Abstract
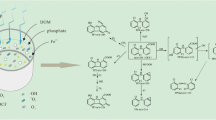
To reveal the characteristics of tetracycline (TC) photocatalytic degradation under Cu(II) coexistence, effects of Cu(II) on TC photocatalytic degradation by ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) as a function of pH, humic acid (HA), and initial Cu(II) concentration were investigated. Interaction of TC with Cu(II) in the treatment process was analyzed by circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, while TC degradation pathway was investigated by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sixty-five percent and ninety-one percent TC degradation within 60 min in the absence and presence of Cu(II), respectively, was reported. Both adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of TC under Cu(II) coexistence increased with increasing pH from 3 to 6, while decreased with further increase in pH. HA inhibited the degradation of TC by ZnO NPs both in the presence as well absence of Cu(II), while TC degradation decreased from 91 to 73% and from 73 to 37% in the presence and absence of Cu(II), respectively. TC degradation by ZnO NPs first increased then decreased with increasing Cu(II). Maximum TC degradation (about 94%) was obtained in the optimum concentration range of Cu(II) (0.05–0.15 mmol/L). In addition, there was a lag effect between TC adsorption and degradation on ZnO NPs. TC degradation was improved via Cu(II)–TC surface complexation and followed N-demethylation and hydroxylation routes. This study could be of potential importance in extrapolating the transformation of TC or other antibiotics under the coexistence of heavy metals in water.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghabeygi S, Hashemi L, Morsali A (2016) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nano-rods via thermal decomposition of zinc(II) coordination polymers and their photocatalytic properties. J Inorg Organomet Polym 26:495–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0312-4
Babel S, Sekartaji PA, Sudrajat H (2017) TiO2 as an effective nanocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of humic acid in water environment. J Water Supply: Res Technol 66:25–35. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2016.102
Bahemmat M, Farahbakhsh M, Kianirad M (2016) Humic substances-enhanced electroremediation of heavy metals contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 312:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.038
Bai H, Wei S, Jiang Z, He M, Ye B, Liu G (2019) Pb(II) bioavailability to algae (Chlorella pyrenoidosa) in relation to its complexation with humic acids of different molecular weight. Ecotoxicol Enviro Saf 167:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.114
Bian SW, Mudunkotuwa I, Rupasinghe T, Grassian V (2011) Aggregation and dissolution of 4 nm ZnO nanoparticles in aqueous environments: influence of pH, ionic strength, size, and adsorption of humic acid. Langmuir 60:6059–6068. https://doi.org/10.1021/la200570na
Cao M, Wang P, Ao Y, Wang C, Hou J, Qian J (2016) Visible light activated photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by a magnetically separable composite photocatalyst: Graphene oxide/magnetite/cerium-doped titania. J Colloid Interface Sci 467:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.01.005
Chen F, Yang Q, Li X, Zeng G, Wang D, Niu C (2017) Hierarchical assembly of graphene-bridged Ag3PO4/Ag/BiVO4 (040) Z-scheme photocatalyst: an efficient, sustainable and heterogeneous catalyst with enhanced visible-light photoactivity towards tetracycline degradation under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B-Environ 200:330–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.021
Chen Q, Wu S, Xin Y (2016) Synthesis of au–CuS–TiO2 nanobelts photocatalyst for efficient photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic oxytetracycline. Chem Eng J 302:377–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.076
Cuprys A, Pulicharla R, Lecka J, Brar SK, Drogui P, Surampalli RY (2018) Ciprofloxacin-metal complexes–stability and toxicity tests in the presence of humic substances. Chemosphere 202:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.117
Deng F, Zhao L, Luo X, Luo S, Dionysiou DD (2018a) Highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic performance of Ag/AgIn5S8 for degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride and treatment of real pharmaceutical industry wastewater. Chem Eng J 333:423–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.022
Deng Y, Tang L, Zeng G, Wang J, Zhou Y, Wang J (2018b) Facile fabrication of mediator-free Z-scheme photocatalyst of phosphorous-doped ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets and bismuth vanadate composites with enhanced tetracycline degradation under visible light. J Colloid Interface Sci 509:219–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.09.016
Doong R, Tsai C (2015) Synergistic effect of Cu adsorption on the enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A by TiO2/titanate nanotubes composites. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 57:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.05.013
Etesami H (2018) Bacterial mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress and decreased accumulation of metals in plant tissues: mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:175–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.032
Fang J, Wang W, Zhu C, Fang L, Jin J, Ni Y, Lu C (2018) CdS/Pt photocatalytic activity boosted by high-energetic photons based on efficient triplet–triplet annihilation up conversion. Appl Catal B environ 217:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.05.069
Gan Y, Zhang M, Xiong J, Zhu J, Li W, Zhang C (2019) Impact of Cu particles on adsorption and photocatalytic capability of mesoporous Cu@TiO2 hybrid towards ciprofloxacin antibiotic removal. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 96:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.11.015
Gu C, Karthikeyan K, Sibley SD, Pedersen JA (2007) Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid. Chemosphere 6:1494–1501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.028
Guo T, Lou C, Zhai W, Tang X, Hashmi MZ, Murtaza R, Li Y, Liu X, Xu J (2018) Increased occurrence of heavy metals, antibiotics and resistance genes in surface soil after long-term application of manure. Sci Total Environ 635:995–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.194
He F, Lu Z, Song M, Tang H, Huo P, Fan W, Dong H, Wu X, Han S (2019) Selective reduction of Cu2+ with simultaneous degradation of tetracycline by the dual channels ion imprinted POPD-CoFe2O4 heterojunction photocatalyst. Chem Eng J 360:750–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.034
Hong Y, Li C, Zhang G, Meng Y, Yin B, Zhao Y (2016) Efficient and stable Nb2O5 modified g-C3N4 photocatalyst for removal of antibiotic pollutant. Chem Eng J 299:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.092
Hu X, Jia L, Cheng J, Sun Z (2019) Magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon materials for adsorption of minocycline from aqueous solution: preparation, characterization and adsorption mechanism. J Hazard Mater 362:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.003
Huang B, Liu Y, Li B, Liu S, Zeng G, Zeng Z (2017) Effect of Cu (II) ions on the enhancement of tetracycline adsorption by Fe3O4@SiO2-chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Carbohyd Polym 157:576–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.025
Hsu LC, Liu YT, Syu CH, Huang MH, Tzou YM, Teah HY (2018) Adsorption of tetracycline on Fe (hydr) oxides: effects of pH and metal cation (Cu2+, Zn2+ and Al3+) addition in various molar ratios. Roy Soc Open Sci 5:171–941. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.171941
Ji Y, Shi Y, Dong W, Wen X, Jiang M, Lu J (2016) Thermo-activated persulfate oxidation system for tetracycline antibiotics degradation in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 298:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.028
Jia S, Yang Z, Yang W, Zhang T, Zhang S, Yang X (2016a) Removal of Cu(II) and tetracycline using an aromatic rings-functionalized chitosan-based flocculant: enhanced interaction between the flocculant and the antibiotic. Chem Eng J 283:495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.003
Jia Z, Mao J, Lu HB, Habibi D, Zhang WC, Zhang LC (2016b) Photocatalytic degradation and absorption kinetics of cibacron brilliant yellow 3G-P by nanosized ZnO catalyst under simulated solar light. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 60:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.10.012
Jiang C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Feng H, Shehzad MA, Wang Y (2018) Complexation electrodialysis as a general method to simultaneously treat wastewaters with metal and organic matter. Chem Eng J 348:952–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.022
Jiang CJ, Aiken G, Hsu-Kim H (2015) Effects of natural organic matter properties on the dissolution kinetics of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 348:11476–11484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02406
Jiang D, Wang T, Xu Q, Li D, Meng S, Chen M (2017) Perovskite oxide ultrathin nanosheets/g-C3N4 2D-2D heterojunction photocatalysts with significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity towards the photodegradation of tetracycline. Appl Catal B-Environ 201:617–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.001
Khalaj M, Kamali M, Khodaparast Z, Jahanshahi A (2018) Copper-based nanomaterials for environmental decontamination–an overview on technical and toxicological aspects. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:813–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.060
Khan MA, Musarrat J (2003) Interactions of tetracycline and its derivatives with DNA in vitro in presence of metal ions. Int J Biol Macromol 33:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-8130(03)00066-7
Li H, Li B, Zhang Z, Tian Y, Ye J, Lv X (2018) Factors influencing the removal of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes by the electrokinetic treatment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 160:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.028
Li M, Liu Y, Liu S, Shu D, Zeng J, Hu X (2017a) Cu(II)-influenced adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by magnetic graphene oxide/nitrilotriacetic acid nanocomposite: competition and enhancement mechanisms. Chem Eng J 319: 219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.016
Li S, Hu JY (2016) Photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline: effect of humic acid on degradation kinetics and mechanisms. J Hazard mater 318:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.100
Li Y, Wang S, Zhang Y, Han R, Wei W (2017b) Enhanced tetracycline adsorption onto hydroxyapatite by Fe(III) incorporation. J Mol Liq 247:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.09.110
Liu C, Xu J, Lee DJ, Yu D, Liu L (2016a) Denitrifying sulfide removal process on high-tetracycline wastewater. Bioresour Technol 205:254–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.026
Liu J, Hu H, Xu Y, Song Y, Lian J, Zhao Y, Wang L, Huang L (2017) Graphene quantum dots modified mesoporous graphite carbon nitride with significant enhancement of photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B environ 207:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.071
Liu J, Lu W, Zhong Q, Wu H, Li Y, Li L (2018a) Effect of pH on the microstructure of β-Ga2O3 and its enhanced photocatalytic activity for antibiotic degradation. J Colloid Interf Sci 519:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.02.070
Liu K, Qin YL, Muhammad Y, Zhu Y, Tang R, Zhang HB (2019) Effect of Fe3O4 content and microwave reaction time on the properties of Fe3O4/ZnO magnetic nanoparticles. J Alloy Compd 781:790–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.085
Liu M, Hou L, Xi B, Li Q, Hu X, Yu S (2016b) Magnetically separable Ag/AgCl-zero valent iron particles modified zeolite X heterogeneous photocatalysts for tetracycline degradation under visible light. Chem Eng J 302:475–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.083
Liu X, Zeng X, Xu S, Chen C, Zhang Z (2016c) Metal oxides as dual-functional adsorbents/catalysts for Cu2+/Cr(VI) adsorption and methyl orange oxidation catalysis. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 60:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.10.043
Liu Y, Kong J, Yuan J, Zhao W, Zhu X, Sun C (2018b) Enhanced photocatalytic activity over flower-like sphere Ag/Ag2CO3/BiVO4 plasmonic heterojunction photocatalyst for tetracycline degradation. Chem Eng J 331:242–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.114
Lou J, Xu X, Gao Y, Zheng D, Wang J, Li Z (2016) Preparation of magnetic activated carbon from waste rice husk for the determination of tetracycline antibiotics in water samples. RSC Adv 6:112166–112174. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA24397E
Lu Z, Yu Z, Dong J, Song M, Liu Y, Liu X (2018) Facile microwave synthesis of a Z-scheme imprinted ZnFe2O4/Ag/PEDOT with the specific recognition ability towards improving photocatalytic activity and selectivity for tetracycline. Chem Eng J 337:228–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.115
Ma Y, Zhou Q, Zhou S, Wang W, Jin J, Xie J (2014) A bifunctional adsorbent with high surface area and cation exchange property for synergistic removal of tetracycline and Cu2+. Chem Eng J 258:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.096
Mirzaei A, Chen Z, Haghighat F, Yerushalmi L (2019) Magnetic fluorinated mesoporous g-C3N4 for photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin: transformation mechanism and toxicity assessment. Appl Catal B-Environ 242:337–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.009
Nasseh N, Taghavi L, Barikbin B, Nasseri MA (2018) Synthesis and characterizations of a novel FeNi3/SiO2/CuS magnetic nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in simulated wastewater. J Clean Prod 179:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.052
Olivera S, Hu C, Nagananda G, Reddy N, Venkatesh K, Muralidhara H (2018) The adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) ions and antibacterial activity studies on hydrothermally synthesized iron oxide and zinc oxide nanocomposite. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 93:342–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.07.042
Pang Y, Kong L, Lei H, Chen D, Yuvaraja G (2018) Combined microwave-induced and photocatalytic oxidation using zinc ferrite catalyst for efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 93:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.08.008
Parolo ME, Avena MJ, Savini MC, Baschini MT, Nicotra V (2013) Adsorption and circular dichroism of tetracycline on sodium and calcium-montmorillonites. Colloid Surf A-Physicochem Eng Asp 417:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.10.060
Patrinoiu G, Ene KD, Munteanu C, Chifiriuc MC, Carp O (2019) Multifunctional ZnO materials prepared by a versatile green carbohydrate-assisted combustion method for environmental remediation applications. Ceram Int 45:2295–2302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.144
Peng H, Xie W, Li D, Wu M, Zhang Y, Xu H (2019) Copper-resistant mechanism of Ochrobactrum MT180101 and its application in membrane bioreactor for treating electroplating wastewater. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.066
Qi N, Wang P, Wang C, Ao Y (2018) Effect of a typical antibiotic (tetracycline) on the aggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles in an aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 341:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.046
Qin Q, Wu X, Chen L, Jiang Z, Xu Y (2018) Simultaneous removal of tetracycline and Cu(II) by adsorption and coadsorption using oxidized activated carbon. RSC Adv 8:1744–1752. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA12402C
Song C, Guo BB, Sun XF, Wang SG, Li YT (2018) Enrichment and degradation of tetracycline using three-dimensional graphene/MnO2 composites. Chem Eng J 358:1139–1146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.119
Sudrajat H, Hartuti S (2018) Easily separable N-doped ZnO microspheres with high photocatalytic activity under visible light. Mater Res Bull 102:319–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.02.048
Sun Y, Yue Q, Gao B, Gao Y, Xu X, Li Q (2014) Adsorption and cosorption of ciprofloxacin and Ni(II) on activated carbon-mechanism study. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 45:681–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.05.013
Tang L, Feng C, Deng Y, Zeng G, Wang J, Liu Y (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ternary Ag/g-C3N4/NaTaO3 photocatalysts under wide spectrum light radiation: the high potential band protection mechanism. Appl Catal B-Environ 230:102–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.02.031
Wang D, Li J, Xu Z, Zhu Y, Chen G (2019) Preparation of novel flower-like BiVO4/Bi2Ti2O7/Fe3O4 for simultaneous removal of tetracycline and Cu2+: adsorption and photocatalytic mechanisms. J Colloid Interf Sci 533:344–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.089
Wang J, Zhang G, Li J, Zhang J, Wang K (2018) Novel three-dimensional flowerlike BiOBr/Bi2SiO5 p−n heterostructured nanocomposite for degradation of tetracycline: enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity and mechanism. Acs Sustain Chem & Eng 6:14221–14229. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02869
Wang R, Zhang J, Liu J, Yu D, Zhong H, Wang Y, Chen M, Tong J, Wei Y (2018a) Effects of chlortetracycline, Cu and their combination on the performance and microbial community dynamics in swine manure anaerobic digestion. J Environ Sci 67:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.08.023
Wang T, Quan W, Jiang D, Chen L, Li D, Meng S (2016) Synthesis of redox-mediator-free direct Z-scheme AgI/WO3 nanocomposite photocatalysts for the degradation of tetracycline with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem Eng J 300:280–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.128
Wang X, Lu M, Ma J, Ning P, Che L (2018b) Synthesis of K-doped g-C3N4/carbon microsphere@ graphene composite with high surface area for enhanced adsorption and visible photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 91:609–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.06.019
Worathitanon C, Jangyubol K, Ruengrung P, Donphai W, Klysubun W, Chanlek N (2019) High performance visible-light responsive Chl-cu/ZnO catalysts for photodegradation of rhodamine B. Appl Catal B-Environ 241:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.048
Wu G, Ma J, Li S, Guan J, Jiang B, Wang L (2018) Magnetic copper-based metal organic framework as an effective and recyclable adsorbent for removal of two fluoroquinolone antibiotics from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interf Sci 528:360–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.05.105
Xiao T, Tang Z, Yang Y, Tang L, Zhou Y, Zou Z (2018) In situ construction of hierarchical WO3/g-C3N4 composite hollow microspheres as a Z-scheme photocatalyst for the degradation of antibiotics. Appl Catal B-Environ 220:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.070
Yang L, Zhong W, Cui J, Wei Z, Wei W (2016) Enhanced removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution by poorly crystalline hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J Dispers Sci Technol 37:956–958. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2015.1077140
Ye Z, Li J, Zhou M, Wang H, Ma Y, Huo P (2016) Well-dispersed nebula-like ZnO/CeO2@ HNTs heterostructure for efficient photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline. Chem Eng J 304:917–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.014
Yu L, Cao W, Wu S, Yang C, Cheng J (2018) Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by MOF/graphite oxide pellets: preparation, characteristic, adsorption performance and mechanism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.110
Yuan X, Wu Z, Zeng G, Jiang L, Zhang J, Xiong T (2018) Synthesis and boosting visible light photoactivity of Ag@ AgI/CdWO4 towards refractory organic pollutants degradation based on interfacial charge transfer. Appl Surf Sci 454:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.163
Zhang H, Song Z, Wang D, Tong Z, Qin Y (2017) A facile synthetic method of ZnO nanoparticles and its role in photocatalytic degradation of refractory organic matters. Desalin Water Treat 90:189–195. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.21233
Zhang J, Gao Y, Jia X, Wang J, Chen Z, Xu Y (2018a) Oxygen vacancy-rich mesoporous ZrO2 with remarkably enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 182:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2018.03.023
Zhang J, Lu M, Wan J, Sun Y, Lan H, Deng X (2018b) Effects of pH, dissolved humic acid and Cu2+ on the adsorption of norfloxacin on montmorillonite-biochar composite derived from wheat straw. Biochem Eng J 130:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2017.11.018
Zheng J, Zhang L (2018) Rational design and fabrication of multifunctional catalyzer CO2SnO4-SnO2/GC for catalysis applications: photocatalytic degradation/catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. Appl Catal B-Environ 231:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.02.061
Zhu Z, Zhang M, Wang W, Zhou Q, Liu F (2018) Efficient and synergistic removal of tetracycline and cu(II) using novel magnetic multi-amine resins. Sci Rep 8:47–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23205-9
Funding
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21576055) and Petrochemical Resources Processing and Process Reinforcement Technology Key Laboratory Project of Guangxi Province (Grant No. 2018Z004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1593 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Liu, K., Muhammad, Y. et al. Effects of divalent copper on tetracycline degradation and the proposed transformation pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 5155–5167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07062-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07062-1