Abstract
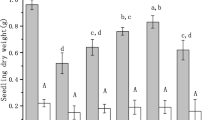
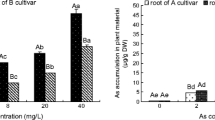
This study describes the role of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) in alleviating arsenic (As) stress in rice (Oryza sativa) germination and early seedling growth. Seeds of rice were primed with different concentrations (10, 20, 50, 100, and 200 mg L−1) of ZnO NPs and As (0, and 2 mg L−1) for 12 days in petri dishes. Two milligrams per liter of As treatment represented a stress condition, which was evidenced by germination rate, seedling length, seedling dry weight, chlorophyll, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) content of rice shoot. ZnO NPs amendment (10–100 mg L−1) increased the germination rate (2.3–8.9%), shoot weight (18.2–42.4%), root weight (5.2–23.9%), and chlorophyll content (3.5–40.1%), while elevated the SOD (2.2–22.8%) and CAT (7.2–60.7%) activities and reduced the MDA content (17.5–30.8%). As concentrations were significantly decreased by 8.4–72.3% and 10.2–56.6%, respectively, in rice roots and shoots with ZnO NPs amendment (10–200 mg L−1) by the As adsorption of ZnO NPs and promoted biomass of rice. All the amendments improved the Zn concentrations in rice shoots and roots. Overall, ZnO NPs provide effective resistance to arsenic toxicity by increasing germination, biomass, and nutrients of Zn and decreasing As uptake in rice.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 April 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13938-y
References
Ali S, Rizwan M, Noureen S, Anwar S, Ali B, Naveed M, Abd Allah EF, Alqarawi AA, Ahmad P (2019) Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:11288–11299
Bashir A, Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZU, Ishaque W, Riaz MA, Maqbool A (2018) Effect of foliar-applied iron complexed with lysine on growth and cadmium (Cd) uptake in rice under Cd stress. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:20691–20699
Cai Y, Xu W, Wang M, Chen W, Li X, Li Y, Cai Y (2019) Mechanisms and uncertainties of Zn supply on regulating rice Cd uptake. Environ Pollut 253:959–965
Chen J, Dou R, Yang Z, You T, Gao X, Wang L (2018) Phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 130:604–612
Conway JR, Adeleye AS, Gardea-Torresdey J, Keller AA (2015) Aggregation, dissolution, and transformation of copper nanoparticles in natural waters. Environ Sci Technol 49:2749–2756
Dannenberg GD, Funck GD, da Silva WP, Fiorentini AM (2019) Essential oil from pink pepper (Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi): chemical composition, antibacterial activity and mechanism of action. Food Control 95:115–120
Huang Q, Zhou S, Lin L, Huang Y, Li F, Song Z (2018) Effect of nanomaterials on arsenic volatilization and extraction from flooded soils. Environ Pollut 239:118–128
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia Ur Rehman M, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SAS, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Khan ZS, Rizwan M, Hafeez M, Ali S, Javed MR, Adrees M (2019) The accumulation of cadmium in wheat (Triticum aestivum) as influenced by zinc oxide nanoparticles and soil moisture conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:19859–19870
Lata S, Samadder SR (2016) Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: a review. J Environ Manag 166:387–406
Li C, Feng S, Shao Y, Jiang L, Lu X, Hou X (2007) Effects of arsenic on seed germination and physiological activities of wheat seedlings. J Environ Sci 19:725–732
Liu RQ, Lal R (2015) Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci Total Environ 514:131–139
Liu WJ, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2013) Silicon has opposite effects on the accumulation of inorganic and methylated arsenic species in rice. Plant Soil 376:423–431
Liu X, Zhang S, Shan X, Zhu YG (2005) Toxicity of arsenate and arsenite on germination, seedling growth and amylolytic activity of wheat. Chemosphere 61:293–301
Ma X, Geisler-Lee J, Deng Y, Kolmakov A (2010) Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: phytotoxicity, uptake and accumulation. Sci Total Environ 408:3053–3061
Mahajan P, Dhoke SK, Khanna AS (2011) Effect of Nano-ZnO particle suspension on growth of mung (Vigna radiata) and gram (Cicer arietinum) seedlings using plant agar method. J Nanotechno 2011:1–7
Milani N, McLaughlin MJ, Stacey SP, Kirby JK, Hettiarachchi GM, Beak DG, Cornelis G (2012) Dissolution kinetics of macronutrient fertilizers coated with manufactured zinc oxide nanoparticles. J Agric Food Chem 60:3991–3998
Munir T, Rizwan M, Kashif M, Shahzad A, Ali S, Amin N, Zahid R, Alam MFE, Imran M (2018) Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the growth and Zn uptake in wheat by seed priming method. Dig J Nanomater Bios 13:315–323
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Zia Ur Rehman M, Waris AA (2019a) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Rizwan M, Ali S, Zia Ur Rehman M, Adrees M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF, Ali L, Hussain A, Chatha SAS, Imran M (2019b) Alleviation of cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) by foliar spray of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biochar to contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 248:358–367
Shahid MA, Balal RM, Khan N, Zotarelli L, Liu GD, Sarkhosh A, Fernández-Zapata JC, Martínez Nicolás JJ, Garcia-Sanchez F (2019) Selenium impedes cadmium and arsenic toxicity in potato by modulating carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism. Ecotox Environ Safe 180:588–599
Sharifan H, Wang XX, Guo BL, Ma XM (2018) Investigation on the modification of physicochemical properties of cerium oxide nanoparticles through adsorption of Cd and As(III)/As(V). ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:13454–13461
Shri M, Kumar S, Chakrabarty D, Trivedi PK, Mallick S, Misra P, Shukla D, Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Tuli R (2009) Effect of arsenic on growth, oxidative stress, and antioxidant system in rice seedlings. Ecotox Environ Safe 72:1102–1110
Singh N, Singh SP, Gupta V, Yadav HK, Ahuja T, Tripathy SS, Rashmi (2013) A process for the selective removal of arsenic from contaminated water using acetate functionalized zinc oxide nanomaterials. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 32:1023–1029
Su YH, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2010) Rice is more efficient in arsenite uptake and translocation than wheat and barley. Plant Soil 328:27–34
Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER, Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2017a) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alleviate heavy metal-induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:59–69
Venkatachalam P, Priyanka N, Manikandan K, Ganeshbabu I, Indiraarulselvi P, Geetha N, Muralikrishna K, Bhattacharya RC, Tiwari M, Sharma N, Sahi SV (2017b) Enhanced plant growth promoting role of phycomolecules coated zinc oxide nanoparticles with P supplementation in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 110:118–127
Wan Y, Camara AY, Huang Q, Yu Y, Wang Q, Li H (2018) Arsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) with selenite fertilization and water management. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 156:67–74
Wang P, Menzies NW, Lombi E, McKenna BA, Johannessen B, Glover CJ, Kappen P, Kopittke PM (2013) Fate of ZnO nanoparticles in soils and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Environ Sci Technol 47:13822–13830
Wang X, Sun W, Zhang S, Sharifan H, Ma X (2018) Elucidating the effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles on arsenic uptake and speciation in rice ( Oryza sativa) in a hydroponic system. Environ Sci Technol 52:10040–10047
Wang X, Sun W, Ma X (2019) Differential impacts of copper oxide nanoparticles and copper(II) ions on the uptake and accumulation of arsenic in rice (Oryza sativa). Environ Pollut 252:967–973
Wissuwa M, Ismail AM, Yanagihara S (2006) Effects of zinc deficiency on rice growth and genetic factors contributing to tolerance. Plant Physiol 142:731–741
Xie YP, He YP, Irwin PL, Jin T, Shi XM (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2325–2331
Ye W, Guo G, Wu F, Fan T, Lu H, Chen H, Li X, Ma Y (2018) Absorption, translocation, and detoxification of Cd in two different castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) cultivars. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:28899–28906
Zhang M, Zhao Q, Xue P, Zhang S, Li B, Liu W (2017) Do Si/As ratios in growth medium affect arsenic uptake, arsenite efflux and translocation of arsenite in rice (Oryza sativa)? Environ Pollut 229:647–654
Zhao L, Zhang H, Wang J, Tian L, Li F, Liu S, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL, White JC, Huang Y, Keller A, Ji R (2019) C60 Fullerols enhance copper toxicity and alter the leaf metabolite and protein profile in cucumber. Environ Sci Technol 53:2171–2180
Funding
We acknowledge the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2019FZJD007), Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Anhui, and the Open Fund of Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Farmland Ecological Conservation and Pollution Prevention (FECPP201904).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3238 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Fang, Q., Yan, S. et al. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.): germination, early growth, and arsenic uptake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 26974–26981 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08965-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08965-0