Abstract
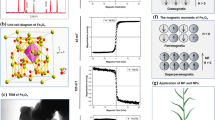
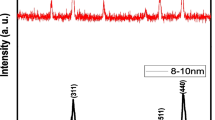
This study investigates the impact of an engineered magnetic nanoparticle (MNP) on a crop plant. For this purpose, a sonochemical synthetic approach was utilized in order to dope magnetic elements (Co and Nd) into technologically important iron oxide NPs. After being characterized by using TEM, SEM, and XRD instruments, the MNPs were hydroponically applied to barley plants with varying doses (from 125 to 1000 mg/L) both in germination (4 days) and early growing stages (3 weeks). Physiological responses, as well as expression of photosystem marker genes, were assessed. Compared to the untreated control, MNP treatment enhanced germination rate (~ 31%), tissue growth (8% in roots, 16% in shoots), biomass (~ 21%), and chlorophyll (a, b) (~ 20%), and carotenoids (~ 22%) pigments. In general, plants showed the highest growth enhancement at 125 or 250 mg/L treatment. However, higher doses diminished the growth indices. Compared to the control, the catalase activity was significantly reduced in the leaves (~ 33%, p < 0.005) but stimulated in the roots (~ 46%, p < 0.005). All tested photosystem marker genes (BCA, psbA, and psaA) were overexpressed in MNP-treated leaves than non-treated control. Moreover, the gene expressions were found to be proportionally increased with increasing MNP doses, indicating a positive correlation between MNPs and the photosynthetic machinery, which could contribute to the enhancement of plant growth.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MNPs:
-
magnetic nanoparticles
- NPs:
-
nanoparticles
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- H2O2 :
-
hydrogen peroxide
- RWC:
-
relative water content
- Ms:
-
saturation magnetization
- Hc:
-
coercivity
- Mr:
-
remanent magnetization
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126 Academic Press
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Korkmaz AD, Sertkol M, Baykal A, Ercan I, Özçelik B (2019) Sonochemical synthesis of CoFe2-xNdxO4 nanoparticles: structural, optical, and magnetic investigation. J Supercond Nov Magn:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05147-z
Atak Ç, Çelik Ö, Olgun A, Alikamanoğlu S, Rzakoulieva A (2007) Effect of magnetic field on peroxidase activities of soybean tissue culture. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 21(2):166–171
BCC Research (2018) https://www.bccresearch.com/market-research/nanotechnology/nanocomposites-nanoparticles-nanoclays-and-nanotubes-global-markets.html
Bhavani P, Manikandan A, Paulraj P, Dinesh A, Durka M, Antony SA (2018) Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) plant extract-assisted combustion synthesis and characterization studies of spinel ZnAl2O4 nano-catalysts. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18(6):4072–4081
Bideskan AE, Mohammadipour A, Fazel A, Haghir H, Rafatpanah H, Hosseini M, Rajabzadeh A (2017) Maternal exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles during pregnancy and lactation alters offspring hippocampal mRNA BAX and Bcl-2 levels, induces apoptosis and decreases neurogenesis. Exp Toxicol Pathol 69(6):329–337
Bostancioglu SM, Tombuloglu G, Tombuloglu H (2018) Genome-wide identification of barley MCs (metacaspases) and their possible roles in boron-induced programmed cell death. Mol Biol Rep 45(3):211–225
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Briat JF, Dubos C, Gaymard F (2015) Iron nutrition, biomass production, and plant product quality. Trends Plant Sci 20:33–40
Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Rengel Z, Zhao F (2012) Function of nutrients: micronutrients. In: Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, pp 191–248
Ding Y, Bai X, Ye Z, Ma L, Liang L (2019) Toxicological responses of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on Eichhornia crassipes and associated plant transportation. Sci Total Environ 671:558–567
Ghafariyan MH, Malakouti MJ, Dadpour MR, Stroeve P, Mahmoudi M (2013) Effects of magnetite nanoparticles on soybean chlorophyll. Environ Sci Technol 47(18):10645–10652
Giraldo JP, Landry MP, Faltermeier SM, McNicholas TP, Iverson NM, Boghossian AA, Strano MS (2014) Plant nanobionics approach to augment photosynthesis and biochemical sensing. Nat Mater 13(4):400–408
Govindjee U (2014) In: Demmig-Adams B, Garab G, Adams W III (eds) Non-photochemical quenching and energy dissipation in plants, algae and cyanobacteria, vol 40. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht
Harwood WA (2018) Methods in molecular biology barley:1–5
Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Castillo-Michel H, Andrews JC, Cotte M, Rico C, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2013) In situ synchrotron X-ray fluorescence mapping and speciation of CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil cultivated soybean (Glycine max). ACS Nano 7(2):1415–1423
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular California agricultural experiment station, 347(2nd edit)
Hu J, Guo H, Li J, Wang Y, Xiao L, Xing B (2017) Interaction of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with Citrus maxima leaves and the corresponding physiological effects via foliar application. J Nanobiotechnol 15(1):51
Kim JH, Lee Y, Kim EJ, Gu S, Sohn EJ, Seo YS, An HJ, Chang YS (2014) Exposure of iron nanoparticles to Arabidopsis thaliana enhances root elongation by triggering cell wall loosening. Environ Sci Technol 48(6):3477–3485
Konate A, He X, Zhang Z, Ma Y, Zhang P, Alugongo G, Rui Y (2017) Magnetic (Fe3O4) nanoparticles reduce heavy metals uptake and mitigate their toxicity in wheat seedling. Sustainability 9(5):790
Le N, Rui Y, Gui X, Li X, Liu S, Han Y (2014) Uptake, transport, distribution and bio-effects of SiO2 nanoparticles in Bt-transgenic cotton. J Nanobiotechnol 12(1):50
Libralato G, Devoti AC, Zanella M, Sabbioni E, Mičetić I, Manodori L, Ghirardini AV (2016) Phytotoxicity of ionic, micro-and nano-sized iron in three plant species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 123:81–88
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11(5):591–592
Lisjak D, Mertelj A (2018) Anisotropic magnetic nanoparticles: a review of their properties, syntheses and potential applications. Prog Mater Sci 95:286–328
López-Millán AF, Duy D, Philippar K (2016) Chloroplast iron transport proteins–function and impact on plant physiology. Front Plant Sci 7:178
Lugojan C, Ciulca S (2011) Evaluation of relative water content in winter wheat. J Hortic Forest Biotechnol 15:173–177
Maher BA, Ahmed IA, Karloukovski V, MacLaren DA, Foulds PG, Allsop D et al (2016) Magnetite pollution nanoparticles in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(39):10797–10801
Manikandan A, Durka M, Antony SA (2015) Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaf extracted green methods, magneto-optical and catalytic properties of spinel CuFe 2 O 4 nano-and microstructures. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 25(5):1019–1031
Manikandan A, Durka M, Amutha Selvi M, Arul Antony S (2016) Sesamum indicum plant extracted microwave combustion synthesis and opto-magnetic properties of spinel MnxCo1-xAl2O4 nano-catalysts. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16(1):448–456
Marmiroli M, Pagano L, Savo Sardaro ML, Villani M, Marmiroli N (2014) Genome-wide approach in Arabidopsis thaliana to assess the toxicity of cadmium sulfide quantum dots. Environ Sci Technol 48(10):5902–5909
Mohammadipour A, Hosseini M, Fazel AR, Haghir H, Rafatpanah H, Pourganji M, Ebrahimzadeh Bideskan A (2016) The effects of exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles during lactation period on learning and memory of rat offspring. Toxicol Ind Health 32(2):221–228
Ooi A, Wong A, Ng TK, Marondedze C, Gehring C, Ooi BS (2016) Growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana under single-wavelength red and blue laser light. Sci Rep 6:33885
Pagano L, Servin AD, De La Torre-Roche R, Mukherjee A, Majumdar S, Hawthorne J, Dhankher OP (2016) Molecular response of crop plants to engineered nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 50(13):7198–7207
Pagano L, Pasquali F, Majumdar S, De la Torre-Roche R, Zuverza-Mena N, Villani M, Maestri E (2017) Exposure of Cucurbita pepo to binary combinations of engineered nanomaterials: physiological and molecular response. Environ Sci Nano 4(7):1579–1590
Pagano L, Maestri E, Caldara M, White JC, Marmiroli N, Marmiroli M (2018) Engineered nanomaterial activity at the organelle level: impacts on the chloroplasts and mitochondria. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(10):12562–12579
Pariona N, Martínez AI, Hernandez-Flores H, Clark-Tapia R (2017) Effect of magnetite nanoparticles on the germination and early growth of Quercus macdougallii. Sci Total Environ 575:869–875
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45
Qian H, Zhu K, Lu H, Lavoie M, Chen S, Zhou Z, Deng Z, Chen J, Fu Z (2016) Contrasting silver nanoparticle toxicity and detoxification strategies in Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella vulgaris: new insights from proteomic and physiological analyses. Sci Total Environ 572:1213–1221
Racuciu M, Creanga D (2007) TMA-OH-coated magnetic nanoparticles internalized in vegetal tissue. Rom J Physiol 52(3/4):395
Rajput VD, Minkina TM, Behal A, Sushkova SN, Mandzhieva S, Singh R, Movsesyan HS (2018) Effects of zinc-oxide nanoparticles on soil, plants, animals and soil organisms: a review. Environ Nanotechnol Monitor Manag 9:76–84
Rastogi A, Zivcak M, Sytar O, Kalaji HM, He X, Mbarki S, Brestic M (2017) Impact of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on plant: a critical review. Front Chem 5:78
Rico CM, Majumdar S, Duarte-Gardea M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2011) Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. J Agric Food Chem 59:3485–3498
Ritchie SW, Nguyan HT, Holaday AS (1990) Leaf water content and gas exchange parameters of two wheat genotypes differing in drought resistance. Crop Sci 30:105–111
Sade N, Galkin E, Moshelion M (2015) Measuring Arabidopsis, tomato and barley leaf relative water content (RWC). Bio-Protocols 5:1–4
Servin AD, Morales MI, Castillo-Michel H, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Munoz B, Zhao L, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2013) Synchrotron verification of TiO2 accumulation in cucumber fruit: a possible pathway of TiO2 nanoparticle transfer from soil into the food chain. Environ Sci Technol 47(20):11592–11598
Silva T, Pokhrel LR, Dubey B, Tolaymat TM, Maier KJ, Liu X (2014) Particle size, surface charge and concentration dependent ecotoxicity of three organo-coated silver nanoparticles: comparison between general linear model-predicted and observed toxicity. Sci Total Environ 468:968–976
Subramanian V, Semenzin E, Hristozov D, Zabeo A, Malsch I, McAlea E, Linkov I (2016) Sustainable nanotechnology decision support system: bridging risk management, sustainable innovation and risk governance. J Nanopart Res 18(4):89
Swift TA, Oliver TA, Galan MC, Whitney HM (2019) Functional nanomaterials to augment photosynthesis: evidence and considerations for their responsible use in agricultural applications. Interface Focus 9(1):20180048
Tombuloglu H, Semizoglu N, Sakcali S, Kekec G (2012) Boron induced expression of some stress-related genes in tomato. Chemosphere 86(5):433–438
Tombuloglu H, Kekec G, Sakcali MS, Unver T (2013) Transcriptome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in barley with their boron responsive expression analysis. Mol Gen Genomics 288(3–4):141–155
Tombuloglu G, Tombuloglu H, Sakcali MS, Unver T (2015) High-throughput transcriptome analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare) exposed to excessive boron. Gene 557(1):71–81
Tombuloglu H, Ozcan I, Tombuloglu G, Sakcali S, Unver T (2016) Aquaporins in boron-tolerant barley: identification, characterization, and expression analysis. Plant Mol Biol Report 34(2):374–386
Tombuloglu H, Tombuloglu G, Slimani Y, Ercan I, Sozeri H, Baykal (2018) Impact of manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles on growth and magnetic character of barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Environ Pollut 243:872–881
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Tombuloglu G, Demir-Korkmaz A, Baykal A, Almessiere M, Ercan I (2019a) Impact of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and ionic iron on physiology of summer squash (Cucurbita pepo): a comparative study. Plant Physiol Biochem 139:56–65
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere M, Baykal A (2019b) Uptake and translocation of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and its impact on photosynthetic genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Chemosphere 226:110–122
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Güngüneş H, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere MA, Sozeri H, Ercan I (2019c) Tracking of SPIONs in barley (Hordeum vulgare L) plant organs during its growth. J Supercond Nov Magn 32:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-5059-7
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere M, Baykal A, Ercan I, Sozeri H (2019d) Tracking of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles in barley (Hordeum vulgare L) and their impact on plant growth, biomass, pigmentation, catalase activity, and mineral uptake. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 11:100223
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Alshammari T, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere M, Baykal A, Demirci T (2019e) Magnetic behavior and nutrient content analyses of barley (Hordeum vulgare L) tissues upon CoNd02Fe1.8O4 magnetic nanoparticle treatment. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00115-x
Tosco T, Sethi R (2018) Human health risk assessment for nanoparticle-contaminated aquifer systems. Environ Pollut 239:242–252
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1996) Ecological effects test guidelines: seed germination/root elongation toxicity test. Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances, Washington, DC, p 7101
Wientjes E, Renger J, Curto AG, Cogdell R, Van Hulst NF (2014) Strong antenna-enhanced fluorescence of a single light-harvesting complex shows photon antibunching. Nat Commun 5(1):1–7
Xiong T, Dumat C, Dappe V, Vezin H, Schreck E, Shahid M, Sobanska S (2017) Copper oxide nanoparticle foliar uptake, phytotoxicity, and consequences for sustainable urban agriculture. Environ Sci Technol 51(9):5242–5251
Yuan J, Chen Y, Li H, Lu J, Zhao H, Liu M, Glushchenko NN (2018) New insights into the cellular responses to iron nanoparticles in Capsicum annuum. Sci Rep 8(1):3228
Zhang P, Ma Y, Zhang Z, He X, Zhang J, Guo Z, Chai Z (2012) Biotransformation of ceria nanoparticles in cucumber plants. ACS Nano 6(11):9943–9950
Zhao L, Sun Y, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Servin AD, Hong J, Niu G, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2013) Influence of CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on cucumber physiological markers and bioaccumulation of Ce and Zn: a life cycle study. J Agric Food Chem 61(49):11945–11951
Funding
This study is supported by Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) fund of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University (IAU) under the project numbers of 2018-139-IRMC and 2019-058-IRMC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 18.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tombuloglu, H., Slimani, Y., Tombuloglu, G. et al. Engineered magnetic nanoparticles enhance chlorophyll content and growth of barley through the induction of photosystem genes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 34311–34321 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09693-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09693-1