Abstract
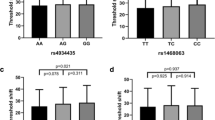
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is one of the most common occupational health risks in industrialized countries. It has been recognized to result from interactions between genetic and environmental factors. This study investigated the influence of genetic mutations in the potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E regulatory subunit 1 (KCNE1) gene on susceptibility to NIHL. A total of 2689 industrial workers in eastern China were recruited to participate. Three single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of KCNE1 were genotyped in noise-exposed workers who were classified into 589 cases and 639 control individuals. Then, main effects of the genotypes and their interactions with environmental factors were evaluated. Results showed that the rs3453 C allele located in KCNE1 3'-UTR region and the rs1805127 G allele in the encoding region were associated with increased risk of NIHL in the Chinese population. There is an association between TAA, TAG, and other (CAA/CGA) haplotypes (rs3453-rs11702354-rs1805127) and increased risk of NIHL with OR = 1.33, 1.43, and 2.93 (P = 0.022, 0.017, and 0.001 respectively) compared with CGG group. Results also showed a significant interaction between rs3453, rs1805127, and high-temperature exposure (P = 0.0002, adjusted OR = 1.85). The cellular evidence indicated that polymorphisms rs3453 and rs1805127 may play key roles in hearing loss through affecting KCNE1 expressions by the way of microRNA and protein respectively. The further animal study is still needed to confirm these mechanisms. KCNE1 rs3453 and rs1805127 may have a potential as biomarkers for screening the susceptibility to NIHL.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding E, Liu J, Shen H, Gong W, Zhang H, Song H, Zhu B (2018) Notch polymorphisms associated with sensitivity of noise induced hearing loss among Chinese textile factory workers. BMC Med Genet 19:168
Doi K, Sato T, Kuramasu T, Hibino H, Kitahara T, Horii A, Matsushiro N, Fuse Y, Kubo T (2005) Meniere’s disease is associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human potassium channel genes, KCNE1 and KCNE3. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 67:289–293
Guo H, Ding E, Bai Y, Zhang H, Shen H, Wang J, Song X, Cai W, Guo J, Zhu B (2017) Association of genetic variations in FOXO3 gene with susceptibility to noise induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. PLoS One 12:e0189186
Konings A, Van Laer L, Pawelczyk M, Carlsson PI, Bondeson ML, Rajkowska E, Dudarewicz A, Vandevelde A, Fransen E, Huyghe J, Borg E, Sliwinska-Kowalska M, Van Camp G (2007) Association between variations in CAT and noise-induced hearing loss in two independent noise-exposed populations. Hum Mol Genet 16:1872–1883
Konings A, Van Laer L, Van Camp G (2009) Genetic studies on noise-induced hearing loss: a review. Ear Hear 30:151–159
Liang C, Li X, Xu Y, Chen Q, Wu Y, Wang W, Li W, Qiu M (2013) KCNE1 rs1805127 polymorphism increases the risk of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of 10 studies. PLoS One 8:e68690
Lopes Kde C, Sartorato EL, da Silva-Costa SM, de Macedo Adamov NS, Gananca FF (2016) Meniere’s disease: molecular analysis of aquaporins 2, 3 and potassium channel KCNE1 genes in Brazilian patients. Otol Neurotol 37:1117–1121
Marcus DC, Wu T, Wangemann P, Kofuji P (2002) KCNJ10 (Kir4.1) potassium channel knockout abolishes endocochlear potential. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C403–C407
Yoshida N, Kristiansen A, Liberman MC (1999) Heat stress and protection from permanent acoustic injury in mice. J Neurosci 19:10116–10124
Neyroud N, Tesson F, Denjoy I, Leibovici M, Donger C, Barhanin J, Faure S, Gary F, Coumel P, Petit C, Schwartz K, Guicheney P (1997) A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome. Nat Genet 15:186–189
Nicolas M, Dememes D, Martin A, Kupershmidt S, Barhanin J (2001) KCNQ1/KCNE1 potassium channels in mammalian vestibular dark cells. Hear Res 153:132–145
Pawelczyk M, Van Laer L, Fransen E, Rajkowska E, Konings A, Carlsson PI, Borg E, Van Camp G, Sliwinska-Kowalska M (2009) Analysis of gene polymorphisms associated with K ion circulation in the inner ear of patients susceptible and resistant to noise-induced hearing loss. Ann Hum Genet 73:411–421
Shen H, Cao J, Hong Z, Liu K, Shi J, Ding L, Zhang H, Du C, Li Q, Zhang Z, Zhu B (2014) A functional Ser326Cys polymorphism in hOGG1 is associated with noise-induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. PLoS One 9:e89662
Sugahara K, Inouye S, Izu H, Katoh Y, Katsuki K, Takemoto T, Shimogori H, Yamashita H, Nakai A (2003) Heat shock transcription factor HSF1 is required for survival of sensory hair cells against acoustic overexposure. Hear Res 182:88–96
Sulkowski WJ, Szymczak W, Kowalska S, Sward-Matyja M (2004) Epidemiology of occupational noise-induced hearing loss (ONIHL) in Poland. Otolaryngol Pol 58:233–236
Tyson J, Tranebjaerg L, Bellman S, Wren C, Taylor JF, Bathen J, Aslaksen B, Sorland SJ, Lund O, Malcolm S, Pembrey M, Bhattacharya S, Bitner-Glindzicz M (1997) IsK and KvLQT1: mutation in either of the two subunits of the slow component of the delayed rectifier potassium channel can cause Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 6:2179–2185
Van Laer L, Carlsson PI, Ottschytsch N, Bondeson ML, Konings A, Vandevelde A, Dieltjens N, Fransen E, Snyders D, Borg E, Raes A, Van Camp G (2006) The contribution of genes involved in potassium-recycling in the inner ear to noise-induced hearing loss. Hum Mutat 27:786–795
Wangemann P (2002) K+ cycling and the endocochlear potential. Hear Res 165:1–9
Wangemann P, Liu J, Marcus DC (1995) Ion transport mechanisms responsible for K+ secretion and the transepithelial voltage across marginal cells of stria vascularis in vitro. Hear Res 84:19–29
Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhang L, Yang Z, Yang L, Wang X, Jiang C, Wang Q, Xia Y, Chen Y, Wu O, Zhu Y (2015) Associations of genetic variations in EYA4, GRHL2 and DFNA5 with noise-induced hearing loss in Chinese population: a case-control study. Environ Health 14:77
Acknowledgments
We thank every worker for their participations in this study.
Funding
The present study was financially supported by Jiangsu Province’s Outstanding Medical Academic Leader program. Project No: CXTDA2017029.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent was obtained from all participants, and this research was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Prevention and Control (Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, E., Wang, H., Han, L. et al. Variations in the potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily E regulatory subunit 1 gene associated with noise-induced hearing loss in the Chinese population. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 18822–18830 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08422-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08422-y