Abstract
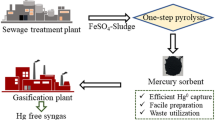
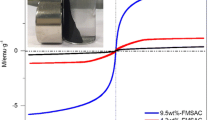
The sewage sludge flocculated with ferrous sulfate (SFS) was prepared by one-step pyrolysis to obtain magnetic Fe-containing carbon. Results showed that only a small amount of FexOy as well as extremely weak magnetism were observed at pyrolysis temperatures of less than 500 °C. SFS tended to exhibit intensive agglomeration, leading to the drastic increase of the crystalline-phase particle size at high pyrolysis temperature. The optimal pyrolysis temperature is 700 °C, corresponding to the production of some sulfides, an optimal content of FexOy, and a suitable BET surface. Hg0 removal efficiency of SFS700 (SFS pyrolyzed at 700 °C) reached 80.7% at the reaction temperature of 125 °C. The presence of O2 and low concentration of SO2 enhanced the Hg0 removal, while the H2O vapor and high SO2 concentration inhibited it. Meanwhile, good resistance for the adsorbent to moderate concentrations of SO2 and H2O was observed. Moreover, the good magnetism performance is conducive to the recovery and utilization of the SFS700 in flue gas. Therefore, SFS can be used for Hg0 removal without any chemical modification after undergoing one-step pyrolysis and this study has guiding significance for the resource utilization and engineering practices.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosy JM, Pasel C, Luckas M, Bittig M, Bathen D (2019) A detailed investigation of adsorption isotherms, enthalpies, and kinetics of mercury adsorption on nonimpregnated activated carbon. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:4208–4221
Carmen SDR, Luís MM, Rui ARB (2013) Treatment of textile dye wastewaters using ferrous sulphate in a chemical coagulation/flocculation process. Environ Technol 34:719–729
Dong J, Xu ZH, Kuznicki SM (2009a) Magnetic multi-functional nano composites for environmental applications. Adv Funct Mater 19:1268–1275
Dong J, Xu ZH, Kuznicki SM (2009b) Mercury removal from flue gases by novel regenerable magnetic nanocomposite sorbents. Environ Sci Technol 43:3266–3271
Duan XL, Yuan CG, Jing TT, Yuan XD (2019) Removal of elemental mercury using large surface area micro-porous concob activated carbon by zinc chloride activation. Fuel 239:830–840
Granite EJ, Pennline HW, Hargis RA (2000) Novel sorbents for mercury removal from flue gas. Ind Eng Chem Res 39:1020–1029
Hamzehlouyan T, Sampara C, Li J, Kumar A, Epling W (2014) Experimental and kinetic study of SO2 oxidation on a Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Appl Catal B 152:108–116
Hung CY, Tsai WT, Chen JW, Lin YQ, Chang YM (2017) Characterization of biochar prepared from biogas digestate. Waste Manage Assoc 66:53–60
Kong LN, Zou SJ, Mei J, Geng Y, Zhao H, Yang SJ (2018) Outstanding resistance of H2S-modified Cu/TiO2 to SO2 for capturing gaseous Hg0 from non-ferrous metal smelting flue gas:performance and reaction mechanism. Environ Sci Technol 52(1000):3–10010
Kushwaha JP, Srivastava VC, Mall ID (2010) Treatment of dairy wastewater by inorganic coagulants: parametric and disposal studies. Water Res 44:5867–5874
Kumar U, Maroufi S, Rajarao R, Mayyas M, Mansuri I, Joshi RK, Sahajwalla V (2017) Cleaner production of iron by using waste macadamia biomass as a carbon resource. J Clean Prod 158:218–224
Lee SS, Lee JY, Keener TC (2009) Bench-scale studies of in-duct mercury capture using cupric chloride-impregnated carbons. Environ Sci Technol 43:2957–2962
Lee Y, Eum PRB, Ryu C, Park YK, Jung JH, Hyun S (2013) Characteristics of biochar produced from slow pyrolysis of Geodae-Uksae 1. Bioresour Technol 130:345–350
Liu W, Vidic RD, Brown TD (2000) Impact of flue gas conditions on mercury uptake by sulfur-impregnated activated carbon. Environ Sci Technol 34:154–159
Liu Y, Kelly DJA, Yang H, Lin CCH, Kuznicki SM, Xu Z (2008) Novel regenerable sorbent for mercury capture from flue gases of coal-fired power plant. Environ Sci Technol 42:6205–6210
Li HL, Zhu L, Wang J, Li LQ, Shi KM (2016) Development of nano-sulfide sorbent for efficient removal of elemental mercury from coal combustion fuel gas. Environ Sci Technol 509:551–9557
Liu T, Man CY, Guo X, Zheng CG (2016) Experimental study on the mechanism of mercury removal with Fe2O3 in the presence of halogens:role of HCl and HBr. Fuel 173:209–216
Liao Y, Chen D, Zou SJ, Xiong SC, Xiao X, Dang H, Chen TH, Yang SJ (2016) A recyclable naturally derived magnetic pyrrhotite for elemental mercury recovery from the flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 50:10562–10569
Liu DJ, Zhou WG, Wu J (2017) Effect of Ce and La on the activity of CuO/ZSM-5 and MnOx/ZSM-5 composites for elemental mercury removal at low temperature. Fu el 194:115–122
Li HH, Wang Y, Wang SK, Wang X, Hu JJ (2017a) Removal of elemental mercury in flue gas at lower temperatures over Mn-Ce based materials prepared by co-precipitation. Fuel 208:576–586
Li HH, Wang SK, Wang X, Tang N, Pan SW, Hu JJ (2017b) Catalytic oxidation of Hg0 in flue gas over Ce modified TiO2 supported Co-Mn catalysts: characterization, the effect of gas composition and co-benefit of NO conversion. Fuel 202:470–482
Li HH, Wang SK, Wang X, Hu JJ (2017c) Activity of CuCl2-modified cobalt catalyst supported on Ti-Ce composite for simultaneous catalytic oxidation of Hg0 and NO in a simulated pre-sco process. Chem Eng J 316:1103–1113
Li N, Wei HQ, Duan YF, Tang HJ, Zhao SL, Hu P, Ren SJ (2018) Experimental study on mercury adsorption and adsorbent regeneration of sulfur-loaded activated carbon. Energy Fuel 32:11023–11029
Liu ZY, Yang W, Xu W, Liu YX (2018) Removal of elemental mercury by bio-chars derived from seaweed impregnated with potassium iodine. Chem Eng J 339:468–478
Liu W, Xu HM, Liao Y, Quan ZW, Li SC, Zhao SJ, Qu Z, Yan NQ (2019) Recyclable CuS sorbent with large mercury adsorption capacity in the presence of SO2 from non-ferrous metal smelting flue gas. Fuel 23:5847–5854
Ma YP, Mu BL, Zhang XJ, Yuan DL, Ma C, Xu HM, Fang SM (2019) Graphene enhanced Mn-Ce binary metal oxides for catalytic oxidation and adsorption of elemental mercury from coal-fired flue gas. Chem Eng J 358:1499–1506
Milicevic S, Boljanac T, Martinovic S, Vlahovic M, Milosevic V, Babic B (2012) Removal of copper from aqueous solutions by low cost adsorbent-Kolubara lignite. Fuel Process Technol 95:1–7
Morris EA, Kirk DW, Jia CQ, Morita K (2012) Roles of sulfuric acid in elemental mercury removal by activated carbon and sulfur-impregnated activated carbon. Environ Sci Technol 46:7905–7912
Ohbi DS, Purewal TS, Shah T, Siores E (2008) Crosslinking reaction mechanism of diisopropyl xanthogen polysulfide accelerator in bromobutyl elastomer for medical device applications. J Appl Polym Sci 107:4013–4020
Pan Z, Tian J, Xu G, Li J, Li G (2011) Characteristics of adsorbents made from biological, chemical and hybrid sludges and their effect on organics removal in wastewater treatment. Water Res 45:819–827
Park J, Lee SS (2018) Adsorption of mercury by activated carbon prepared from dried sewage sludge in simulated flue gas. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 68:1077–1084
Qiao SH, Chen J, Li JF, Qu Z, Liu P, Yan NQ (2009) Adsorption and catalytic oxidation of gaseous elemental mercury in flue gas over MnOx/alumina. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:3317–3122
Rui B, António P, Marco SL, José AP (2010) Combination of long term aerated storage and chemical coagulation/flocculation to winery wastewater treatment. Desalination 263:226–232
Scala F, Clack H (2008) Mercury emissions from coal combustion: modeling and comparison of Hg capture in a fabric filter versus an electrostatic precipitator. J Hazard Mater 152:616–623
Tan ZQ, Sun LS, Xiang J, Zeng HC, Liu ZH, Hu S (2012) Gas-phase elemental mercury removal by novel carbon-based sorbents. Carbon 50:362–371
Wilcox J, Rupp E, Ying SC, Lee DH, Negreira AS, Kerchofer A (2012) Mercury adsorption and oxidation in coal combustion and gasification processes. Int J Coal Geol 90:4–20
Wang XQ, Wang P, Ning P, Ma YX, Wang F, Guo XL, Lan Y (2015) Adsorption of gaseous elemental mercury with activated carbon impregnated with ferric chloride. RSC Adv 5:24899–24907
Xu HM, Yuan Y, Liao Y, Xie JK, Qu Z, Yan NQ (2017) [MoS4]2− cluster bridges in Co-Fe layered double hydroxides for mercury uptake from S-Hg mixed flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 51:10109–10116
Xu W, Hussain A, Liu YX (2018) A review on modification methods of adsorbents for elemental mercury from flue gas. Chem Eng J 346:692–711
Xu Y, Luo GQ, He SW, Deng FF, Pang QC, Xu YQ, Yao H (2019a) Efficient removal of elemental mercury by magnetic chlorinated biochars derived from co-pyrolysis of Fe(NO3)3−laden wood and polyvinyl chloride waste. Fuel 239:982–990
Xu Y, Luo GQ, Pang QC, He SW, Deng FF, Xu YQ, Yao H (2019b) Adsorption and catalytic oxidation elemental mercury over regenerable magnetic Fe-Ce mixed oxides modified by non-thermal plasma treatment. Chem Eng J 358:1454–1463
Yang S, Guo Y, Yan N, Wu D, He H, Xie J, Qu Z, Yang C, Jia J (2010) A novel muti-functional magnetic Fe-Ti-V spinel catalyst for elemental mercury capture and callback from flue gas. Chem Commun 46:8377–8379
Yani S, Zhang DK (2010) An experimental study of sulphate transformation during pyrolysis of an Australian lignite. Fuel Process Technol 91:313–321
Yang SJ, Yan NQ, Guo YF, Wu DQ, He HP, Qu Z, Li JF, Jia PZ (2011a) Gaseous elemental mercury capture from flue gas using magnetic nanosized (Fe3-xMnx)1-δO4. Environ Sci Technol 45:1540–1546
Yang SJ, Guo YF, Yan NQ, Wu DQ, He HP, Xie JK, Qu Z, Jia JP (2011b) Remarkable effect of the incorporation of titanium on the catalytic activity and SO2 poisoning resistance of magnetic Mn-Fe spinel for elemental mercury capture. Appl Catal B Environ 101:698–708
Yang SJ, Guo YF, Yan NQ, Wu DQ, He HP, Qu Z, Jia JP (2011c) Elemental mercury capture from flue gas by magnetic Mn-Fe spinel: effect of chemical heterogeneity. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:9650–9656
Yang JP, Zhao YC, Zhang JY, Zheng CG (2014) Regenerable cobalt oxide loaded magnetosphere catalyst from fly ash for mercury removal in coal combustion flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 48:14837–14843
Yang X, Xu GR, Yu HR, Zhang Z (2016) Preparation of ferric-activated sludge-based adsorbent from biological sludge for tetracycline removal. Bioresour Technol 211:566–573
Yu J, Sun LS, Berrueco C, Fidalgo B, Paterson N (2018) Influence of temperature and particle size on structural characteristics of chars from Beechwood pyrolysis. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 130:127–134
Yang S, Liu C, Liu Z, Yang B, Xiang K, Zhang C (2018) High catalytic activity and SO2-poisoning resistance of Pd/CuCl2/γ-Al2O3 catalyst for elemental mercury oxidation. Catal Commun 105:1–5
Zhang AC, Zheng WW, Song J, Hu S, Liu ZC, Xiang J (2014) Cobalt manganese oxides modified titania catalysts for oxidation of elemental mercury at low flue gas temperature. Chem Eng J 236:29–38
Zhou Q, Duan YF, Hong YG, Zhu C, She M, Zhang J (2015) Experimental and kinetic studies of gas-phase mercury adsorption by raw and bromine modified activated carbon. Fuel Process Technol 134:325–332
Zhao B, Yi HH, Tang XL, Li Q, Liu DD, Gao FY (2016) Copper modified activated coke for mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas. Chem Eng J 286:585–593
Zou S, Liao Y, Huang SN, Geng Y, Yang S (2017) H2S-modified Fe-Ti spinel:a recyclable magnetic sorbent for recovering gaseous elemental mercury from flue gas as a co-benefit of wet electrostatic precipitators. Environ Sci Technol 51:3426–3434
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Test Center of Wuhan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 582 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, H., He, Z. et al. Removal of elemental mercury from flue gas using the magnetic Fe-containing carbon prepared from the sludge flocculated with ferrous sulfate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 30254–30264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08133-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08133-4