Abstract
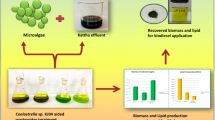
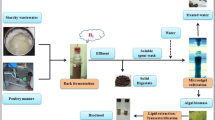
In this study, a novel two-step integrated process is proposed to facilitate the microalgae biofuel production as well as fresh cheese whey wastewater (FCWW) treatment simultaneously. The pre- and post-treatment of high-strength FCWW were performed by means of coagulation and algal cultivation, respectively. The pre-treatment of FCWW for maximum removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), turbidity (TUR) and total solids (TS) as responses was obtained by statistical optimization of coagulation parameters. The maximum removal of COD, TUR and TS at the optimum level of variables was obtained as 68.09%, 47.80% and 73.63%, respectively. The pre-treated FCWW was further treated by Chlorella pyrenoidosa and observed a significant reduction in the above-mentioned responses (87–94%). The maximum algal biomass yield and lipid productivity were observed as 2.44 g L−1 and 77.41 mg L−1 day−1, respectively. Based on promising results of FCWW treatment and its use as a third-generation biodiesel feedstock, a cost-benefit analysis of the developed process was assessed for microalgal oil production. The total profit earned by the integrated process model was $9.59 million year−1. Accordingly, the estimated production cost of algal oil (TAG) from the developed system was estimated to be $79.03 per barrel.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APHA:
-
American Public Health Association
- BOD:
-
Biological oxygen demand
- CCD:
-
Central composite design
- CD:
-
Chitosan dose
- CFS:
-
Chitosan FCWW sludge
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- DNS:
-
3,5-Dinitrosalicyclic acid
- FCWW:
-
Fresh cheese whey wastewater
- GC:
-
Gas chromatography
- LEA:
-
Lipid-extracted algal biomass
- M:
-
Molar
- MO:
-
Multi-objective
- NTU:
-
Nephelometric turbidity unit
- OpEx:
-
Operation expenses
- ORP:
-
Open raceway pond
- PP:
-
Process parameter
- RPM:
-
Rotation per minute
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- SS:
-
Stirring speed
- ST:
-
Stirring time
- TAG:
-
Triacyl glycerol
- TS:
-
Total solids
- TUR:
-
Turbidity
References
Altaher H (2012) The use of chitosan as a coagulant in the pre-treatment of turbid sea water. J Hazard Mater 233:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.06.061
Amaro HM, Guedes AC, Malcata FX (2011) Advances and perspectives in using microalgae to produce biodiesel. Appl Energy 88:3402–3410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.12.014
Ansari FA, Shriwastav A, Gupta SK, Rawat I, Bux F (2017) Exploration of microalgae biorefinery by optimizing sequential extraction of major metabolites from Scenedesmus obliquus. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:3407–3412. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b04814
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Water environment Federation, Washington DC
Bahr M, Díaz I, Dominguez A, González Sánchez A, Muñoz R (2014) Microalgal-biotechnology as a platform for an integral biogas upgrading and nutrient removal from anaerobic effluents. Environ Sci Technol 48:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403596m
Bellou S, Baeshen MN, Elazzazy AM, Aggeli D, Sayegh F, Aggelis G (2014) Microalgal lipids biochemistry and biotechnological perspectives. Biotechnol Adv 32:1476–1493
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37(8):911–917. https://doi.org/10.1139/o59-099
Carvalho A, Prazeresa AR, Rivas J (2013) Cheese whey wastewater: characterization and treatment. Sci Total Environ 445(446):385–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.038
Chandra R, Ghosh UK, Nayak JK (2017) Phycoremediation potential of marine microalga Tetraselmis indica on secondary treated domestic sewage for nutrient removal and biodiesel production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(26):20868–20875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9734-6
Chang BP, Thakur S, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2019) Novel sustainable biobased flame retardant from functionalized vegetable oil for enhanced flame retardancy of engineering plastic. Sci Rep 9:15971. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52039-2
Chen F, Zhang Y (1997) High cell density mixotrophic culture of Spirulina platensis on glucose for phycocyanin production using a fed-batch system. Enzym Microb Technol 20(3):221–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(96)00116-0
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.02.001
Choi HJ (2016) Dairy wastewater treatment using microalgae for potential biodiesel application. Environ Eng Res 21:393–400. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2015.151
Chung YC (2006) Improvement of aquaculture wastewater using chitosan of different degrees of deacetylation. Environ Technol 27:1199–1208. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332708618734
Cirne I, Boaventura J, Guedes Y, Lucas E (2016) Methods for determination of oil and grease contents in wastewater from the petroleum industry. Chem Chem Technol 10(4):437–444
da Rosa Andrade M, Vieira Costa JA (2008) Culture of microalga Spirulina platensis in alternative sources of nutrients. Cienc. e Agrotecnologia 32(5):1551–1556. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542008000500029
Davis R, Aden A, Pienkos PT (2011) Techno-economic analysis of autotrophic microalgae for fuel production. Appl Energy 88:3524–3531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.04.018
Economou CN, Marinakis N, Moustaka-Gouni M, Kehayias G, Aggelis G, Vayenas DV (2015) Lipid production by the filamentous cyanobacterium Limnothrix sp. growing in synthetic wastewater in suspended- and attached-growth photobioreactor systems. Ann Microbiol 65:1941–1948
El-Sheekh MM, Gheda SF, El-Sayed AEKB, Shady AMA, El-Sheikh ME, Schagerl M (2019) Outdoor cultivation of the green microalga Chlorella vulgaris under stress conditions as a feedstock for biofuel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05108-y
Fadare DA, Bamiro OA, Oni AO (2010) Energy and cost analysis of organic fertilizer production in Nigeria. Energy 35:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.09.030
Faria A, Gonçalves L, Peixoto JM, Peixoto J, Brito AG, Martins G (2016) Resources recovery in the dairy industry: bioelectricity production using a continuous microbial fuel cell. J Clean Prod 140:971–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.027
Ficara E, Uslenghi A, Basilico D, Mezzanotte V (2014) Growth of microalgal biomass on supernatant from biosolid dewatering. Water Sci Technol 69:896–902. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.805
Girard JM, Roy ML, Hafsa MB, Gagnon J, Faucheux N, Heitz M, Tremblay R, Deschênes JS (2014) Mixotrophic cultivation of green microalgae Scenedesmus obliquus on cheese whey permeate for biodiesel production. Algal Res 5:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2014.03.002
Gregory J, Guibai L (1991) Effects of dosing and mixing conditions on polymer flocculation of concentrated suspensions. Chem Eng Commun 108:3–21
Guo T, Englehardt J, Wu T (2014) Review of cost versus scale: water and wastewater treatment and reuse processes. Water Sci Technol 69(2):223–234. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.734
Hedge JE, Hofreiter BT (1962) In: Whistler RL, Miller JN (eds) Carbohydrate chemistry, vol 17. New York, Academic Press
Hoffman J, Pate RC, Drennen T, Quinn JC (2017) Techno-economic assessment of open microalgae production systems. Algal Res 23:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.01.005
Hupfauf B, Süß M, Dumfort A, Füssl-Le H (2016) Cultivation of microalgae in municipal wastewater and conversion by hydrothermal carbonization: a review. Chem Bio Eng Rev 3:186–200
Kanaga K, Pandey A, Kumar S, Geetanjali (2016) Multi-objective optimization of media nutrients for enhanced production of algae biomass and fatty acid biosynthesis from Chlorella pyrenoidosa NCIM 2738. Bioresour Technol 200:940–950
Kim BH, Choi JE, Cho K, Kang Z, Ramanan R, Moon DG, Kim HS (2018) Influence of water depth on microalgal production, biomass harvest, and energy consumption in high rate algal pond using municipal wastewater. J Microbiol Biotechnol 28(4):630–637. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1801.01014
Kumar V, Othman N, Asharuddin S (2017) Applications of natural coagulants to treat wastewater—a review. In MATEC Web of Conferences EDP Sciences. 103:06016. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201710306016
Levine RB, Costanza-Robinson MS, Spatafora GA (2011) Neochloris oleoabundans grown on anaerobically digested dairy manure for concomitant nutrient removal and biodiesel feedstock production. Biomass Bioenergy 35:40–49
Lu W, Wang Z, Wang X, Yuan Z (2015) Cultivation of Chlorella sp. using raw dairy wastewater for nutrient removal and biodiesel production: characteristics comparison of indoor bench-scale and outdoor pilot-scale cultures. Bioresour Technol 192:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.05.094
Ma X, Gao M, Gao Z, Wang J, Zhang M, Ma Y, Wang Q (2018) Past, current, and future research on microalga-derived biodiesel: a critical review and bibliometric analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(11):10596–10610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1453-0
Markandeya T, Shukla SP, Mohan D (2017) Toxicity of disperse dyes and its removal from wastewater using various adsorbents: a review. Res J Environ Toxicol 11(2):72–89
Marquez FJ, Sasaki K, Kakizono T, Nishio N, Nagai S (1993) Growth characteristics of Spirulina platensis in mixotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. J Ferment Bioeng 76(5):408–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/0922-338X(93)90034-6
Martins RC, Quinta-Ferreira RM (2010) Final remediation of post-biological treated milk whey wastewater by ozone. Int J Chem React Eng 8(1):1542–6580. https://doi.org/10.2202/1542-6580.2310
Meier L, Perez R, Azocar LM, Rivas M, Jeison D (2015) Photosynthetic carbon dioxide uptake by microalgae: an attractive tool for biogas upgrading. Biomass Bioenergy 73:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.10.032
Miller GL (1959) Use of Dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Mohan SV, Rohit MV, Chiranjeevi P, Chandra R, Navaneeth B (2019) Heterotrophic microalgae cultivation to synergize biodiesel production with waste remediation: progress and perspectives. Bioresour Technol 184:169–178
Molazadeh M, Ahmadzadeh H, Pourianfar HR, Lyon S, Rampelotto PH (2019) The use of microalgae for coupling wastewater treatment with CO2 bio-fixation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:42. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00042
Momeni MM, Kahforoushan D, Abbasi F, Ghanbarian S (2018) Using chitosan/CHPATC as coagulant to remove color and turbidity of industrial wastewater: optimization through RSM design. J Environ Manag 211:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.01.031
Monod J (1942) Recherches sur la croissance des cultures bacte'riennes (Studies on the growth of bacterial cultures). Actual Sci Industrielles 911:1–215
Murphy CF, Allen DT (2011) Energy-water nexus for mass cultivation of algae. Environ Sci Technol 45:5861–5868. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200109z
NYMEX (n.d.) (USA) Crude Oil WTI Price. https://www.nasdaq.com/markets/crude-oil.aspx?timeframe=5m, 21-04-2019
Pandey A, Srivastava S, Kumar S (2019a) Sequential optimization of essential nutrients addition in simulated dairy effluent for improved Scenedesmus sp. ASK22 growth, lipid production and nutrients removal. Biomass Bioenergy 128:105319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.105319
Pandey A, Srivastava S, Kumar S (2019b) Phyco-remediation of dairy effluents and biomass valorization: a sustainable approach. In: Gupta SK, Bux F (eds) Application of microalgae in wastewater treatment, Biorefinery approaches of wastewater treatment, vol 2. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 195–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13909-4_9
Pandey A, Gupta A, Sunny A, Kumar S, Srivastava S (2020) Multi-objective optimization of media components for improved algae biomass, fatty acid and starch biosynthesis from Scenedesmus sp. ASK22 using desirability function approach. Renew Energy 150:476–486
Pereira MI, Chagas BM, Sassi R, Medeiros GF, Aguiar EM, Borba LH, Silva EP, Neto JC, Rangel AH (2019) Mixotrophic cultivation of Spirulina platensis in dairy wastewater: effects on the production of biomass, biochemical composition and antioxidant capacity. PLoS One 14(10):e0224294. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224294
Prandini JM, da Silva MLB, Mezzari MP, Pirolli M, Michelon W, Soares HM (2016) Enhancement of nutrient removal from swine wastewater digestate coupled to biogas purification by microalgae Scenedesmus spp. Bioresour Technol 202:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.082
Renault F, Sancey B, Badot PM, Crini G (2009) Chitosan for coagulation/flocculation process—an eco-friendly approach. Euro Polym J 45:1337–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2008.12.027
Rivas J, Prazeres AR, Carvalho F, Beltrán F (2010) Treatment of cheese whey wastewater: combined coagulation–flocculation and aerobic biodegradation. J Agric Food Chem 58(13):7871–7877. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf100602j
Rogers JN, Rosenberg JN, Guzman BJ, Oh VH, Mimbela LE, Ghassemi A, Betenbaugh MJ, Oyler GA, Donohue MD (2014) A critical analysis of paddlewheel-driven raceway ponds for algal biofuel production at commercial scales. Algal Res 4:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.11.007
Salla AC, Margarites AC, Seibel FI, Holz LC, Brião VB, Bertolin TE, Colla LM, Costa JA (2016) Increase in the carbohydrate content of the microalgae Spirulina in culture by nutrient starvation and the addition of residues of whey protein concentrate. Bioresour Technol 209:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.02.069
Saritha V, Srinivas N, Srikanth Vuppala NV (2017) Analysis and optimization of coagulation and flocculation process. Appl Water Sci 7:451–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2013.11.007
Singh P, Guldhe A, Kumari S, Rawat I, Bux F (2015) Investigation of combined effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and iron on lipid productivity of microalgae Ankistrodesmusfalcatus KJ671624 using response surface methodology. Biochem Eng J 94:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.10.019
Solovchenko A, Pogosyan S, Chivkunova O, Selyakh I, Semenova L, Voronova E, Scherbakov P, Konyukhov I, Chekanov K, Kirpichnikov M, Lobakova E (2014) Phycoremediation of alcohol distillery wastewater with a novel Chlorella sorokiniana strain cultivated in a photobioreactor monitored on-line via chlorophyll fluorescence. Algal Res 6:234–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2014.01.002
Sudhakar K, Premalatha M (2012) Techno-economic analysis of microalgal carbon sequestration and oil production. Int J Chem Res 4(4):0974–4290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.09.005
Tsolcha ON, Tekerlekopoulou AG, Christos SA, Stamatia B, George A, Matina K, Maria MG, Dimitrios VV (2016) Treatment of second cheese whey effluents using a Choricystis-based system with simultaneous lipid production. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:2349–2359
Tsolcha ON, Tekerlekopoulou AG, Akratos CS, Antonopoulou G, Aggelis G, Genitsaris S, Moustaka-Gouni M, Vayenas DV (2018) A Leptolyngbya-based microbial consortium for agro-industrial wastewaters treatment and biodiesel production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(18):17957–17966
Uggetti E, Sialve B, Latrille E, Steyer J-P (2014) Anaerobic digestate as substrate for microalgae culture: the role of ammonium concentration on the microalgae productivity. Bioresour Technol 152:437–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.11.036
Vishali S, Rashmi P, Karthikeyan R (2016) Evaluation of wasted biomaterial, crab shells (Portunus sanguinolentus), as a coagulant, in paint effluent treatment. Desalin Water Treat 57:13157–13165. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1055812
Wang JP, Chen YZ, Wang Y, Yuan SJ, Yu HQ (2011) Optimization of the coagulation-flocculation process for pulp mill wastewater treatment using a combination of uniform design and response surface methodology. Water Res 45:5633–5640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.023
Wu J-Y, Lay C-H, Chen C-C, Wu S-Y (2017) Lipid accumulating microalgae cultivation in textile wastewater: environmental parameters optimization. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 79:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.02.017
Xin C, Addy MM, Zhao J, Cheng Y, Cheng S, Mu D, Liu Y, Ding R, Chen P, Ruan R (2016) Comprehensive techno-economic analysis of wastewater-based algal biofuel production: a case study. Bioresour Technol 211:584–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.102
Acknowledgements
A.P. wishes to express his thanks to Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), Government of India for Institute PhD fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 811 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, A., Srivastava, S. & Kumar, S. Development and cost-benefit analysis of a novel process for biofuel production from microalgae using pre-treated high-strength fresh cheese whey wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 23963–23980 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08535-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08535-4