Abstract
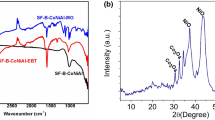
The present study aims at evaluating the batch scale potential of cotton shell powder (CSP), Moringa oleifera leaves (ML), and magnetite-assisted composites of Moringa oleifera leaves (MLMC) and cotton shell powder (CSPMC) for the removal of brilliant green dye (BG) from synthetic wastewater. This is the first attempt to combine biosorbents with nanoparticles (NPs) for the removal of BG. The surface properties of ML, CSP, and their composites were characterized with Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX). The impact of dosage of the adsorbents (1–4 g/L), initial concentrations of BG (20–320 mg/L), pH (6–12), and contact time (15–180 min) on BG removal was evaluated. The BG removal was in order of CSPMC > MLMC > CSP > ML (98.8–86.6% > 98.2–82.0% > 92.3–70.7% > 89.0–57.4%) at optimum dosage (2 g/L) and pH (8). Moreover, maximum adsorption (252.17 mg/g) was obtained with CSPMC. The experimental results showed better fit with Freundlich adsorption isotherm model and kinetic data revealed that sorption followed pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The values of Gibbs free energy and mean free energy of sorption showed that physical adsorption was involved in the removal of BG. FTIR results confirmed that –O-H, –C-OH, =C-H, –C-H, =–CH3, HC ≡ CH, C=C, –C=O, –C-N, and –C-O-C– groups were involved in the removal of BG. The results revealed that application of low-cost biosorbents combined with NPs is very effective and promising for the removal of textile dyes from wastewater.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas M, Trari M (2015) Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study on the removal of Congo Red from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto apricot stone. Process Saf Environ Prot 98:424–436
Abdel-Aziz SM, Prasad R, Hamed AA, Abdelraof M (2018) Fungal nanoparticles: a novel tool for a green biotechnology?, Fungal Nanobionics: Principles and Applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 61–87
Acuner E, Dilek F (2004) Treatment of tectilon yellow 2G by Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochem 39:623–631
Adeli M, Yamini Y, Faraji M (2017) Removal of copper, nickel and zinc by sodium dodecyl sulphate coated magnetite nanoparticles from water and wastewater samples. Arab J Chem 10:S514–S521
Ahmad I, Akhtar MJ, Jadoon IBK, Imran M, Ali S (2017) Equilibrium modeling of cadmium biosorption from aqueous solution by compost. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5277–5284
Ahmad M, Usman AR, Rafique MI, Al-Wabel MI (2019) Engineered biochar composites with zeolite, silica, and nano-zerovalent iron for the efficient scavenging of chlortetracycline from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–17
Akar T, Sayin F, Turkyilmaz S, Akar ST (2017) The feasibility of Thamnidium elegans cells for color removal from real wastewater. Process Saf Environ Prot 105:316–325
Al-Ghouti M, Khraisheh M, Allen S, Ahmad M (2003) The removal of dyes from textile wastewater: a study of the physical characteristics and adsorption mechanisms of diatomaceous earth. J Environ Manag 69:229–238
Al-Sabagh A, Moustafa Y, Hamdy A, Killa H, Ghanem R, Morsi R (2018) Preparation and characterization of sulfonated polystyrene/magnetite nanocomposites for organic dye adsorption. Egypt J Pet 27:403–413
Ali RM, Hamad HA, Hussein MM, Malash GF (2016) Potential of using green adsorbent of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions: adsorption kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic, mechanism and economic analysis. Ecol Eng 91:317–332
Aliabadi HM, Saberikhah E, Pirbazari AE, Khakpour R, Alipour H (2018) Triethoxysilylpropylamine modified alkali treated wheat straw: an efficient adsorbent for methyl orange adsorption. Cellul Chem Technol 52:129–140
Amina SX, Wu K, Si Y, Yousaf B (2018) Synergistic effects and mechanisms of hydroxyl radical-mediated oxidative degradation of sulfamethoxazole by Fe (II)-EDTA catalyzed calcium peroxide: implications for remediation of antibiotic-contaminated water. Chem Eng J 353:80–91
Anastopoulos I, Kyzas GZ (2014) Agricultural peels for dye adsorption: a review of recent literature. J Mol Liq 200:381–389
Anirudhan T, Ramachandran M (2015) Adsorptive removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by surfactant modified bentonite clay (organoclay): kinetic and competitive adsorption isotherm. Process Saf Environ Prot 95:215–225
Arshad A, Zakaria M, Junyang X (2016) Energy prices and economic growth in Pakistan: a macro-econometric analysis. Renew Sust Energ Rev 55:25–33
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Ghezelbash GR, Dil EA, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2016) Biosorption of malachite green by novel biosorbent Yarrowia lipolytica isf7: application of response surface methodology. J Mol Liq 214:249–258
Asgher M, Kausar S, Bhatti HN, Shah SAH, Ali M (2008) Optimization of medium for decolorization of solar golden yellow R direct textile dye by Schizophyllum commune IBL-06. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 61:189–193
Babarinde A, Onyiaocha GO (2016) Equilibrium sorption of divalent metal ions onto groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) shell: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. Chem Int 2
Bagtash M, Zolgharnein J (2018) Removal of brilliant green and malachite green from aqueous solution by a viable magnetic polymeric nanocomposite: simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of 2 dyes by PLS using original and first derivative spectra. J Chemom 32:e3014
Benelli G (2018) Plant-borne compounds and nanoparticles: challenges for medicine, parasitology and entomology. Springer
Benguella B, Benaissa H (2002) Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by chitin: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Res 36:2463–2474
Carvalho M, Henriques F, Ferreira L, Godinho M, Cruz M (2013) Iron oxide nanoparticles: the influence of synthesis method and size on composition and magnetic properties. J Solid State Chem 201:144–152
Daneshvar N, Ayazloo M, Khataee A, Pourhassan M (2007) Biological decolorization of dye solution containing malachite green by microalgae Cosmarium sp. Bioresour Technol 98:1176–1182
El-Chaghaby GA, Ramis ES, Ahmad AF (2018) Rice straw and rice straw ash for the removal of brilliant green dye from wastewater. Asian Journal of Applied Chemistry Research 1–9
Faraji M, Yamini Y, Rezaee M (2010) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, functionalization, characterization, and applications. J Iran Chem Soc 7:1–37
Geetha P, Latha M, Koshy M (2015) Biosorption of malachite green dye from aqueous solution by calcium alginate nanoparticles: equilibrium study. J Mol Liq 212:723–730
Gemeay AH, Aboelfetoh EF, El-Sharkawy RG (2018) Immobilization of green synthesized silver nanoparticles onto amino-functionalized silica and their application for indigo carmine dye removal. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:16
Gole VL, Gogate PR (2014) Degradation of brilliant green dye using combined treatment strategies based on different irradiations. Sep Purif Technol 133:212–220
Guiza S (2017) Biosorption of heavy metal from aqueous solution using cellulosic waste orange peel. Ecol Eng 99:134–140
Gunasundari E, Kumar S (2017) Adsorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamic analysis of Cu (II) ions onto the dried algal biomass (Spirulina platensis). J Ind Eng Chem 56:129–144
Gupta VK, Mohan D, Sharma S, Sharma M (2000) Removal of basic dyes (rhodamine B and methylene blue) from aqueous solutions using bagasse fly ash. Sep Sci Technol 35:2097–2113
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, ur Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SA, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Imran M, Suddique M, Shah G, Ahmad I, Murtaza B, Shah N, Mubeen M, Ahmad S, Zakir A, Schotting R (2018) Kinetic and equilibrium studies for cadmium biosorption from contaminated water using Cassia fistula biomass. Int J Environ Sci Technol:1–10
Jain SN, Gogate PR (2018) Efficient removal of acid green 25 dye from wastewater using activated Prunus Dulcis as biosorbent: batch and column studies. J Environ Manag 210:226–238
Juang R-S, Swei S-L (1996) Effect of dye nature on its adsorption from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon. Sep Sci Technol 31:2143–2158
Kanchi S, Bisetty K, Kumar G, Sabela M (2017) Robust adsorption of Direct Navy Blue-106 from textile industrial effluents by bio-hydrogen fermented waste derived activated carbon: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Arab J Chem 10:S3084–S3096
Kannan R, Lakshmi S, Aparna N, Prabhakar S, Thilagaraj WR (2016) Eco-friendly treatment of textile dye from aqueous solution using encapsulated biosorbent matrix beads: kinetics and breakthrough analysis. International Journal of Industrial Chemistry 7:265–275
Karaer H, Uzun İ (2013) Adsorption of basic dyestuffs from aqueous solution by modified chitosan. Desalin Water Treat 51:2294–2305
Kataria N, Garg V (2017) Removal of Congo red and brilliant green dyes from aqueous solution using flower shaped ZnO nanoparticles. J Environ Chem Eng 5:5420–5428
Klabunde KJ, Mulukutla RS (2001) 7 chemical and catalytic aspects of nanocrystals. Nanoscale Materials in Chemistry 223
Kumar A, Jena HM (2016) Removal of methylene blue and phenol onto prepared activated carbon from Fox nutshell by chemical activation in batch and fixed-bed column. J Clean Prod 137:1246–1259
Laskar N, Kumar U (2019) Removal of brilliant green dye from water by modified Bambusa Tulda: adsorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1649–1662
Li J, Zhang Q, Feng J, Yan W (2013) Synthesis of PPy-modified TiO2 composite in H2SO4 solution and its novel adsorption characteristics for organic dyes. Chem Eng J 225:766–775
Lodha S, Jain A, Punjabi PB (2011) A novel route for waste water treatment: photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. Arab J Chem 4:383–387
Mahmoodi NM, Hayati B, Arami M, Lan C (2011) Adsorption of textile dyes on pine cone from colored wastewater: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 268:117–125
Maqbool A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ishaque W, Rasool N, Rehman MZ, Bashir A, Abid M, Wu L (2018) Management of tannery wastewater for improving growth attributes and reducing chromium uptake in spinach through citric acid application. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:10848–10856
Matić P, Jakobek L, Ukić Š (2018) An equilibrium and kinetic study of phenolic acids adsorption onto β-glucan. Croat J Food Sci Technol 10:73–80
Matouq M, Jildeh N, Qtaishat M, Hindiyeh M, Al Syouf MQ (2015) The adsorption kinetics and modeling for heavy metals removal from wastewater by Moringa pods. J Environ Chem Eng 3:775–784
Mian MM, Liu G, Yousaf B, Fu B, Ullah H, Ali MU, Abbas Q, Munir MAM, Ruijia L (2018) Simultaneous functionalization and magnetization of biochar via NH3 ambiance pyrolysis for efficient removal of Cr (VI). Chemosphere 208:712–721
Nadeem R, Manzoor Q, Iqbal M, Nisar J (2016) Biosorption of Pb (II) onto immobilized and native Mangifera indica waste biomass. J Ind Eng Chem 35:185–194
Nandi BK, Goswami A, Purkait MK (2009) Adsorption characteristics of brilliant green dye on kaolin. J Hazard Mater 161:387–395
Nausheen S, Bhatti HN, Hanif MA (2017) Enhanced removal of golden XGL dye by clay composites: batch and column studies. Pol J Environ Stud 26:2113–2123
Nourmoradi H, Zabihollahi S, Pourzamani H (2016) Removal of a common textile dye, navy blue (NB), from aqueous solutions by combined process of coagulation–flocculation followed by adsorption. Desalin Water Treat 57:5200–5211
Odenbach S (2009) Colloidal magnetic fluids: basics, development and application of ferrofluids 763. Springer
Okoli CP, Diagboya PN, Anigbogu IO, Olu-Owolabi BI, Adebowale KO (2017) Competitive biosorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II) ions from aqueous solutions using chemically modified moss biomass (Barbula lambarenensis). Environ Earth Sci 76:33
Pang YL, Lim S, Ong HC, Chong WT (2016) Research progress on iron oxide-based magnetic materials: synthesis techniques and photocatalytic applications. Ceram Int 42:9–34
Pink RM (2016) Water rights in Southeast Asia and India. Springer
Rai A, Chauhan PS, Bhattacharya S (2018) Remediation of industrial effluents, water remediation. Springer, pp 171–187
Rehman R, Mahmud T, Irum M (2015) Brilliant green dye elimination from water using Psidium guajava leaves and Solanum tuberosum peels as adsorbents in environmentally benign way. J Chem 2015:1–8
Rehman R, Muhammad SJ, Arshad M (2019) Brilliant green and acid orange 74 dyes removal from water by Pinus roxburghii leaves in naturally benign way: an application of green chemistry. J Chem 2019:1–10
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Adrees M, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Farid M, Abbas F (2017) Effect of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of globally important food crops: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 322:2–16
Rizwan M, Ali S, ur Rehman MZ, Adrees M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF, Ali L, Hussain A, Chatha SA, Imran M (2019) Alleviation of cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) by foliar spray of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biochar to contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 248:358–367
Saha P (2010) Study on the removal of methylene blue dye using chemically treated rice husk. Asian J Water Environ Pollut 7:31–41
Saksornchai E, Kavinchan J, Thongtem S, Thongtem T (2018) Simple wet-chemical synthesis of superparamagnetic CTAB-modified magnetite nanoparticles using as adsorbents for anionic dye Congo red removal. Mater Lett 213:138–142
Saravanan A, Kumar PS, Renita AA (2018) Hybrid synthesis of novel material through acid modification followed ultrasonication to improve adsorption capacity for zinc removal. J Clean Prod 172:92–105
Sattar MS, Shakoor MB, Ali S, Rizwan M, Niazi NK, Jilani A (2019) Comparative efficiency of peanut shell and peanut shell biochar for removal of arsenic from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05185-z
Sayğılı GA, Sayğılı H, Koyuncu F, Güzel F (2015) Development and physicochemical characterization of a new magnetic nanocomposite as an economic antibiotic remover. Process Saf Environ Prot 94:441–451
Selim Y, Mohamed A (2017) Role of dyestuff in improving dye-sensitized solar cell performance. Renewable Energy Sustain Develop 3:79–82
Shah GM, Nasir M, Imran M, Bakhat HF, Rabbani F, Sajjad M, Farooq ABU, Ahmad S, Song L (2018) Biosorption potential of natural, pyrolysed and acid-assisted pyrolysed sugarcane bagasse for the removal of lead from contaminated water. PeerJ 6:e5672
Sharma S, Hasan A, Kumar N, Pandey LM (2018) Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using immobilized Agrobacterium fabrum biomass along with iron oxide nanoparticles as biosorbent. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Shen J, Lu Y, Liu J-K, Yang X-H (2016) Design and preparation of easily recycled Ag2WO4@ ZnO@ Fe3O4 ternary nanocomposites and their highly efficient degradation of antibiotics. J Mater Sci 51:7793–7802
Shojaei TR, Salleh MAM, Tabatabaei M, Mobli H, Aghbashlo M, Rashid SA, Tan T (2019) Applications of nanotechnology and carbon nanoparticles in agriculture, synthesis, technology and applications of carbon nanomaterials. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 247–277
Singh K, Senapati K, Sarma K (2017) Synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with green tea polyphenols and their use for removal of dye pollutant from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2214–2221
Subramani S, Thinakaran N (2017) Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption behaviour of textile dyes onto chitosan. Process Saf Environ Prot 106:1–10
Suganya S, Kumar S (2018) Influence of ultrasonic waves on preparation of active carbon from coffee waste for the reclamation of effluents containing Cr (VI) ions. J Ind Eng Chem 60:418–430
Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J, Abulfaraj M, Alqahtani F, Koulouridis I, Jaber BL (2013) World incidence of AKI: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1482–1493
Tarley CRT, Arruda MAZ (2004) Biosorption of heavy metals using rice milling by-products. Characterisation and application for removal of metals from aqueous effluents. Chemosphere 54:987–995
Tran HV, Bui LT, Dinh TT, Le DH, Huynh CD, Trinh AX (2017) Graphene oxide/Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposite: a recoverable and recyclable adsorbent for organic dyes removal. Application to methylene blue. Mater Res Exp 4:035701
Tufail S, Khan J (2013) Impact of working capital management on profitability of textile sector of Pakistan, Proceedings of 3rd international conference on business management, pp 1–29
Tahir MB, Ali S, Rizwan M (2019) A review on remediation of harmful dyes through visible light driven WO3 photocatalytic nanomaterials. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02385-5
Vinoth S, Shankar SG, Gurusaravanan P, Janani B, Devi JK (2019) Anti-larvicidal activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Sargassum polycystum against mosquito vectors. J Clust Sci 30:171–180
Yousaf B, Liu G, Abbas Q, Wang R, Ullah H, Mian MM, Rashid A (2018) Enhanced removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous media using a highly stable and magnetically separable rosin-biochar-coated TiO 2@ C nanocomposite. RSC Adv 8:25983–25996
Zazycki MA, Godinho M, Perondi D, Foletto EL, Collazzo GC, Dotto GL (2018) New biochar from pecan nutshells as an alternative adsorbent for removing reactive red 141 from aqueous solutions. J Clean Prod 171:57–65
Zhang M, Chang L, Zhao Y, Yu Z (2018) Fabrication of zinc oxide/polypyrrole nanocomposites for brilliant green removal from aqueous phase. Arab J Sci Eng:1–11
Zhou Y, Xiao H, Wang S, Pan X, Wang Z, An C, Zhang J (2016) Synthesis of layer-expanded MoS2 nanosheets/carbon fibers nanocomposites for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. Mater Chem Phys 183:18–23
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to COMSATS University Islamabad for financial support under COMSATS Research Grant Program (CRGP) with number 16-73/CRGP/CIIT//IBD/15/735 for the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Capsule: Biosorbents combined with nanoparticles are effective for the removal of brilliant green dye from aqueous solution
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imran, M., Islam, A.U., Tariq, M.A. et al. Synthesis of magnetite-based nanocomposites for effective removal of brilliant green dye from wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 24489–24502 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05706-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05706-w