Abstract
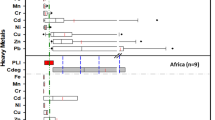
The deposition of toxic metals in the ecosystem contributes to the exposure and bioaccumulation of metals in the food chain, thus affecting human health. This study aimed to access the distribution of metal pollution emitted from automobiles in the dust, soil, and plant samples collected from the roadsides of national highways. Furthermore, metals were also determined in fuels and vehicular emissions. High contents of Pb, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn were found in roadsides as compared to control (35 km away from roads). The comparison among plants indicated that Calotropis procera and Rumex dentatus contained significantly higher metals than other plants. The concentrations of Pb, Cd, Cr, and Fe in plants were above the safe limits of the WHO/FAO. Significant and positive correlations were found between Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, and Zn in the dust and soil samples and Cd and Cr in dust and plants. According to the results of the PCA analysis, all metals formed the first two components explaining 89.5% of the total variance. The source of these metals was attributed to automobile exhaust and dust depositions. The findings of the present study suggest that roadside plants are heavily infested with heavy metals due to vehicular smoke pollution, so the consumption of vegetation facing vehicular pollution may lead to certain physiological disorders and diseases.

Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidemi OO (2011) Levels of Pb, Fe, Cd and Co in soils of automobile workshop in Osun state, Nigeria. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 15(2):279–282
Agrawal M, Singh B, Agrawal SB, Bell JNB, Marshall F (2006) The effect of air pollution on yield and quality of mung bean grown in peri-urban areas of Varansi. Water Air Soil Pollut 169:239–254
Akinyemi AJ, Miah MR, Ijomone OM, Tsatsakis A, Soares FA, Tinkov AA, Skalny AV, Venkataramani V, Aschner M (2019) Lead (Pb) exposure induces dopaminergic neurotoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans: involvement of the dopamine transporter. Toxicol Rep 6:833–840
Aksoy A (2008) Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.): a possible biomonitor of metal pollution. Pak J Bot 40:791–799
Aksoy A, Demirezen D (2006) Fraxinus excelsior as a biomonitor of heavy metal pollution. Polish J Environ Stud Manag Tools Document 16B:3–4
Amusan AA, Bada SB, Salami AT (2003) Effect of traffic density on heavy metal contents of soil and vegetation along roadside of Osun state, Nigeria. West African J Appl Ecol 4:107–112
Anwar S, Nawaz MF, Gul S, Rizwan M, Ali S, Kareem A (2016) Uptake and distribution of minerals and heavy metals in commonly grown leafy vegetable species irrigated with sewage water. Environ Monit Assess 188(9):541
Awan MA, Ahmed SH, Aslam MR, Qazi IA (2011) Determination of Total suspended particulate matter and heavy metals in ambient air of four cities of Pakistan. Iranica J Energy Environ 2(2):128–132
Bhardwaj P, Chaturvedi KA, Prasad P (2009) Effect of enhanced lead and cadmium in soil on physiological and biochemical attributes of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Nature Sci 7:1–13
Bono R, Piccioni P, Traversi D, Degan R, Grosa M, Bosello G, Gilli G, Arossa W, Bugiani M (2007) Urban air quality and carboxyhemoglobin levels in a group of traffic policemen. Sci Total Environ 376(1–3):109–115
Cai K, Zhang M, Yu Y, Kim K (2019) Pollution, source, and relationship of trace metal(loid)s in soil-wheat system in Hebei plain, northern China. Agronomy 9(7):391
CODEX (2007) Standard for pickled fruits and vegetables. CODEX STAN 260–2007 http://www.codexalimentarius.org/committees-task-forces. Retrieved 10–11–2013
Daud M (2009) Use of various plants as biomonitors to estimate atmospheric pollution. Ph.D thesis. Institute of Chemistry, University of the Punjab, Pakistan
Debnath B, Singh WS, Manna K (2019) Sources and toxicological effects of lead on human health. Indian J Med Spec 10:66–71
Desouza RJ, Varun M, Masih J, Paul MS (2010) Identification of Calotropis procera L. as a potential phytoaccumulator of heavy metals from contaminated soils in urban north Central India. J Hazard Mater 184:1–8
Elbagermi ME, Edwards HGM, Alajtal AI (2012) Monitoring of heavy metal content in fruits and vegetables collected from production and market sites in the Misurata area of Libya. ISRN Anal Chem 2012, article ID 827645, 5 pages, 2012. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/827645
EPA (2017) Basic information of lead (Pb) air pollution. Published by EPA, Washington DC, USA
FAO/WHO (2001) Codex Alimentarius Commission. Food additive and contaminants. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, ALINORM 01/ 12A. pp 1–289
Farooq H, Jamil Y, Ahmad MR, Afzal M, Khan SA (2012) Lead pollution measurement along national highway and motorway in Punjab, Pakistan. J Basic Appl Sci 8:463–467
Florence TM, Batley GE (1977) Determination of the chemical forms of trace metals in natural water, with special reference to copper, lead, cadmium and zinc. Talanta 24:151–158
Ghaedi M, Shokrollal A, Ahmadi F, Rajabi HR, Soylak M (2008) Cloud point extraction for the determination of copper, nickel and cobalt ions in environmental samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 150:1–15
Ghorani-Azam A, Riahi-Zanjani B, Balali-Mood M (2016) Effects of air pollution on human health and practical measures for prevention in Iran. J Res Med Sci Off J Isfahan Univ Med Sci 21:65
Gujar BR, Butler TM, Lawrence MG (2008) Evaluation of emissions and air quality in megacities. Atmos Environ 42:1539–1606
Ilyas SZ (2006) Air pollution studies and determination of smoke particle size in Siryab road Quetta, Pakistan. World App Sci J 1:122–126
Jung CM (2008) Heavy metal concentrations in soils and factors affecting metal uptake by plants in the vicinity of a Korean Cu-W mine. Sensors 8:2413–2423
Kadir MM, Janjua NZ, Kristensen S, Fatmi Z, Sathiakumar N (2008) Status of children’s blood lead levels in Pakistan: implications for research and policy. Public Health 122(7):708–715
Karar K, Gupta AK, Kumar A, Kantibiswas A (2006) Characterization and identification of the sources of chromium, zinc, lead, cadmium, nickel, manganese and iron in pm10 particulates at the two sites of Kolkata, India. Environ Monit Assess 120:347–360
Liu HM, Yang K, Xiao ZW (2018) Research progress of soil cadmium pollution control and exogenous regulation. Crop Res 32:449–453
Lone MI, Raza SH, Muhammad S, Naeem MA, Khalid M (2006) Lead contents in soil and wheat tissue along roads with different traffic loads in Rawalpindi district. Pak J Bot 38:1035–1042
Lyanda AA (2018) Serum heavy metal levels in teenagers currently or formerly employed as gas station attendants. Bangladesh J Med Sci 17(2):224–229
Mahajan P, Kaushal J (2018) Role of phytoremediation in reducing cadmium toxicity in soil and water. J Toxicol Volume 2018, Article ID 4864365, 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4864365
Masindi V, Muedi KL (2018) Environmental contamination by heavy metals. Heavy Metals 19:2019. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.76082
Naveed NH, Batool AI, Rehman FU, Hameed U (2010) Leaves of roadside plants as bioindicator of traffic related lead pollution during different seasons in Sargodha, Pakistan. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 4:770–774
Nawazish S, Hussain M, Ashraf M, Ashraf MY, Jamil A (2012) Effect of automobile related metal pollution (Pb2+ & Cd2+) on some physiological attributes of wild plants. Int J Agric Biol 14(6):953–958
Nawazish S, Bukhari SM, Muhammad A, Khan IU, Alhassan AJ, Hussain M, Zaidi A (2017) Correlation analysis of toxic metals on motorway and national highway. Kuwait J Sci 44(2)
Oudijk G (2010) The rise and fall of organometallic additives in automotive gasoline. Environ Forensic 11(1–2):17–49
Park JH, Kim SJ, Ahn JS, Lim DH, Han YS (2018) Mobility of multiple heavy metalloids in contaminated soil under various redox conditions: effects of iron sulfide presence and phosphate competition. Chemosphere 197:344–352
Paul R, White F, Luby S (2003) Trends in lead content of petrol in Pakistan. Bull World Health Organ 81:468–468
Paunov M, Koleva L, Vassilev A, Vangronsveld J, Goltsev V (2018) Effects of different metals on photosynthesis: cadmium and zinc affect chlorophyll fluorescence in durum wheat. Int J Mol Sci 19(3):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030787
Pirzada H, Ahmad SS, Rashid A, Shah T (2009) Multivariate analysis of selected roadsides plants (Dalbrgia sisso and Cannabis sativa) for lead pollution monitoring. Pak J Bot 41:1729–1736
Plesnicar A, Zupancic N (2005) Heavy metal contamination of roadside soil along Ljubljana-Obrezje highway. RMZ- Mater Geoenviron 52:403–418
Pulles T, Denier van der Gon H, Appelman W, Verheul M (2012) Emission factors for heavy metals from diesel and petrol used in European vehicles. Atmos Environ 61:641–651
Pundyte N, Baltrenaite E, Pereira P, Paliulis D (2011) Anthropogenic effects on heavy metals and macronutrients accumulation in soil and wood of Pinus sylvestris L. J Environ Eng Landscape Manag 19:34–43
Rabier J, Schwob IL, Notonier R, Fogliani B, Madjebi SB (2008) Anatomical element localization by EDXS in Grevillea exul var. Exul under nickel stress. Environ Pollut 156:1156–1163
Rafaj P, Kiesewetter G, Gül T, Schöpp W, Cofala J, Klimont Z, Purohit P, Heyes C, Amann M, Borken-Kleefeld J, Cozzi L (2018) Outlook for clean air in the context of sustainable development goals. Glob Environ Chang 53:1–11
Rajput M, Agrawal M (2004) Physiological and yield responses of pea plants to ambient air pollution. Indian J Plant Physiol 9:9–14
Raju G, Kumar NP (2017) Study on blood lead levels in children. IAIM 4(12):84–93
Rusin M, Gospodarek J, Nadgórska-Socha A, Barczyk G, Boligłowa E, Dabioch M (2018) Effect of petroleum-derived substances on life history traits of bird cherry-oat aphid (Rhopalosiphum padi L.) and on the growth and chemical composition of winter wheat. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(27):27000–27012
Saqib M, Jaffar M (2004) High volume sampling and dithizone scrubbing based estimation of aerosols lead levels at Islamabad. Pak J Chem Soc Pak 26:52–56
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005) Lead toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17(1):35–52
Stevovic S, Devrnja N, Dragosavac DC (2011) Environmental impact quantification and correlation between site location and contents and structure of Tansy. Afr J Biotechnol 10:5075–5083
Violante A, Cozzolino V, Perelomov L, Caporale AG, Pigna M (2010) Mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10:268–292
Walkley A (1947) A critical examination of a rapid method for determination, organic carbon in soils: effects of variations in digestion conditions and organic soils constituents. Soil Sci 63:251–263
Waseem A, J Arshad, F Iqbal, A Sajjad, Z Mehmood, and G Murtaza (2014) Pollution status of Pakistan: a retrospective review on heavy metal contamination of water, soil, and vegetables. BioMed Research Int Volume 2014, Article ID 813206, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/813206
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
WHO (World Health Organization) (1996) Trace elements in human nutrition and health. World Health Organization, Geneva
WHO (World Health Organization) (2002) The worldwide problem of lead in petrol. Bull World Health Organ 2002:80
WHO (World Health Organization) (2019) Lead poisoning and health. 23 August 2019. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lead-poisoning-and-health
Wolf B (1982) A comprehensive system of leaf analyses and its use for diagnosing crop nutrient status. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 13:1035–1059
Yousra M, Mahmood-ul-Hassan M, Sarwar S, Naeem S (2019) Adsorption of lead, cadmium, and nickel on benchmark soils of Pakistan. Eurasian Soil Sci 52(9):1063–1074
Zhou F, Yin G, Gao Y, Liu D, Xie J, Ouyang L, Fan Y, Yu H, Zha Z, Wang K, Shao L (2019) Toxicity assessment due to prenatal and lactational exposure to lead, cadmium and mercury mixtures. Environ Int 133:105192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anwar, S., Naz, A., Ashraf, M.Y. et al. Evaluation of inorganic contaminants emitted from automobiles and dynamics in soil, dust, and vegetations from major highways in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 32494–32508 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09198-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09198-x