Abstract
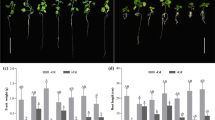
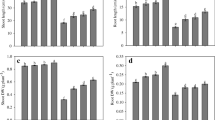
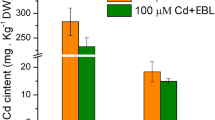
Contamination of soils with cadmium (Cd) is a serious problem worldwide. Solanum nigrum L. is reported as a Cd hyperaccumulator, but its enrichment capacity is limited. 2,4-Epibrassinolide (2,4-EBL) plays important roles in plant response to various stresses. Little is known about its effect on Cd tolerance in S. nigrum. Current study was performed to demonstrate effects of 2,4-EBL on plant growth, photosynthesis activity, activities of antioxidants, and Cd concentration in plants by nutrient solution contaminated with Cd. Results revealed that S. nigrum exhibited toxicity to Cd stress, including reducing plant height, root length, and chlorophyll content and increasing malondialdehyde (MDA) content. Exogenous application of 2,4-EBL significantly enhanced the contents of proline and soluble sugar and decreased the MDA content. Meanwhile, the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT) markedly increased compared with the control. Interesting, 2,4-EBL promoted photosynthesis by increasing the chlorophyll content, Fv/Fm. And increase in chlorophyll content is caused by increased expression of synthetic genes and decreased expression of degraded genes. 2,4-EBL also decreased accumulation of Cd in S. nigrum compared with single Cd stress. According to the present results, 2,4-EBL can effectively be used to alleviate the damage of Cd stress in S. nigrum and probably in other solanaceae.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzal J, Hu C, Imtiaz M, Elyamine A, Rana M, Imran M, Farag M (2018) Cadmium tolerance in rice cultivars associated with antioxidant enzymes activities and Fe/Zn concentrations. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(8):4241–4252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2018-y
Ahmad H, Hayat S, Ali M, Imran Ghani M, Zhihui C (2017) Regulation of growth and physiological traits of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) through various levels of 28-Homobrassinolide under salt stress conditions. Can J Plant Sci CJPS-2016-0404. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjps-2016-0404
Ali B, Hayat S, Fariduddin Q, Ahmad A (2008a) 24-Epibrassinolide protects against the stress generated by salinity and nickel in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 72(9):1387–1392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.012
Ali B, Hasan SA, Hayat S, Hayat Q, Yadav S, Fariduddin Q, Ahmad A (2008b) A role for brassinosteroids in the amelioration of aluminium stress through antioxidant system in mung bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Environ Exp Bot 62(2):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.07.014
Alves LR, Monteiro CC, Carvalho RF, Ribeiro PC, Tezotto T, Azevedo RA, Gratão PL (2017) Cadmium stress related to root-to-shoot communication depends on ethylene and auxin in tomato plants. Environ Exp Bot 134:102–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.11.008
Anjum SA, Tanveer M, Hussain S, Bao M, Wang L, Khan I, Ullah E, Tung SA, Samad RA, Shahzad B (2015) Cadmium toxicity in Maize (Zea mays L.): consequences on antioxidative systems, reactive oxygen species and cadmium accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(21):17022–17030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4882-z
Anuradha S, Rao SSR (2007) The effect of brassinosteroids on radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seedlings growing under cadmium stress. Plant Soil Environ 53(11):465–472
Astolfi S, Zuchi S, Passera C (2004) Role of sulphur availability on cadmium-induced changes of nitrogen and sulphur metabolism in maize (Zea mays L.) leaves. J Plant Physiol 161(7):795–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2003.11.005
Bączek KR, Juzoń K, Borek M, Antonkiewicz J (2019) Photosynthetic response of cabbage in cadmium-spiked soil. Photosynthetica 57(3):731–739. https://doi.org/10.32615/ps.2019.070
Bajguz A (2000) Effect of brassinosteroids on nucleic acids and protein content in cultured cells of Chlorella vulgaris. Plant Physiol Biochem 38(3):209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0981-9428(00)00733-6
Bajguz A (2002) Brassinosteroids and lead as stimulators of phytochelatins synthesis in Chlorella vulgaris. J Plant Physiol 159(3):321–324. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00654
Bajguz A, Hayat S (2009) Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 47(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.10.002
Bajguz A, Tretyn A (2003) The chemical structures and occurrence of brassinosteroids in plants. Brassinosteroids:1–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-0948-4_1
Chaffei C, Pageau K, Suzuki A, Gouia H, Ghorbel MH, Masclaux-Daubresse C (2004) Cadmium toxicity induced changes in nitrogen management in Lycopersicon esculentum leading to a metabolic safeguard through an amino acid storage strategy. Plant Cell Physiol 45(11):1681–1693. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pch192
Chen J-X, Wang X-F (2006) Plant physiology experiment guide. South China University of Technology Press, Guangzhou (in Chinese)
Cui J-X, Zhou Y-H, Ding J-G, Xia X-J, Shi K, Chen S-C, Asami T, Chen Z, Yu J-Q (2010) Role of nitric oxide in hydrogen peroxide-dependent induction of abiotic stress tolerance by brassinosteroids in cucumber. Plant Cell Environ 34(2):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02248.x
Dong Y-J, Chen W-F, Bai X-Y, Liu F-Z, Wan Y-S (2018) Effects of exogenous nitric oxide and 24-epibrassinolide on physiological characteristics of peanut under cadmium stress. Pedosphere 28(6):926–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1002-0160(17)60376-x
Eichacker LA, Soll J, Lauterbach P, Rüdiger W, Klein RR, Mullet JE (1990) In vitro synthesis of chlorophyll a in the dark triggers accumulation of chlorophyll a apoproteins in barley etioplasts. J Biol Chem 265(23):13566–13571
Fariduddin Q, Yusuf M, Chalkoo S, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2011) 28-homobrassinolide improves growth and photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus L. through an enhanced antioxidant system in the presence of chilling stress. Photosynthetica 49 (1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-011-0022-2
Gallego SM, Benavides MP (2019) Cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Academic Press, American. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-814864-8.00010-3
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: Insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.04.006
Guo J-K, Zhou R, Ren X-H, Jia H-L, Hua L, Xu H-H, Lv X, Zhao J, Wei T (2018) Effects of salicylic acid, epi-brassinolide and calcium on stress alleviation and Cd accumulation in tomato plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:491–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.010
Hasan SA, Hayat S, Ali B, Ahmad A (2008) 28-Homobrassinolide protects chickpea (Cicer arietinum) from cadmium toxicity by stimulating antioxidants. Environ Pollut 151(1):60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.03.006
Hasan SA, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2011) Brassinosteroids protect photosynthetic machinery against the cadmium induced oxidative stress in two tomato cultivars. Chemosphere 84(10):1446–1451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.047
Hayat S, Khalique G, Wani AS, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad A (2014) Protection of growth in response to 28-homobrassinolide under the stress of cadmium and salinity in wheat. Int J Biol Macromol 64:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.11.021
He J, Qin J, Long L, Ma Y, Li H, Li K, Jiang X, Liu T, Polle A, Liang Z, Luo Z-B (2011) Net cadmium flux and accumulation reveal tissue-specific oxidative stress and detoxification in Populus canescens. Physiol Plant 143(1):50–63. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2011.01487.x
Hédiji H, Djebali W, Belkadhi A, Cabasson C, Moing A, Rolin D, Brouquisse R, Gallusci P, Chaïbi W (2015) Impact of long-term cadmium exposure on mineral content of Solanum lycopersicum plants: consequences on fruit production. S Afr J Bot 97:176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2015.01.010
Howell WM, Keller GE, Kirkpatrick JD, Jenkins RL, Hunsinger RN, Mclaughlin EW (2007) Effects of the plant steroidal hormone, 24-epibrassinolide, on the mitotic index and growth of onion (Allium cepa) root tips. GMR Genet Mol Res 6(1):50–58
Janeczko A, Koscielniak J, Pilipowicz M, Szarek-Lukaszewska G, Skoczowski A (2005) Protection of winter rape photosystem 2 by 24-epibrassinolide under cadmium stress. Photosynthetica 43(2):293–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-005-0048-4
Joshi P, Misra AN, Nayak L, Biswal B (2013) Response of mature, developing and senescing chloroplast to environmental stress. In: Plastid Development in Leaves during Growth and Senescence. Adv Photosynth Respir 36:641–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5724-0_28
Kapoor D, Rattan A, Gautam V, Bhardwaj R (2015) Alleviation of cadmium and mercury stress by supplementation of steroid hormone to Raphanus sativus seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B 86(3):661–666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0501-5
Khan AR, Ullah I, Khan AL, Hong SJ, Waqas M, Park GS, Kwak Y, Choi JB, Jung BK, Park M, Lee IJ, Shin JH (2014) Phytostabilization and physicochemical responses of korean ecotype Solanum nigrum L. to cadmium contamination. Water Air Soil Pollut 225(10):2147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2147-y
Khan MIR, Iqbal N, Masood A, Mobin M, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Modulation and significance of nitrogen and sulfur metabolism in cadmium challenged plants. Plant Growth Regul 78(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0071-9
Khan MA, Khan S, Khan A, Alam M (2017) Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci Total Environ 601–602:1591–1605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.030
Lei W, Peishi Q, Ming X (2011) Phytoremediation Prospects of Heavy Metals by Indigenous Plants Growing in Industrially Polluted Soils. 2011 International Conference on Computer Distributed Control and Intelligent Environmental Monitoring. https://doi.org/10.1109/cdciem.2011.281
Li H (2000) Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical experiments. Higher Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Li Y, Jin X-X, Ding G-H, Zhu H, Yu L-J (2015) Alleviation of exogenous brassinolide on Solanum nigrum L. under cadmium stress. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 21(4):717–724 (in Chinese)
Liu N, Lin Z-F (2011) Detection of cell viability of whole plant leaves by Evans blue staining. J Plant Physiol 47(6):570–574 (in Chinese)
Liu Y-R (2017) Cloning of formaldehyde-resistant fungus AnYAP1 gene and its functional study. Dissertation, Harbin Normal University(in Chinese)
Lu L-L (2009) Study on the mechanism of cadmium uptake and transport by super-accumulating plant Sedum alfredii Hance. Dissertation, University of Zhejiang (in Chinese)
Lysenko EA, Klaus AA, Pshybytko NL, Kusnetsov VV (2014) Cadmium accumulation in chloroplasts and its impact on chloroplastic processes in barley and maize. Photosynth Res 125(1–2):291–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-014-0047-z
McCormac AC, Fischer A, Kumar AM, Söll D, Terry MJ (2001) Regulation of HEMA1 expression by phytochrome and a plastid signal during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 25(5):549–561. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00986.x
Mehta P, Jajoo A, Mathur S, Bharti S (2010) Chlorophyll a fluorescence research revealing effects of high salt stress on Photosystem II in wheat leaves. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(1):16–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.10.006
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Kumar R, Seth CS, Gupta DK (2006) Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation. Chemosphere 65(6):1027–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.03
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9(10):490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009
Muradoglu F, Gundogdu M, Ercisli S, Encu T, Balta F, Jaafar H, Zia-Ul-Haq M (2015) Cadmium toxicity affects chlorophyll a and b content, antioxidant enzyme activities and mineral nutrient accumulation in strawberry. Biol Res 48(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-015-0001-3
Núñez M, Mazzafera P, Mazorra LM, Siqueira WJ, Zullo MAT (2004) Influence of a Brassinosteroid Analogue on Antioxidant Enzymes in Rice Grown in Culture Medium with NaCl. Biol Plant 47(1):67–70. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1027380831429
Pinto A, Mota A, Devarennes A, Pinto F (2004) Influence of organic matter on the uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron by sorghum plants. Sci Total Environ 326(1–3):239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.01.004
Pospíšilová J (1998) Raghavendra, a.s. (ed.): photosynthesis. a comprehensive treatise. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Qian H-F, Li J-J, Pan X-J, Jiang H-Y, Sun L-W, Fu Z-W (2010) Photoperiod and temperature influence cadmium’s effects on photosynthesis-related gene transcription in Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(6):1202–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.07.006
Rady MM, Osman AS (2012) Response of growth and antioxidant system of heavy metal-contaminated tomato plants to 24-epibrassinolide. Afr J Agric Res 7(21):3249–3254
Sandalio LM, Dalurzo HC, Gómez M, Romero-Puertas MC, del Río LA (2001) Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J Exp Bot 52(364):2115–2126. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.364.2115
Sanità di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41(2):105–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0098-8472(98)00058-6
Santos LR, Batista BL, Lobato AKS (2017) Brassinosteroids mitigate cadmium toxicity in cowpea plants. Photosynthetica 56(2):591–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-017-0700-9
Schutzendubel A (2002) Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J Exp Bot 53(372):1351–1365. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1351
Sharma SS, Schat H, Vooijs R (1998) In vitro alleviation of heavy metal-induced enzyme inhibition by proline. Phytochemistry 49(6):1531–1535. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(98)00282-9
Shu S, Tang Y-Y, Yuan Y-H, Sun J, Zhong M, Guo S-R (2016) The role of 24-epibrassinolide in the regulation of photosynthetic characteristics and nitrogen metabolism of tomato seedlings under a combined low temperature and weak light stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 107:344–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.06.021
Six L, Smolders E (2014) Future trends in soil cadmium concentration under current cadmium fluxes to European agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 485–486:319–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.109
Soares C, de Sousa A, Pinto A, Azenha M, Teixeira J, Azevedo RA, Fidalgo F (2016) Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on ROS content, antioxidant system, lipid peroxidation and Ni uptake in Solanum nigrum L. under Ni stress. Environ Exp Bot 122:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.09.010
Tai Z-L, Yin X-Q, Fang Z-G, Shi G-L, Lou L-Q, Cai Q-S (2017) Exogenous GR24 alleviates cadmium toxicity by reducing cadmium uptake in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) seedlings. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(8):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080852
Thijssen S, Cuypers A, Maringwa J, Smeets K, Horemans N, Lambrichts I, Van Kerkhove E (2007) Low cadmium exposure triggers a biphasic oxidative stress response in mice kidneys. Toxicology 236(1–2):29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.03.022
Wang X-K (2006) Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical experiments. Higher Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang H-H, Feng T, Peng X-X, Yan M-L, Zhou P-L, Tang X-K (2009) Ameliorative effects of brassinosteroid on excess manganese-Induced oxidative stress in Zea mays L. leaves. Agric Sci China 8(9):1063–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1671-2927(08)60314-4
Wang Y, Jiang X, Li K, Wu M, Zhang R, Zhang L, Chen G (2014) Photosynthetic responses oforyza satival.seedlings to cadmium stress: physiological, biochemical and ultrastructural analyses. BioMetals 27(2):389–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9720-0
Wani AS, Tahir I, Ahmad SS, Dar RA, Nisar S (2017) Efficacy of 24-epibrassinolide in improving the nitrogen metabolism and antioxidant system in chickpea cultivars under cadmium and/or NaCl stress. Sci Hortic 225:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.06.063
Wei S-H, Zhou Q-X, Wang X, Cao W, Ren L-P, Song Y-F (2004) Potential of weed species applied to remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals. J Environ Sci 16(5):868–873. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-0742.2004.05.036
Xu L-L, Dong Y-J, Kong J, Liu S (2013) Effects of root and foliar applications of exogenous NO on alleviating cadmium toxicity in lettuce seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 72(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-013-9834-3
Yan H-P, Peng Y-L, Zhao X-Q, Lv Y-Y (2016) Effect of exogenous 24-epibrassinolide on seed germination and seedling growth of maize under different stress. J Nucl Agric Sci 30(5):0988–0996 (in Chinese)
Zhang SS, Cai ZY, Wang XL (2009) The primary signaling outputs of brassinosteroids are regulated by abscisic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(11):4543–4548. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900349106
Zhang K-P, Wang G-Y, Bao M-C, Wang L-C, Xie X-Y (2019) Exogenous application of ascorbic acid mitigates cadmium toxicity and uptake in Maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:19261–19271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05265-0
Zong L-G, Sun J-K, Shen Q-Y, Zhang X-P (2007) Effects of pollution on the growth of several leafy vegetables and their toxic symptoms. Asian J Ecotoxicol 2(1):63–68 (in Chinese)
Zouari M, Elloumi N, Ahmed CB, Delmail D, Rouina BB, Abdallah FB, Labrousse P (2016) Exogenous proline enhances growth, mineral uptake, antioxidant defense, and reduces cadmium-induced oxidative damage in young date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Ecol Eng 86:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.11.016
Acknowledgment
This work was completed in “Plant Biology” Key Laboratories of Universities in Heilongjiang Province.
Funding
This work was supported by the Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation (C2017039), Startup Scientific Research Fund from Harbin Normal University for Doctor (KGB201218), and Master’s Innovative Research Project from Harbin Normal University (HSDSSCX2018-58).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, R., Sun, W., Jin, X. et al. Analysis of 2,4-epibrassinolide created an enhancement tolerance on Cd toxicity in Solanum nigrum L.. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 16784–16797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08228-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08228-y