
OECD (1984) Alga growth inhibition test. Test Guideline No. 201. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Ohsawa N, Ogata Y, Okada N, Itoh N (2001) Physiological function of bromoperoxidase in the red marine alga, Corallina pilulifera: production of bromoform as an allelochemical and the simultaneous elimination of hydrogen peroxide. Phytochemistry 58:683–692
Shao MW, Sun X, Xu NJ (2011) Inhibitory effects of marine red algae Gracilaria lemaneiformis on two HAB algae and the relationship with environmental factors. J Mar Sci 29(2):100–106 (in Chinese)
Sun YY, Zhang J, Liu HJ, Li C, Wang CH (2011) Effects of macroalga Gracilaria lemaneiformis on the growth of the three species of red tide microalgae under laboratory conditions. Mar Sci Bull 30(3):328–333 (in Chinese)
Sun YY, Zhang J, Xu SZ, Li WH, Wang CH (2012) Growth inhibition of Karenia mikimitoi by extracts from Gracilaria lemaneiformis using five solvents. Inform Technol Agric Eng 134:199–210
Sun YY, Wang H, Guo GL, Pu YF, Yan BL, Wang CH (2015) Green alga Ulva pertusa—a new source of bioactive compounds with antialgal activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(13):10351–10359
Sun YY, Wang H, Guo GL, Pu YF, Yan BL, Wang CH (2016) Isolation, purification and identification of antialgal substances in green alga Ulva prolifera for antialgal activity against the common harmful red tide microalgae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1449–1459
Sun YY, Meng K, Su ZX, Guo GL, Pu YF, Yan BL, Wang CH (2017) Isolation and purification of antialgal compounds from the red alga Gracilaria lemaneiformis for activity against common harmful red tide microalgae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(5):4964–4972
Sun YY, Zhou WJ, Guo GL, Pu YF, Su ZX (2018a) Isolation and purification of phenylpropanoid antialgal substances from Gracilaria lemaneiformis and their growth inhibition effects on six species of red tide microalgae. J Fish China 42(7):1019–1025
Sun YY, Xing JZ, Zhang JS, Zhou WJ, Pu YF (2018b) Sesquiterpenoids with antialgal activity against the common red tide microalgae from marine macroalgae Porphyra yezoensis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(8):7844–7859
Sun YY, Zhou WJ, Guo GL, Su ZX, Pu YF (2018c) Antialgal compounds with antialgal activity against the common red tide microalgae from a green algae Ulva pertusa. Ecotox Environ Safe 157:61–66
Sun YY, Dong SS, Zhou WJ, Guo L, Guo GL, Zhang X (2019) A comprehensive review of secondary metabolites with antialgal activity from marine macroalgae against red tide microalgae. J Coast Res (SI) 93:1–14
Suzuki Y, Takabayashi T, Kawaguchi T (1998) Isolation of allelopathic substance from the crustose coralline algae, Lithophyllum spp. and its effect on the brown Algae, Laminaria religiosa miyabe (phaeophyta). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 225:69–77
Takedai F, Sakamaki T, Xu K, Chiba N, Nishimura O, Sudo R (2003) Effect of potential allelochemicals extracted from Sargassum horneri on the growth of red tide microalgae. J Environ Syst Eng 748:25–32
Tanabe H, Kamishima H, Yoshinari K (1993) Inhibitory effect of red alga lectin and skipjack fat on the growth of the red tide plankton Chattonella antiqua. J Ferment Bioeng 75(5):387–388
Tang YZ, Gobler CJ (2011) The green macroalga, Ulva lactuca, inhibits the growth of seven common harmful algal bloom species via allelopathy. Harmful Algae 10:480–488
Tang KX, Yuan DX, Lin SB, Lin YS, You XP, Shen DY, Chen ME, Hong WS (2003) Depression and affect of red tide on main water quality index by Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Mar Environ Sci 22(2):24–27 (in Chinese)
Tang YZ, Kang Y, Berry D, Gobler CJ (2015) The ability of the red macroalga, Porphyra purpurea (Rhodophyceae) to inhibit the proliferation of seven common harmful microalgae. J Appl Phycol 27:531–544
Tian ZJ (2009) Inhibition effect of allelochemicals from large seaweeds on Gymnodinium breve. Master of science and engineering thesis, Ocean University of China. (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Yu ZM, Song XX, Zhang SD (2006) Effects of macroalgae on growth of 2 species of bloom microalgae and interactions between these microalgae in laboratory culture. Environ Sci 27(2):274–280 (in Chinese)
Wang RJ, Xiao H, Zhang PY, Qu L, Cai HJ, Tang XX (2007) Allelopathic effects of Ulva pertusa, Corallina pilulifera and Sargassum thunbergii on the growth of the dinoflagellates Heterosigma akashiwo and Alexandrium tamarense. J Appl Phycol 19(2):109–121
Wang Y, Zhou B, Tang XX (2009) Effects of two species of macroalgae-Ulva pertusa and Gracilaria lemaneiformis-on growth of Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae). J Appl Phycol 21(4):375–385
Wang YH, Shen SF, Sun QH, Fen MX, Zheng Y (2012a) Antialgal and antibiotic action of lectins from two species of Gracilaria. J Fujian Normal Univ 28(4):94–98 (in Chinese)
Wang R, Wang Y, Tang X (2012b) Identification of the toxic compounds produced by Sargassum thunbergii to red tide microalgae. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 30:778–785 (in Chinese)
Wu L (2016) Effects of temperature and extracts of macroalgae and seagrass on the growth and carbohydrate yield of marine benthic dinoflagellates. Dissertation, Jinan University. (in Chinese)
Xu Y (2005) Studies on the allelopathic effects of Enteromorpha linza on Heterosigma akaskiwo. Dissertation, Ocean University of China. (in Chinese)
Xu FH (2008) The interaction between macro-algae and micro-algae and its responses to enriched CO2. Master's thesis, Qingdao University. (in Chinese)
Xu YJ, Qian LM, Jiao NZ (2004) Nitrogen nutritional character of Gracilaria as bioindicators and restoral plants of eutrophication. J Fish Sci China 11(3):276–280
Xu Y, Dong SL, Jin Q (2005a) Study on inhibitory effects of nine macroalgae on the growth of Heterosigma akashiwo. Period Ocean Univ China 35(3):475–477 (in Chinese)
Xu YJ, Qian LM, Jiao NZ (2005b) Influences of adding macroalgae Gracilaria lemaneiformis to Skeletonema costatum’s bloom. J Oceanogr Taiwan Strait 24(4):533–539
Ye CP, Zhang MC (2013) Allelopathic effect of macroalga Gracilaria tenuistipitata (Rhodophyta) on the photosynthetic apparatus of red-tide causing microalga Prorocentrum micans. IERI Procedia 5:209–215
Yu J, Lu HM, Yang YF (2010) Effect of the extracts from Gracilaria lemaneiformis on the growth and ultrastructure of Scippsiella trochoidea. J Shenzhen Univ Sci Eng 27(2):199–205 (in Chinese)
Yu J, Dai XL, Zhang ZL, Zhang ZY, Chen RZ, Huang GQ, Su Q, Li WH (2017) Characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication assessment in water quality of Gracilaria asiatica and Gracilaria tenuistipitata growing sea area. J South Agric 48(8):1511–1517 (in Chinese)
Zhang M (2011) Primary studies on metabolic composition and metabolic mechanism of five economic seaweeds. Dissertation, Suzhou University. (in Chinese)
Zhang YY, Chen MZ, Yu J, Lin YX (2005) Studies on the antimutagenic and antitumour effects of phycobiliproteins from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Chin J Mar Drugs 24(3):159–162 (in Chinese)
Zhang M, Li RX, Yi JF, Shen SD, Hu CM, Ying SY, Tang J, Zhang T, Xu P (2012) Analysis of the fatty acid composition of four economic seaweeds. Mar Sci 36(4):7–12 (in Chinese)
Funding
This work was supported by Jiangsu Province fifth “333 project” training funding (BRA2020263); Special Foundation for A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions; Excellent Young Teachers and Principals Program of Jiangsu Province, China; Haiyan project of Lianyungang City; and Innovation Training Program for College Students of Jiangsu Ocean University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ying-ying Sun performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; Jing Zhou contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; Xiu Han, Zi-xuan Yang, and Xin Zhang performed the experiment; Nai-sheng Zhang helped perform the analysis with constructive discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All the authors agreed to participate in the study.
Consent to publish
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vitor Manuel Oliveira Vasconcelos
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Yy., Zhou, J., Han, X. et al. Several natural products isolated from a red alga Gracilaria lemaneiformis and its evaluation of antialgal activity against six common red tide microalgae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 22409–22426 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11755-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11755-3