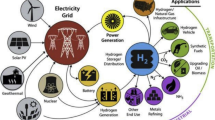
Abstract
Hydrogen can play a crucial role in increasing energy security and reducing greenhouse gases in Pakistan. Hydrogen can only be a clean and sustainable fuel if it is generated from renewable energy sources (RES). Thus, it is important to evaluate viability of RES for hydrogen production. This study developed a two-stage fuzzy MCDM (Multi-criteria decision-making) approach to select the most efficient RES. In the first stage, fuzzy analytical hierarchy process (AHP) obtained the relative weights of four criteria for the selection of best RES. These criteria included commercial potential, environmental impacts, economic benefits, and social acceptance. In the second stage, data envelopment analysis (DEA) measured the relative efficiency of RES using weights of criteria as outputs, and the cost of RES-based electricity generation as input. The results indicated that wind and solar are the most efficient sources of hydrogen production in Pakistan. Municipal solid waste (MSW) and biomass can also be considered a feedstock for the hydrogen economy. Geothermal reported to be the less efficient source and thus is not recommended at present. Sensitivity analysis confirmed the robustness of results obtained using the developed framework.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar C, Beskese A, Temur GT (2018) Sustainability analysis of different hydrogen production options using hesitant fuzzy AHP. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:18059–18076
Afgan NH, Veziroglu A, Carvalho MG (2007) Multi-criteria evaluation of hydrogen system options. Int J Hydrog Energy 32:3183–3193
Ahmad N, Hussain T, Awan AN, Sattar A, Arslan C, Tusief MQ, Mariam Z (2017) Efficient and eco-friendly management of biodegradable municipal solid waste (MSW) using naturally aerated windrow composting technique in district Lahore Pakistan. Earth Sci Pak 1:1–4
Ball M, Weeda M (2015) The hydrogen economy–vision or reality? Int J Hydrog Energy 40:7903–7919
Banaeian N, Mobli H, Fahimnia B, Nielsen IE, Omid M (2018) Green supplier selection using fuzzy group decision making methods: a case study from the agri-food industry. Comput Oper Res 89:337–347
Baykara SZ (2018) Hydrogen: a brief overview on its sources, production and environmental impact. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:10605–10614
Bieber N, Ker JH, Wang X, Triantafyllidis C, van Dam KH, Koppelaar RHEM, Shah N (2018) Sustainable planning of the energy-water-food nexus using decision making tools. Energy Policy 113:584–607
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res 2:429–444
Cook WD, Ramón N, Ruiz JL, Sirvent I, Zhu J (2019) DEA-based benchmarking for performance evaluation in pay-for-performance incentive plans. Omega 84:45–54
Duffie JA, Beckman WA, Worek WM (2013) Solar engineering of thermal processes. Wiley Online Library, Hoboken
Ghaffar MA (1995) The energy supply situation in the rural sector of Pakistan and the potential of renewable energy technologies. Renew Energy 6:941–976
Gondal IA, Masood SA, Khan R (2018) Green hydrogen production potential for developing a hydrogen economy in Pakistan. Int J Hydrog Energy 43:6011–6039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.01.113
Hosseini SE, Wahid MA (2016) Hydrogen production from renewable and sustainable energy resources: promising green energy carrier for clean development. Renew Sust Energ Rev 57:850–866
Ivy J (2004) Summary of electrolytic hydrogen production: milestone completion report. National Renewable Energy Lab, Golden
Kamran M (2018) Current status and future success of renewable energy in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 82:609–617
Krmac E, Djordjević B (2019) A new DEA model for evaluation of supply chains: a case of selection and evaluation of environmental efficiency of suppliers. Symmetry (Basel) 11:565
LaPlante AE, Paradi JC (2015) Evaluation of bank branch growth potential using data envelopment analysis. Omega 52:33–41
Melaina M, Penev M, Heimiller D (2013) Resource assessment for hydrogen production: hydrogen production potential from fossil and renewable energy resources. National Renewable Energy Lab.(NREL), Golden
Mohsin M, Zhou P, Iqbal N, Shah SAA (2018) Assessing oil supply security of South Asia. Energy 155:438–447
Nikolaidis P, Poullikkas A (2017) A comparative overview of hydrogen production processes. Renew Sust Energ Rev 67:597–611
Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (2016) Pakistan livestock census 2006. Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, Islamabad
Pilavachi PA, Chatzipanagi AI, Spyropoulou AI (2009) Evaluation of hydrogen production methods using the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:5294–5303
Pode R (2010) Addressing India’s energy security and options for decreasing energy dependency. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:3014–3022
Ren J, Fedele A, Mason M, Manzardo A, Scipioni A (2013) Fuzzy multi-actor multi-criteria decision making for sustainability assessment of biomass-based technologies for hydrogen production. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:9111–9120
Rufuss DDW, Kumar VR, Suganthi L et al (2018) Techno-economic analysis of solar stills using integrated fuzzy analytical hierarchy process and data envelopment analysis. Sol Energy 159:820–833
Saaty TL (2014) Analytic heirarchy process. Wiley StatsRef Stat Ref online
Shah SAA, Valasai GD, Memon AA et al (2018) Techno-economic analysis of solar PV electricity supply to rural areas of Balochistan, Pakistan. Energies 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11071777
Shah SAA, Solangi YA, Ikram M (2019a) Analysis of barriers to the adoption of cleaner energy technologies in Pakistan using modified Delphi and fuzzy analytical hierarchy process. J Clean Prod 235:1037–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.020
Shah SAA, Zhou P, Walasai GD, Mohsin M (2019b) Energy security and environmental sustainability index of South Asian countries: a composite index approach. Ecol Indic 106:105507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105507
Solangi YA, Tan Q, Mirjat NH, Valasai GD, Khan MWA, Ikram M (2019) An integrated Delphi-AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS approach toward ranking and selection of renewable energy resources in Pakistan. Processes 7:118
Stökler S, Schillings C, Kraas B (2016) Solar resource assessment study for Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:1184–1188
Tahir ZR, Asim M (2018) Surface measured solar radiation data and solar energy resource assessment of Pakistan: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 81:2839–2861
Tajbakhsh A, Hassini E (2015) A data envelopment analysis approach to evaluate sustainability in supply chain networks. J Clean Prod 105:74–85
Wang Y, Shah SAA, Zhou P (2018) City-level environmental performance in China. Energy Ecol Environ 3:149–161
Wang L-W, Le K-D, Nguyen T-D (2019) Assessment of the energy efficiency improvement of twenty-five countries: a DEA approach. Energies 12:1535
Xu L, Wang Y, Shah SAA et al (2019a) Economic viability and environmental efficiency analysis of hydrogen production processes for the decarbonization of energy systems. Processes 7:494
Xu L, Wang Y, Solangi YA, Zameer H, Shah S (2019b) Off-grid solar PV power generation system in Sindh, Pakistan: a techno-economic feasibility analysis. Processes 7:308
Yoshida T, Kojima K (2015) Toyota MIRAI fuel cell vehicle and progress toward a future hydrogen society. Electrochem Soc Interface 24:45–49
Yu D (2014) Hydrogen production technologies evaluation based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multiattribute decision making method. J Appl Math 2014:1–10
Zadeh LA (1978) Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1:3–28
Zaigham NA, Nayyar ZA (2010) Renewable hot dry rock geothermal energy source and its potential in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:1124–1129
Zhou P, Ang BW, Poh K-L (2008a) A survey of data envelopment analysis in energy and environmental studies. Eur J Oper Res 189:1–18
Zhou P, Ang BW, Poh KL (2008b) Measuring environmental performance under different environmental DEA technologies. Energy Econ 30:1–14
Zuberi MJS, Ali SF (2015) Greenhouse effect reduction by recovering energy from waste landfills in Pakistan. Renew Sust Energ Rev 44:117–131
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by (1) the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 71873064), Research on OFDI driving low-carbon upgrading of China’s equipment manufacturing global value chain: theoretical mechanism, implementation path and performance evaluation, (2) OFDI (18YJA790085) General Projects of Humanities and Social Sciences of the Ministry of Education (Planning Projects) (Grant No. 18YJA790085), Performance evaluation of OFDI driving low-carbon upgrading of China’s equipment manufacturing global value chain, and (3) (2017ZDIXM084) Key Project of Philosophy and Social Science Research in Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (Grant No. 2017ZDIXM084), Research on the development path and countermeasures of equipment manufacturing industry in Jiangsu Province under the “One Belt One Road” initiative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Muhammad Shahbaz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Shah, S.A.A., Zameer, H. et al. Evaluating renewable energy sources for implementing the hydrogen economy in Pakistan: a two-stage fuzzy MCDM approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 33202–33215 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06431-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06431-0