Abstract
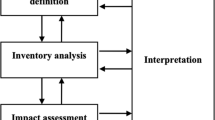
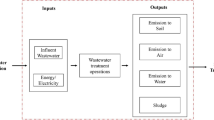
Industrial processes, such as smelting and mining, lead to antimony (Sb) contamination, which poses an environmental and human health risk. In this study, the energy consumption and environmental impacts of a passive biological treatment system were quantitatively evaluated using life cycle assessment (LCA), and the results were compared with that of an adsorption purification system. The results showed that the biosystem had a lower energy consumption compared with the adsorption system, with an energy savings of 27.39%. The environmental impacts of the bioreactor were also lower regarding acidification, ecotoxicity, carcinogens, climate change, resource depletion, and respiratory effects. The construction resulted in the most energy consumption (99%) for the passive bioreactor. Therefore, adopting environmentally friendly construction materials could make the biosystem a more energy-efficient option. Results demonstrated that the bioreactor in this research can have great potential for Sb mine drainage applications in terms of energy savings and environmental remediation without diminishing performance. The study findings can be useful for deciding the most energy effective process for mine drainage remediation. In addition, the identification of the energy and environmental impacts of the processes provide valuable information for the design of future systems that consume less materials and utilize new construction materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acero AP, Rodríguez C, Ciroth A (2016) Impact assessment methods in life cycle assessment and their impact categories. GreenDelta. LCIA methods
Anderson CG (2001) Hydrometallurgically treating antimony-bearing industrial wastes. J Miner Met Mater Soc 53:18–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-001-0156-y
Arnold M, Kangas P, Mäkinen A, Lakay E, Isomäki N, Lavén G, Gericke M, Pajuniemi P, Kaartinen T, Wendling L (2019) Mine water as a resource: selective removal and recovery of trace antimony from mine-impacted water. Mine Water Environ 38(2):431–446
Bergmann MH, Koparal AS (2011) Electrochemical antimony removal from accumulator acid: results from removal trials in laboratory cells. J Hazard Mater 196:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.073
Bregoli L, Chiarini F, Gambarelli A, Sighinolfi G, Gatti AM, Santi P, Martelli AM, Cocco L (2009) Toxicity of antimony trioxide nanoparticles on human hematopoietic progenitor cells and comparison to cell lines. Toxicology 262(2):121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.05.017
Ge Z, Gao Z, Sun R, Zheng L (2012) Mix design of concrete with recycled clay-brick-powder using the orthogonal design method. Constr Build Mater 31:289–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.01.002
He M, Wang X, Wu F, Fu Z (2012) Antimony pollution in China. Sci Total Environ 421:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.009
Heijungs R, Guinée J, Kleijn R, Rovers V (2007) Bias in normalization: causes, consequences, detection and remedies. Int J Life Cycle Assess 12(4):211–216. https://doi.org/10.1065/lca2006.07.260
Hengen TJ, Squillace MK, O’Sullivan AD, Stone JJ (2014) Life cycle assessment analysis of active and passive acid mine drainage treatment technologies. Conserv Recycl 86:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2014.01.003
Hertwich EG, Mateles SF, Pease WS, McKone TE (2009) Human toxicity potentials for life cycle assessment and toxics release inventory risk screening. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(4):928–939. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620200431
Houghton J (2009) Global warming: the complete briefing. Cambridge university press
Ilgen AG, Majs F, Barker AJ, Douglas TA, Trainor TP (2014) Oxidation and mobilization of metallic antimony in aqueous systems with simulated groundwater. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 132:16–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2014.01.019
International Standard Organization (1997) ISO 14040: Environmental management-life cycle assessment-principles and framework
Johnson DB, Hallberg KB (2005) Acid mine drainage remediation options: a review. Sci Total Environ 338(1–2):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.09.002
JRC European Commission (2010) ILCD handbook - international reference life cycle data system. General guide for Life Cycle Assessment – Detailed guidance. Institute for Environment and sustainability
Kadir A (2012) An overview of wastes recycling in fired clay bricks. Int J Integr Eng 4(2):53–69
Kalin M (2004) Passive mine water treatment: the correct approach. Ecol Eng 22(4–5):299–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.06.008
Kårelid V, Larsson G, Björlenius B (2017) Pilot-scale removal of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater: comparison of granular and powdered activated carbon treatment at three wastewater treatment plants. J Environ Manag 193:491–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.02.042
Lees F (2012) Lees’ loss prevention in the process industries: hazard identification, assessment and control. Butterworth-Heinemann
Luo J, Luo X, Crittenden J, Qu J, Bai Y, Peng Y, Li J (2015) Removal of antimonite (Sb (III)) and antimonate (Sb (V)) from aqueous solution using carbon nanofibers that are decorated with zirconium oxide (ZrO2). Environ Sci Technol 49(18):11115–11124. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02903
Martínez NM, Basallote MD, Meyer A, Cánovas CR, Macías F, Schneider P (2019) Life cycle assessment of a passive remediation system for acid mine drainage: towards more sustainable mining activity. J Clean Prod 211:1100–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.224
Moynahan OS, Zabinski CA, Gannon JE (2002) Microbial community structure and carbon-utilization diversity in a mine tailings revegetation study. Restor Ecol 10(1):77–87. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1526-100X.2002.10108.x
Mubarak H, Chai LY, Mirza N, Yang ZH, Pervez A, Tariq M, Shaheen S, Mahmood Q (2015) Antimony (Sb)–pollution and removal techniques–critical assessment of technologies. Toxicol Environ Chem 97(10):1296–1318. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2015.1095549
Renou S, Thomas JS, Aoustin E, Pons MN (2008) Influence of impact assessment methods in wastewater treatment LCA. J Clean Prod 16(10):1098–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2007.06.003
Salam MA, Mohamed RM (2003) Removal of antimony(III) by multi-walled carbon nanotubes from model solution and environmental samples. Chem Eng Res Des 91(7):1352–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2013.02.007
Sun M, Xiao T, Ning Z, Xiao E, Sun W (2015) Microbial community analysis in rice paddy soils irrigated by acid mine drainage contaminated water. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(6):2911–2922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.008
Sun W, Sun X, Li B, Xu R, Young LY, Dong Y, Zhang M, Kong T, Xiao E, Wang Q (2020a) Bacterial response to sharp geochemical gradients caused by acid mine drainage intrusion in a terrace: relevance of C, N, and S cycling and metal resistance. Environ Int 138:105601
Sun X, Kong T, Haggblom MM, Kolton M, Li F, Dong Y, Huang Y, Li B, Sun W (2020b) Chemolithoautotrophic diazotrophy dominates the nitrogen fixation process in mine tailings. Environ Sci Technol
UNEP/SETAC (2005) Life cycle approaches: the road from analysis to practice. United Nations Environment Program
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2018) Particulate matter (PM) basics. https://wwwepagov/pm-pollution/particulate-matter-pm-basics Access 5 July 2019
Vince F, Aoustin E, Bréant P, Marechal F (2008) LCA tool for the environmental evaluation of potable water production. Desalination 220(1–3):37–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.021
Wang H, Chen F, Mu S, Zhang D, Pan X, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2013) Removal of antimony (Sb (V)) from Sb mine drainage: biological sulfate reduction and sulfide oxidation–precipitation. Bioresour Technol 146:799–802
Wang X, Anctil A, Masten SJ (2019) Energy consumption and environmental impact analysis of ozonation catalytic membrane filtration system for water treatment. Environ Eng Sci 36(2):149–157. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2018.0270
Wang X, He M, Xi J, Lu X (2011) Antimony distribution and mobility in rivers around the world’s largest antimony mine of Xikuangshan, Hunan Province, China. Microchem J 97(1):4–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.05.011
Watson RT, Zinyowera MC, Moss RH (1996) Technologies, policies and measures for mitigating climate change. Switzerland: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Xi JH, He MC, Lin CY (2011) Adsorption of antimony(III) and antimony(V) on bentonite: kinetics, thermodynamics and anion competition. Microchem J 97(1):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.05.017
Xu R, Li B, Xiao E, Young LY, Sun X, Kong T, Kong T, Dong Y, Wang Q, Yang Z, Chen L, Sun W (2020) Uncovering microbial responses to sharp geochemical gradients in a terrace contaminated by acid mine drainage. Environ Pollut 261:114226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114226
Xu W, Liu RP, Qiu JH, Peng RM (2015) Adsorption of antimony(V) onto Mn(II)-enriched surfaces of manganeseoxide and Fe-Mn binary oxide. Chemosphere 138:616–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.039
Xu Y, Ohki A, Maeda S (2001) Adsorption and removal of antimony from aqueous solution by an activated alumina. Toxicol Environ Chem 80(3–4):133–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240109359004
Yellishetty M, Mudd GM, Ranjith PG (2011) The steel industry, abiotic resource depletion and life cycle assessment: a real or perceived issue. J Clean Prod 19(1):78–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.08.020
Funding
This research was supported by the GDAS’ Project of Science and Technology Development (2020GDASYL-20200302007, 2019GDASYL-0103052, 2020GDASYL-20200103088, and 2019GDASYL-0301002), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (202002020072), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771301), the Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program (2017BT01Z176), Guangdong Introducing Innovative and Entrepreneurial Talents (2017GC010570), the High-level Leading Talent Introduction Program of GDAS (2016GDASRC-0103), and Guangdong Foundation for Program of Science and Technology Research (2019B121205006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Loubet
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 287 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Ning, Z., Sun, W. et al. Energy and environmental impact assessment of a passive remediation bioreactor for antimony-rich mine drainage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 35040–35050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09816-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09816-8