Abstract
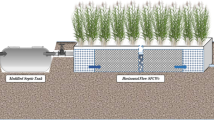
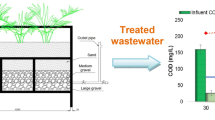
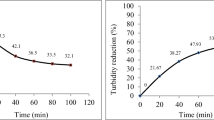
This work was aimed at investigating the feasibility of the slope wetland system (SWs) for improving the polluted river water. According to the characteristics of polluted river water with different hydraulic retention time (HRT) changes, a field simulation device was set up. In this experiment, a SWs simulation device was set up to study pollutant removal of SWs under different hydraulic conditions. It was found that the effect of mixed fillers (zeolite and ceramsite) as the bed was better than that of the gravel fillers as the bed. The improvement of each treatment index was about 5% (P < 0.05). When HRT = 5 days, the removal rate of chemical oxygen demand (COD) was 28.02%, total nitrogen (TN) was 32.99%, ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) was 32.49%, and total phosphorus (TP) was 38.15%. At the same time, it was found that the characteristic moderate extension of HRT is conducive to the removal of pollutants in SWs. The growth of plants in the environment of the gravel matrix was worse than that of mixed fillers (zeolite and ceramsite). It was found that physical adsorption was the main form of pollution removal on the SWs fillers by Fourier infrared spectrum (FTIR) analysis. Based on the analysis of the microbial community in the packing of the device, it is indicated that the enrichment of microorganisms appeared during the experiment, forming the dominant bacteria against the polluted river water.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi T, Mojiri A (2019) Constructed wetland modified by biochar/zeolite addition for enhanced wastewater treatment. Environ Technol Innov 17:16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100602
Alka S, Shahir S, Ibrahim N, Chai T-T, Mohd Bahari Z, Abd Manan F (2020) The role of plant growth promoting bacteria on arsenic removal: a review of existing perspectives. Environ Technol Innov 17:100602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100602
Alver A (2019) Evaluation of conventional drinking water treatment plant efficiency according to water quality index and health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):27225–27238
Ansola G, Arroyo P, Saenz de Miera LE (2014) Characterisation of the soil bacterial community structure and composition of natural and constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 473-474:63–71
Bai X, Zhu X, Jiang H, Wang Z, He C, Sheng L, Zhuang J (2020) Purification Effect of Sequential Constructed Wetland for the Polluted Water in Urban River. Water 12(4):1054
Bhatia M, Goyal D (2014) Analyzing remediation potential of wastewater through wetland plants: a review. Environ Prog 33(1):9–27
Bonanno G, Vymazal J, Cirelli GL (2018) Translocation, accumulation and bioindication of trace elements in wetland plants. Sci Total Environ 631-632:252–261
Button M, Nivala J, Weber KP, Aubron T, Müller RA (2015) Microbial community metabolic function in subsurface flow constructed wetlands of different designs. Ecol Eng 80:162–171
Chen G (2012) Review on the study of pollutants migration and transformation mechanism in constructed wetland. J Anhui Agric Sci 40(4):2209–2210 2212
Chen G, Shao L, Chen Z, Li Z, Zhang B, Chen H, Wu Z (2011) Low-carbon assessment for ecological wastewater treatment by a constructed wetland in Beijing. Ecol Eng 37(4):622–628
Chen Y, Guan J, Hu H, Gao H, Zhang L (2015) Structural change and interfacial interaction in blended rubber composites filled with silica–kaolin hybrid fillers: a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study. Spectrosc Lett 49:118–127
Cui L, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Li W, Zhao X, Li S, Wang Y (2012) Identification and modelling the HRT distribution in subsurface constructed wetland. J Environ Monit 14(11):3037–3044
Dordio AV, Carvalho AJP (2013) Organic xenobiotics removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of the supportmatrix. J Hazard Mater 10(252–253):272–292
Dzakpasu M, Scholz M, McCarthy V, Jordan SN (2014) Assessment of long-term phosphorus retention in an integrated constructed wetland treating domestic wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:305–313
Dzakpasu M, Wang X, Zheng Y, Ge Y, Xiong J, Zhao Y (2015) Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus removal by a surface-flow constructed wetland for polluted river water treatment. Water Sci Technol 71(6):904–912
Fukui S, Ishida H, Yagura Y, Yoshiaki T (2013) Changes in species composition and species richness of the Moliniopsis japonica community after harvesting in hillside seepage bog. J Jpn Inst Landsc Archit 76(5):457–460
Gaur AM, Rana DS (2015) Effect of CoCl2–BaCl2 fillers on morphology, dielectric constant and conductivity of PVDF composite for pressure sensing application. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:2293–2299
Ghosh D, Gopal B (2010) Effect of hydraulic retention time on the treatment of secondary effluent in a subsurface flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 36:1044–1051
Hounsou MB, Ahamide B, Agbossou EK, Gaiser THE (2011) Evaluation of water quality in the Oueme River (Benin). Environmentalist 31(4):407–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-011-9356-3
Huang J, Cao C, Yan C, Guan W, Liu J (2018) Comparison of Iris pseudacorus wetland systems with unplanted systems on pollutant removal and microbial community under nanosilver exposure. Sci Total Environ 624:1336–1347
Huang X, Lei S, Wang G, Zeng B (2020) A wetland plant, Phalaris arundinacea, accumulates nitrogen and phosphorus during senescence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:38928–38936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09285-z
Jubany I, Lafuente J, Baeza JA, Carrera J (2009) Total and stable washout of nitrite oxidizing bacteria from a nitrifying continuous activated sludge system using automatic control based on Oxygen Uptake Rate measurements. Water Res 43(11):2761–2772
Kaur P, Singh S, Singh N, Singh J (2017) Effect of rhizobacteria on arsenic uptake by macrophyte Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms. Int J Phytoremediation 20(2):114–120
Kilulya Kessy F, Msagati Titus AM, Mamba Bhekie B, Ngila JC, Tamara B (2011) Imidazolium ionic liquids as disolving solvents for chemical-grade cellulose in the determination of fatty acids using gas cheromatography-mass spectrometry. BioResources 6(3):3272–3288
Lavelli V, Fregapane G, Salvador MD (2007) Effect of storage on secoiridoid and tocopherol contents and antioxidant activity of monovarietal extra virgin olive oils. J Agric Food Chem 55(18):7630–7630
Li HY, Zhang GX, Xu-Qian LI, Gao R, Deng CN (2012) Water purification mechanism of Zhalong wetland. Sci Geogr Sin 22(17):12982–12991
Liu T, Xu S, Lu S, Qin P, Bi B, Ding H, Liu Y, Guo X, Liu X (2019) A review on removal of organophosphorus pesticides in constructed wetland: performance, mechanism and influencing factors. Sci Total Environ 651:2247–2268
Long Y, Yi H, Chen S, Zhang Z, Cui K, Bing Y, Zhuo Q, Li B, Xie S, Guo Q (2016) Influences of plant type on bacterial and archaeal communities in constructed wetland treating polluted river water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:19570–19579
Lu M, Pei FF, Song XK, Guo Z (2011) Study on the purification effects of constructed wetland plants in TP disposal in living wastewater. Appl Mech Mater 137:357–361
Lu S, Zhang X, Wang J, Pei L (2016) Impacts of different media on constructed wetlands for rural household sewage treatment. J Clean Prod 127:325–330
Martín M, Gargallo S, Hernández-Crespo C, Oliver N (2013) Phosphorus and nitrogen removal from tertiary treated urban wastewaters by a vertical flow constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 61:34–42
O’Neill A, Foy RH, Phillips DH (2011) Phosphorus retention in a constructed wetland system used to treat dairy wastewater. Bioresour Technol 102:5024–5031
Poirier S, Desmond-Le QE, Madigou C, Bouchez T, Chapleur O (2016) Anaerobic digestion of biowaste under extreme ammonia concentration: identification of key microbial phylotypes. Bioresour Technol 207:92–101
Rai PK (2019) Heavy metals/metalloids remediation from wastewater using free floating macrophytes of a natural wetland. Environ Technol Innov 15:100393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100393
Rice SP (2017) Tributary connectivity, confluence aggradation and network biodiversity. Geomorphology 277:6–16
Schwartz C, Amasino R (2013) Nitrogen recycling and flowering time in perennial bioenergy crops. Front Plant Sci 4:76
Shangguan H, Liu J, Zhu Y, Tong Z, Yonghong W (2015) Start-up of a spiral periphyton bioreactor (SPR) for removal of COD and the characteristics of the associated microbial community. Bioresour Technol 193:456–462
Stefanakis A (2019) The role of constructed wetlands as green infrastructure for sustainable urban water management. Sustain 11(24):6981
Vymazal J (2011) Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: five decades of experience†. Environ Sci Technol 45(1):61–69
Wan X, Gao M, Ye M, Wang YK, Xu H, Wang M, Wang XH (2018) Formation, characteristics and microbial community of aerobic granular sludge in the presence of sulfadiazine at environmentally relevant concentrations. Bioresour Technol 250:486–494
Wang KY, Zheng SS, Guo ZL, Xu WB (2012) Advance in improving the removal efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus of ecological floating bed system. Wetland Sci 10(1):116–120
Wang H, Quan B, Bo G, Zhang Y, Liu L, Zhang J, Zhang X, Zhang C (2020a) Advanced oxidation treatment of dissolved organic matter from wastewater treatment plant secondary effluent using scattering electrical reactor. J Clean Prod 267:122258
Wang H, Wang J, Bo G, Wu S, Luo L (2020b) Degradation of pollutants in polluted river water using Ti/IrO2-Ta2O5 coating electrode and evaluation of electrode characteristics. J Clean Prod 273:123019
Wang H, Wang J, Lu H, Bo G, Zhang X, Cao Y, Liu L, Zhang J, Zhang W (2020c) Analysis of coating electrode characteristics in the process of removing pollutants from wastewater. Fresenius Environ Bull 29(2):715–721
Wang H, Zhong H, Bo G (2018d) Existing forms and changes of nitrogen inside of horizontal subsurface constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(1):771–781
Wei H, Ma J, Su Y, Xie B (2020) Effect of nutritional energy regulation on the fate of antibiotic resistance genes during composting of sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 297:122513
Williams KP, Gillespie JJ, Sobral BW, Nordberg EK, Snyder EE, Shallom JM, Dickerman AW (2010) Phylogeny of gammaproteobacteria. J Bacteriol 192:2305–2314
Xu R, Zhang Y, Liu R, Cao Y, Wang G, Ji L, Xu Y (2019) Effects of different substrates on nitrogen and phosphorus removal in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16229–16238
Yadav AK, Kumar N, Sreekrishnan TR, Satya S, Bishnoi NR (2010) Removal of chromium and nickel from aqueous solution in constructed wetland: mass balance, adsorption–desorption and FTIR study. Chem Eng J 160:122–128
Zhang C-B, Liu W-L, Wang J, Ge Y, Gu B-H, Chang J (2012) Effects of plant diversity and hydraulic retention time on pollutant removals in vertical flow constructed wetland mesocosms. Ecol Eng 49:244–248
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Li Y, Jiang Y (2017) Effects of HRT on the efficiency of denitrification and carbon source release in constructed wetland filled with bark. Watar Sci Technol 75:2908–2915
Zhang L, Chen J, Lei Z, He H, Wang Y, Yonghui LY (2019) Preparation of soybean oil factory sludge catalyst and its application in selective catalytic oxidation denitration process. J Clean Prod 225:220–226
Funding
This work was supported by the Research and Demonstration on Key Technologies of Urban Landscape River Water System Connection and Typical Black and Stinky River Treatment in Northern Area (2017ZX07103-001).
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jia Wang: Validation, formal analysis, visualization, software, data curation
Yonggang Gu: Conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, writing—original draft
Hao Wang: Validation, formal analysis, visualization
Zhaoxin Li: Resources, writing—review and editing, supervision
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Informed consent to participate in the study was freely given.
Consent to publish
All authors agreed to publish their data to a journal and provided informed consent for publication of the images in figures and tables.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Gu, Y., Wang, H. et al. Investigation on the treatment effect of slope wetland on pollutants under different hydraulic retention times. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 9107–9119 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11292-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11292-z