Abstract
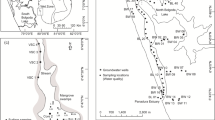
To regulate the water level and minimize the occurrence of water eutrophication in shallow lakes, dams and gates are often constructed in rivers. However, this practice may result in a deterioration of water quality in some estuaries. In the present study, using the correction of Nemerow pollution index (CNPI) and a redundancy analysis (RDA), water samples from different dammed rivers around Taihu Lake were compared to assess the pollution risk and identify the factors responsible for water eutrophication. The average total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), total organic carbon (TOC) concentrations, and chemical oxygen demand (CODMn) were 2.45 ± 2.28, 0.08 ± 0.06, 43.01 ± 18.75, and 10.78 ± 4.86 mg L−1, respectively. The CNPI values indicated that approximately 76.47% of the estuarine water was moderately polluted (1 < CNPI < 7.28). A positive correlation was observed between dam construction and nutrient concentrations (e.g., rTN = 0.38, p < 0.05; rTP = 0.89, p < 0.01). Under the effects of dam construction, land use change, estuary shape, and meteorological conditions, there was a clear spatial variation of the TN concentrations. Dams that were closed all year round accelerated the TN accumulation in the water around them. The pollution risk in a trumpet-shaped estuary was higher than that in other regions (t = 2.92, p = 0.02). Endogenous release of pollutants was an important factor that may have a priming effect on algal blooms and should be given more attention. In Wuli Lake, exogenous pollution was the dominant pollutant source. A total of 74.49% of the nitrogen losses with the runoff into the estuarine water in 2018 were derived from urban domestic sewage and constructed land, with the load being 4.40 times higher than in 2000. The RDA results revealed that dam construction was the main factor (43.70%) affecting water quality, while meteorological conditions, land use types, estuary shape, and other factors contributed 56.30%. Scientific regulation and control of dam operation is important to protect the water environment of Taihu Lake.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barletta M, Lima ARA, Costa MF (2019) Distribution, sources and consequences of nutrients, persistent organic pollutants, metals and micro-plastics in South American estuaries. Sci Total Environ 651:1199–1218
Buckley C, Hynes S, Mechan S (2012) Supply of an ecosystem service-Farmers’ willingness to adopt riparian buffer zones in agricultural catchments. Environ Sci Policy 24:101–109
Chen Y, Fan C, Teubner K, Dokulil M (2003) Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: an 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 506:273–279
Chen X, Wang YH, Ye C, Zhou W, Cai ZC, Yang H, Xiao H (2018) Atmospheric nitrogen deposition associated with the eutrophication of Taihu Lake. J Chem ID 4017107:1–10
Chinese National Environmental Protection Administration (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods (In Chinese). China Environmental Science Press, pp 200-284
Deng XW, Qi M, Ren R, Liu JR, Sun XX, Xie P, Chen J (2019) The relationships between odors and environmental factors at bloom and non-bloom area in Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 218:569–576
Dokulil M, Chen W, Cai Q (2000) Anthropogenic impacts to large lakes in China: the Tai Hu example. Aquat Ecosyst Health 3:81–94
Du CG, Li YM, Wang Q, Liu G, Zheng ZB, Mu M, Li Y (2017) Tempo-spatial dynamics of water quality and its response to river flow in estuary of Taihu Lake based on GOCI imagery. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:28079–28101
Ewa SG, Grazyna MB (2002) Deposition of copper in the eutrophic, Submontane Ddobczyce Dam Reservoir (Southern Poland)—role of speciation. Water Air Soil Pollut 140:203–218
Gao B, Yan XY, Jiang XS, Ti CP (2014) Research progress in estimation of agricultural sources pollution of the Lake Taihu region (In Chinese). J Lake Sci 26:822–828
Geospatial Data Cloud (GDC), China (2019) http://www.gscloud.cn/. [Accessed in Jan 1, 2019]
Guan YF, Wang JZ, Ni HG, Zeng EY (2009) Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, China: assessment of mass loading, input source and environmental fate. Environ Pollut 157:618–624
Guo HY, Wang XR, Zhu JG (2004) Quantification and index of non-point source pollution in Taihu Lake region with GIS. Environ Geochem Health 26:147–156
Huang YP (2001) Water environment and its pollution control in Taihu Lake (In Chinese). Beijing Science Press pp 231–233
Huang L, Fang HW, He GJ, Jiang HL, Wang CH (2016) Effects of internal loading on phosphorus distribution in the Taihu Lake driven by wind waves and lake currents. Environ Pollut 219:760–773
Ji XL, Randy AD, Zhang MH (2016) Comparison of seven water quality assessment methods for the characterization and management of highly impaired river systems. Environ Monit Assess 188:1–15
Jiangsu Provincial Academy of Environmental Science (JPAES), China (2008) Technical specification of water environment comprehensive treatment plan about the main rivers in Lake Tailu basin (In Chinese). JPAES pp 1–4
Johns PJ, O’sullivan E (1989) The natural history of Slapton Ley Nature Research X VII: nitrogen and phosphorus losses from the catchment-an export coefficient approach. Field Stud 7:285–309
Koelmans AA, Van der Heijde A, Knijff LM, Aalderink RH (2001) Integrated modelling of eutrophication and organic contaminant fate and effects in aquatic ecosystems. a review. Water Res 35:3517–3536
Kurunc A, Yurekli K, Okman C (2006) Effects of Kilickaya Dam on concentration and load values of water quality constituents in Kelkit Stream in Turkey. J Hydrol 317:17–30
Le C, Zha Y, Li Y, Sun D, Lu H, Yin B (2010) Eutrophication of lake waters in China: cost, causes, and control. Environ Manag 45:662–668
Legorburu I, Rodríguez JG, Ángel B, Menchaca I, Solaun O, Valencia V, Galparsoro I, Larreta J (2013) Source characterization and spatio-temporal evolution of the metal pollution in the sediments of the Basque estuaries (Bay of Biscay). Mar Pollut Bull 66:25–38
Li SY, Gu S, Tan X, Zhang QF (2009a) Water quality in the upper Han River basin, China: the impacts of land use/land cover in riparian buffer zone. J Hazard Mater 165:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.123
Li XY, Ma YJ, Xu HY, Wang JH, Zhang DS (2009b) Impact of land use and land cover change on environmental degradation in lake Qinhai watershed, northeast Qinhai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad Dev 20:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.885
Li YP, Tang CY, Yu ZB, Acharya K (2014) Correlations between algae and water quality: factors driving eutrophication in Lake Taihu, China. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:169–182
Li Q, Chen L, Liu L, Wu Z (2016a) Embryotoxicity and genotoxicity evaluation of sediments from Yangtze River estuary using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4908–4918
Li YP, Tang CY, Wang JW, Acharya K, Du W, Gao XM, Luo LC, Li HY, Dai SJ, Mercy L, Yu ZB, Pan BZ (2016b) Effect of wave-current interactions on sediment resuspension in large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:1–11
Liu Z, Li WX, Zhang YM, Zhang LJ, Zhang HL, Li Y, Cai JB, Zhuang W, He F (2010) Estimation of non-point source pollution load in Taihu Lake Basin (In Chinese). J Ecol Rural Environ 26:45–48
National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), China (1990–2017). http://www.stats.gov.cn/. [Accessed in Jan 1, 2019]
National Earth System Science Data Center (NESSDC), China (2019). http://lake.geodata.cn/. [Accessed in Jan 1, 2019]
Qin BQ, Zhu GW (2006) The nutrient forms, cycling and exchange flux in the sediment and overlying water system in lakes from the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. Sci China Earth Sci 49:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-006-8101-0
Qin BQ, Hu WP, Gao G, Luo LC, Zhang JS (2004) Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chin Sci Bull 49:54–64
Qin B, Gao G, Zhu G, Zhang Y, Song Y, Tang X, Xu H, Deng J (2012) Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response. Chin Sci Bull 58:961–970
R Development Core Team (2018) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R 21 Foundation for statistical computing, Vienna
Rafael M, Enrique MO, Jose GB, Joan A (2010) Tailoring dam structures to water quality predictions in new reservoir projects: assisting decision-making using numerical modeling. J Environ Manag 91:1255–1267
Robson BJ, Hamilton DP (2003) Summer flow event induces a cyanobacterial bloom in a seasonal Western Australian estuary. Mar Freshw Res 54:139–151
Shim MJ, Yang YM, Oh DY, Lee SH, Yoon YY (2015) Spatial distribution of heavy metal accumulation in the sediments after dam construction. Environ Monit Assess 187:733
Smith VH (2003) Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: a global problem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:126–139
Su XM, Alan DS, Xue QJ, Zhao YY, Tang XM, Xie LQ (2017) Temporal patterns of phyto- and bacterioplankton and their relationships with environmental factors in Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 184:299–308
Su Q, Qin HP, Fu GT (2019) Environmental and ecological impacts of water supplement schemes in a heavily polluted estuary. Sci Total Environ 472:704–711
Sun D, Hu C, Qiu Z, Shi K (2015) Estimating phycocyanin pigment concentration in productive inland waters using Landsat measurements: a case study in Lake Dianchi. Opt Express 23:3055–3074
Swati S, Umesh S (2015) Nemerow’s pollution index: for ground water quality assessment. J Environ Sci Pollut Res 1:23–31
Wang MH, Shi W, Tang JW (2011) Water property monitoring and assessment for China’s inland Lake Taihu from MODIS-Aqua measurements. Remote Sens Environ 115:841–854
Wang JJ, Zhao QH, Pang Y, Hu KM (2017) Research on nutrient pollution load in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:17829–17838
Wang JL, Fu ZB, Qiao HX, Liu FX (2018) Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Sci Total Environ 650:1392–1402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.137
Wei GL, Yang ZF, Cui BS, Li B, Chen H, Bai JH, Dong SK (2009) Impact of dam construction on water quality and water self-purification capacity of the Lancang River, China. Water Resour Manag 23:1763–1780
Wu ZS, Wang XY, Chen YW, Cai YJ, Deng JC (2018) Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci Total Environ 612:914–922
Xie RR, Pang Y, Bao K (2014) Spatiotemporal distribution of water environmental capacity-a case study on the western areas of Taihu Lake in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:5465–5473
Xu H, Hans WP, Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55:420–432
Xu XB, Yang GS, Tan Y, Tang XG, Jiang H, Sun XX, Zhuang QL, Li HP (2017) Impacts of land use changes on net ecosystem production in the Taihu Lake Basin of China from 1985 to 2010. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 122:1–18
Yang HC, Wang GQ, Wang LJ, Zheng BH (2015) Impact of land use changes on water quality in headwaters of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11448–11460
Yang Z, Zhang M, Shi XL, Kong FX, Ma RH, Yu Y (2016) Nutrient reduction magnifies the impact of extreme weather on cyanobacterial bloom formation in large shallow Lake Taihu (China). Water Res 103:302–310
Yang K, Yu ZY, Luo Y, Yang Y, Zhao L, Zhou XL (2018) Spatial and temporal variations in the relationship between lake water surface temperatures and water quality: a case study of Dianchi Lake. Sci Total Environ 624:859–871
Yu H, Zhang LL, Yan SW (2011) Atmospheric wet deposition characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in Taihu Lake and contributions to the lake (In Chinese). Res Environ Sci 24:1210–1219
Zarfl C, Lumsdon AE, Berlekamp J, Tydecks L, Tockner K (2015) A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquat Sci 77:161–170
Zhang HJ, Chen F (2010) Non-point pollution statistics and control measures in Taihu Basin (In Chinese). Water Resour Prot 26:87–90
Zhang YL, Shi K, Zhou YQ, Liu XJ, Qin BQ (2016) Monitoring the river plume induced by heavy rainfall events in large, shallow, Lake Taihu using MODIS 250 m imagery. Remote Sens Environ 173:109–121
Zhu W, Tan YQ, Wang CR, Feng GY, Chen MH, Liu YP, Li M (2018) The trend of water quality variation and analysis in typical area of Lake Taihu, 2010-2017 (In Chinese). J Lake Sci 30:296–305
Acknowledgments
We thank the Taihu Laboratory for Lake Ecosystem Research, for providing laboratory assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41673107), National Water Pollution Control and Treatment Science and Technology Major Project (2017ZX07203-005), “973” project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2014CB953801), and PAPD (164320H116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vedula VSS Sarma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 2685 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Wang, Y., Cai, Z. et al. Response of the nitrogen load and its driving forces in estuarine water to dam construction in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 31458–31467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09454-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09454-0