Abstract
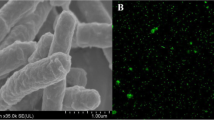
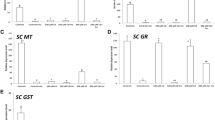
Phytoremediation assisted by plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) is considered an effective strategy for cadmium (Cd) removal in contaminated sites. This study uses a hydroponic experiment to investigate how Sphingobium yanoikuyae Sy310 affects Cd accumulation capacity and tolerance of Salix matsudana Koidz (S. matsudana) roots. The results showed that Cd induced growth change and physiological response on S. matsudana roots, displaying with reduced root length, increased antioxidant enzyme activities, and most importantly, enhanced cell wall polysaccharide contents. The Sy310 inoculation enhanced Cd accumulation in roots and alleviated the Cd toxic effects by regulating root growth, antioxidant enzyme system, and cell wall polysaccharide remodeling. Under Cd stress, Sy310 significantly induced increased root length and biomass, as well as higher root IAA level and Cd retention in cell walls. The Sy310 inoculation enhanced root pectin and hemicellulose 1 content, and pectin methylesterase activity, indicating that more amount of -COOH and -OH in cell walls for binding Cd. With Sy310-regulated extensive Cd regional sequestration in root cell walls and enhanced catalase activity, the root H2O2 and malondialdehyde content decreased, which contributes to improve Cd tolerance of S. matsudana roots. Furthermore, the Sy310 inoculation did not affect root cell wall structure and oxidative stress in the absence of Cd, representing a well-symbiotic relationship between Sy310 and S. matsudana. Therefore, Sy310 plays an important role in expediting the phytoremediation process of Cd with S. matsudana and has practical application potential.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjum NA, Sofo A, Scopa A, Roychoudhury A, Gill SS, Iqbal M, Lukatkin AS, Pereira E, Duarte AC, Ahmad I (2015) Lipids and proteins-major targets of oxidative modifications in abiotic stressed plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(6):4099–4121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3917-1
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2003) Zinc alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Ceratophyllum demersum L.: a free floating freshwater macrophyte. Plant Physiol Biochem 41(4):391–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0981-9428(03)00035-4
Ashraf S, Ali Q, Zahir ZA, Ashraf S, Asghar HN (2019) Phytoremediation: environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:714–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.068
Babu AG, Shea PJ, Sudhakar D, Jung IB, Oh BT (2015) Potential use of Pseudomonas koreensis AGB-1 in association with Miscanthus sinensis to remediate heavy metal (loid)-contaminated mining site soil. J Environ Manag 151:160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.12.045
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G (1973) An improved method for the assay of hydroxylysine. Anal Biochem 56(1):10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(73)90163-2
Brader G, Compant S, Mitter B, Trognitz F, Sessitsch A (2014) Metabolic potential of endophytic bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 27:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.09.012
Chen G, Liu Y, Wang R, Zhang J, Owens G (2013) Cadmium adsorption by willow root: the role of cell walls and their subfractions. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(8):5665–5672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1506-3
Chen B, Zhang Y, Rafiq MT, Khan KY, Pan F, Yang X, Feng Y (2014) Improvement of cadmium uptake and accumulation in Sedum alfredii by endophytic bacteria Sphingomonas SaMR12: effects on plant growth and root exudates. Chemosphere 117:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.078
Chen Y, Fu JW, Han YH, Rathinasabapathi B, Ma LQ (2016) High As exposure induced substantial arsenite efflux in As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata. Chemosphere 144:2189–2194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.001
Cosgrove DJ (2005) Growth of the plant cell wall. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(11):850–861. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1746
Dai M, Liu W, Hong H, Lu H, Liu J, Jia H, Yan C (2018) Exogenous phosphorus enhances cadmium tolerance by affecting cell wall polysaccharides in two mangrove seedlings Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh and Kandelia obovata (S, L.) Yong differing in cadmium accumulation. Mar Pollut Bull 126:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.083
DuBois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28(3):350–356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70(2):616–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90488-7
Germaine K, Keogh E, Garcia-Cabellos G, Borremans B, Lelie D, Barac T, Oeyen L, Vangronsveld J, Moore FP, Moore ER, Campbell CD, Ryan D, Dowling DN (2004) Colonisation of poplar trees by gfp expressing bacterial endophytes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48(1):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsec.2003.12.009
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Haferburg G, Kothe E (2007) Microbes and metals: interactions in the environment. J Basic Microbiol 47(6):453–467. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200700275
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hu HJ, Chen YL, Wang YF, Tang YY, Chen SL, Yan SZ (2017) Endophytic Bacillus cereus effectively controls Meloidogyne incognita on tomato plants through rapid rhizosphere occupation and repellent action. Plant Dis 101(3):448–455. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-06-16-0871-RE
Kan Q, Wu W, Yu W, Zhang J, Xu J, Rengel Z, Chen L, Cui X, Chen Q (2016) Nitrate reductase-mediated NO production enhances Cd accumulation in Panax notoginseng roots by affecting root cell wall properties. J Plant Physiol 193:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2016.01.017
Kierul K, Borriss R, Chen XH, Voigt B, Carvalhais LC, Albrecht D (2015) Influence of root exudates on the extracellular proteome of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Microbiology 161(1):131–147. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.083576-0
Kong XS, Zhao YX, Tian K, He XB, Jia YY, He ZH, Wang WW, Xiang CG, Tian XJ (2020) Insight into nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on cadmium phytoextraction of hydroponically grown Salix matsudana Koidz cuttings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:8406–8417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07499-4
Krzesłowska M (2010) The cell wall in plant cell response to trace metals: polysaccharide remodeling and its role in defense strategy. Acta Physiol Plant 33(1):35–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0581-z
Kumar PS, Ramakrishnan K, Kirupha SD, Sivanesan S (2010) Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of cadmium adsorption from aqueous solution onto rice husk. Braz J Chem Eng 27(2):347–355. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0104-66322010000200013
Levesque-Tremblay G, Pelloux J, Braybrook SA, Muller K (2015) Tuning of pectin methylesterification: consequences for cell wall biomechanics and development. Planta 242(4):791–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2358-5
Li T, Tao Q, Shohag MJI, Yang X, Sparks DL, Liang Y (2014) Root cell wall polysaccharides are involved in cadmium hyperaccumulation in Sedum alfredii. Plant Soil 389(1–2):387–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2367-3
Li Y, Zhou C, Huang M, Luo J, Hou X, Wu P, Ma X (2016) Lead tolerance mechanism in Conyza canadensis: subcellular distribution, ultrastructure, antioxidative defense system, and phytochelatins. J Plant Res 129(2):251–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-015-0776-x
Li D, Shu Z, Ye X, Zhu J, Pan J, Wang W, Chang P, Cui C, Shen J, Fang W, Zhu X, Wang Y (2017) Cell wall pectin methyl-esterification and organic acids of root tips involve in aluminum tolerance in Camellia sinensis. Plant Physiol Biochem 119:265–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.09.002
Liu D, Li TQ, Jin XF, Yang XE, Islam E, Mahmood Q (2008) Lead induced changes in the growth and antioxidant metabolism of the lead accumulating and non-accumulating ecotypes of Sedum alfredii. J Integr Plant Biol 50(2):129–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00608.x
Lux A, Martinka M, Vaculik M, White PJ (2011) Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot 62(1):21–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq281
Ma Y, Oliveira RS, Nai F, Rajkumar M, Luo Y, Rocha I, Freitas H (2015) The hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola harbors metal-resistant endophytic bacteria that improve its phytoextraction capacity in multi-metal contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 156:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.03.024
Nahakpam S, Shah K (2010) Expression of key antioxidant enzymes under combined effect of heat and cadmium toxicity in growing rice seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 63(1):23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-010-9508-3
Pan F, Meng Q, Wang Q, Luo S, Chen B, Khan KY, Yang X, Feng Y (2016) Endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 promotes cadmium accumulation by increasing glutathione bio synthesis in Sedum alfredii Hance. Chemosphere 154:358–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.120
Pramanik K, Mitra S, Sarkar A, Maiti TK (2018) Alleviation of phytotoxic effects of cadmium on rice seedlings by cadmium resistant PGPR strain Enterobacter aerogenes MCC 3092. J Hazard Mater 351:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.03.009
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Freitas H (2009) Endophytic bacteria and their potential to enhance heavy metal phytoextraction. Chemosphere 77(2):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.047
Rogers A, McDonald K, Muehlbauer MF, Hoffman A, Koenig K, Newman L, Taghavi S, Lelie D (2012) Inoculation of hybrid poplar with the endophytic bacterium Enterobacter sp. 638 increases biomass but does not impact leaf level physiology. GCB Bioenergy 4(3):364–370. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1757-1707.2011.01119.x
Romero-Puertas MC, Terrón-Camero LC, Peláez-Vico MÁ, Olmedilla A, Sandalio LM (2019) Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as key indicators of plant responses to Cd stress. Environ Exp Bot 161:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.10.012
Saravanan A, Kumar PS, Carolin CF, Sivanesan S (2017) Enhanced adsorption capacity of biomass through ultrasonication for the removal of toxic cadmium ions from aquatic system: temperature influence on isotherms and kinetics. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 21(3). https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)hz.2153-5515.0000355
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR, Ishaque W, Kamran MA, Matloob A, Rehim A, Hussain S (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.116
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2009) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.10.007
Singh P, Shah K (2014) Evidences for reduced metal-uptake and membrane injury upon application of nitric oxide donor in cadmium stressed rice seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 83:180–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.07.018
Sun P, Tian Q, Chen J, Zhang W (2009) Aluminium-induced inhibition of root elongation in Arabidopsis is mediated by ethylene and auxin. J Exp Bot 61(2):347–356. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp306
Tanaka H, Dhonukshe P, Brewer PB, Friml J (2006) Spatiotemporal a symmetric auxin distribution: a means to coordinate plant development. Cell Mol Life Sci 63(23):2738–2754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-006-6116-5
Tu S, Ma L, Luongo T (2004) Root exudates and arsenic accumulation in arsenic hyperaccumulating Pteris vittata and non-hyperaccumulating Nephrolepis exaltata. Plant Soil 258(1):9–19. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:plso.0000016499.95722.16
Waigi MG, Sun K, Gao YZ (2017) Sphingomonads in microbe-assisted phytoremediation: tackling soil pollution. Trends Biotechnol 35(9):883–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2017.06.014
Waller F, Achatz B, Baltruschat H, Fodor J, Becker K, Fischer M, Heier T, Hückelhoven R, Neumann C, Wettstein D, Franken P, Kogel KH (2005) The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica reprograms barley to salt-stress tolerance, disease resistance, and higher yield. PANS 102(38):13386–13391. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504423102
Wang HO, Xu R, You LM, Zhong GR (2013) Characterization of Cu-tolerant bacteria and definition of their role in promotion of growth, Cu accumulation and reduction of Cu toxicity in Triticum aestivum L. Ecotox Environ Safe 94:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.04.005
Wang WW, Cheng LK, Hao JW, Guan X, Tian XJ (2016a) Phytoextraction of initial cutting of Salix matsudana for Cd and Cu. Int J Phytoremediation 00–00. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1183574
Wang WW, Wu YJ, Akbar S, Jia XQ, He ZH, Tian XJ (2016b) Effect of heavy metals combined stress on growth and metals accumulation of three Salix species with different cutting position. Int J Phytoremediation 18:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2015.1131237
Wu K, Li J, Luo J, Liu Y, Song Y, Liu N, Rafiq MT, Li T (2018) Effects of elevated CO2 and endophytic bacterium on photo synthetic characteristics and cadmium accumulation in Sedum alfredii. Sci Total Environ 643:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.131
Xiong J, An L, Lu H, Zhu C (2009) Exogenous nitric oxide enhances cadmium tolerance of rice by increasing pectin and hemicellulose contents in root cell wall. Planta 230(4):755–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-0984-5
Xu SS, Lin SZ, Lai ZX (2015) Cadmium impairs iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana by increasing the polysaccharide contents and the iron-binding capacity of root cell walls. Plant Soil 392(1–2):71–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2443-3
Yang JL, Li YY, Zhang YJ, Zhang SS, Wu YR, Wu P, Zheng SJ (2008) Cell wall polysaccharides are specifically involved in the exclusion of aluminum from the rice root apex. Plant Physiol 146(2):602–611. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.111989
Yang W, Zhao F, Zhang X, Ding Z, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Yang X (2014) Variations of cadmium tolerance and accumulation among 39 Salix clones: implications for phytoextraction. Environ Earth Sci 73(7):3263–3274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3636-4
Zhao YY, He CX, Wu ZC, Liu XW, Cai MM, Jia W, Zhao XH (2019) Selenium reduces cadmium accumulation in seed by increasing cadmium retention in root of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Environ Exp Bot 158:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.11.017
Zhong H, Lauchli A (1993) Changes of cell wall composition and polymer size in primary roots of cotton seedlings under high salinity. J Exp Bot 44(4):773–778. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/44.4.773
Zhu XF, Lei GJ, Jiang T, Liu Y, Li GX, Zheng SJ (2012) Cell wall polysaccharides are involved in P-deficiency-induced cd exclusion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 236(4):989–997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1652-8
Zhu XF, Wang ZW, Dong F, Lei GJ, Shi YZ, Li GX, Zheng SJ (2013) Exogenous auxin alleviates cadmium toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana by stimulating synthesis of hemicellulose 1 and increasing the cadmium fixation capacity of root cell walls. J Hazard Mater 263(2):398–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.09.018
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Elizabeth Tokarz at Yale University for her assistance with English language and grammatical editing. We greatly appreciate the anonymous reviewers for the insightful comments that improved this manuscript greatly.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Sanxin Forestry Project in Jiangsu Province (No. LYSX[2016]46), the National Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2016YFD0600204), the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31530007), the State General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31870598), the specimen platform of China and the teaching specimens sub-platform (2005DKA21403-JK), and the Jiangsu Provincial Water Conservancy Science Technology Project (No. ZQ2018107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 836 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, X., Pang, L., Chen, Y. et al. Bacteria Sphingobium yanoikuyae Sy310 enhances accumulation capacity and tolerance of cadmium in Salix matsudana Koidz roots. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 19764–19773 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08474-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08474-0