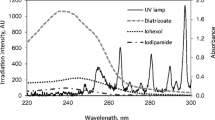
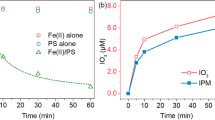
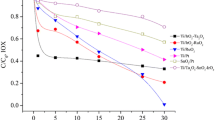
Abstract
Efficient abatement of an iodinated X-ray contrast media iohexol by an emerging sulfite autoxidation advanced oxidation process is demonstrated, which is based on transition metal ion–catalyzed autoxidation of sulfite to form active oxidizing species. The efficacy of the combination of sulfite and transition metal ions (Ag(I), Mn(II), Co(II), Fe(II), Cu(II), Fe(III), or Ce(III)) was tested for iohexol abatement. Co(II) and Cu(II) are proven to show more pronounced catalytic activity than other metals at pH 8.0. According to the quenching studies, sulfate radical (SO4•−) is identified to be the primary species for oxidation of iohexol. Increasing dosages of metal ion or sulfite and higher pH values are favorable for iohexol abatement. Inhibition of iohexol abatement is observed in the absence of dissolved oxygen, which is vital for the production of SO5•− and subsequent formation of SO4•−. Overall, activation of sulfite to produce reactive radicals with extremely low Co(II) or Cu(II) concentrations (in the range of μg L−1) in circumneutral conditions is confirmed, which offers a potential SO4•−-based advanced oxidation process in treatment of aquatic organic contaminants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alipázaga MV, Coichev N (2003) Synergistic effect of some transition metal ions on the sulfite induced autoxidation of Cu(II)/tetraglycine complex. Analytical applications. Anal Lett 36:2255–2275
Brandt C, van Eldik R (1995) Transition metal-catalyzed oxidation of sulfur(IV) oxides. Atmospheric-relevant processes and mechanisms. Chem Rev 95:119–190
Chan TW, Graham NJ, Chu W (2010) Degradation of iopromide by combined UV irradiation and peroxydisulfate. J Hazard Mater 181:508–513
Chen J, Qian Y, Liu H, Huang T (2016a) Oxidative degradation of diclofenac by thermally activated persulfate: implication for ISCO. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(4):3824–3833
Chen J, Zhang L, Huang T, Li W, Wang Y, Wang Z (2016b) Decolorization of azo dye by peroxymonosulfate activated by carbon nanotube: radical versus non-radical mechanism. J Hazard Mater 320:571–580
Chen L, Tang M, Chen C, Chen M, Luo K, Xu J, Zhou D, Wu F (2017) Efficient bacterial inactivation by transition metal catalyzed auto-oxidation of sulfite. Environ Sci Technol 51:12663–12671
Cheng L, Wei M, Huang L, Pan F, Xia D, Li X, Xu A (2014) Efficient H20 oxidation of organic dyes catalyzed by simple copper(II) ions in bicarbonate aqueous solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:3478–3485
Conklln MH, Hoffmann MR (1988) Metal ion-sulfur(IV) chemistry. 2. Kinetic studies of the redox chemistry of copper(II)-sulfur(IV) complexes. Environ Sci Technol 22:891–898
Dong H, Qiang Z, Hu J, Sans C (2017) Accelerated degradation of iopamidol in iron activated persulfate systems: roles of complexing agents. Chem Engin J 316:288–295
Duirk SE, Lindell C, Cornelison CC, Kormos J, Ternes TA, Attene-Ramos M, Osiol J, Wagner ED, Plewa MJ, Richardson SD (2011) Formation of toxic iodinated disinfection by-products from compounds used in medical imaging. Environ Sci Technol 45:6845–6854
Guo Y, Lou X, Fang C, Xiao D, Wang Z, Liu J (2013) Novel photo-sulfite system: toward simultaneous transformations of inorganic and organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 47:11174–11181
Hu J, Dong H, Qu J, Qiang Z (2017) Enhanced degradation of iopamidol by peroxymonosulfate catalyzed by two pipe corrosion products (CuO and delta-MnO2). Water Res 112:1–8
Humphrey RE, Ward MH, Hinze W (2002) Spectrophotometric determination of sulfite with 4,4′-dithio-dipyridine and 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid). Anal Chem 42:698–702
Jiang B, Liu Y, Zheng J, Tan M, Wang Z, Wu M (2015) Synergetic transformations of multiple pollutants driven by Cr(VI)-sulfite reactions. Environ Sci Technol 49:12363–12371
Kong X, Jiang J, Ma J, Yang Y, Pang S (2018) Comparative investigation of x-ray contrast medium degradation by UV/chlorine and UV/H2O2. Chemosphere 193:655–663
Li Q, Wang L, Zhao Y et al (2014a) Oxidation rate of magnesium sulfite catalyzed by cobalt ions. Environ Sci Technol 48:4145–4152
Li X, Shi W, Cheng Q, Huang L, Wei M, Cheng L, Zeng Q, Xu A (2014b) Catalytic activation of dioxygen to hydroxyl radical and efficient oxidation of o-aminophenol by cobalt(II) ions in bicarbonate aqueous solution. Appl Catal A Gen 475:297–304
Lutze HV, Kerlin N, Schmidt TC (2015) Sulfate radical-based water treatment in presence of chloride: formation of chlorate, inter-conversion of sulfate radicals into hydroxyl radicals and influence of bicarbonate. Water Res 72:349–360
Neta P, Huie RE, Ross AB (1988) Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem Ref Data 17:1027–1284
Ning B, Graham NJD (2008) Ozone degradation of iodinated pharmaceutical compounds. J Environ Engin 134:944–953
Pan C, Gao Q, Stanbury DM (2015) Kinetics of the benzaldehyde-inhibited oxidation of sulfite by chlorine dioxide. Inorg Chem 55:366–370
Pasiukbronikowska W, Bronikowski T, Ulejczyk M (1986) Mechanism and kinetics of autoxidation of calcium sulfite slurries. Environ Sci Technol 26:1976–1981
Perez S, Barcelo D (2007) Fate and occurrence of X-ray contrast media in the environment. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1235–1246
Qian Y, Xue G, Chen J (2018) Oxidation of cefalexin by thermally activated persulfate: kinetics, products, and antibacterial activity change. J Hazard Mater 354:153–160
Richardson SD, Fasano F, Ellington JJ, Crumley FG, Buettner KM, Evans JJ, Blount BC, Silva LK, Waite TJ, Luther GW, McKague AB, Miltner RJ, Wagner ED, Plewa MJ (2008) Occurrence and mammalian cell toxicity of iodinated disinfection byproducts in drinking water. Environ Sci Technol 42:8330–8338
Sun B, Dong H, He D, Rao D, Guan X (2016) Modeling the kinetics of contaminants oxidation and the generation of manganese(III) in the permanganate/bisulfite process. Environ Sci Technol 50:1473–1482
Ternes TA, Hirsch R (2000) Occurrence and behavior of X-ray contrast media in sewage facilities and the aquatic environment. Environ Sci Technol 34:2741–2748
Wendel FM, Lutke Eversloh C, Machek EJ et al (2014) Transformation of iopamidol during chlorination. Environ Sci Technol 48:12689–12697
Xie P, Guo Y, Chen Y, Wang Z, Shang R, Wang S, Ding J, Wan Y, Jiang W, Ma J (2017) Application of a novel advanced oxidation process using sulfite and zero-valent iron in treatment of organic pollutants. Chem Engin J 314:240–248
Xu Z, Li X, Hu X, Yin D (2017) Distribution and relevance of iodinated X-ray contrast media and iodinated trihalomethanes in an aquatic environment. Chemosphere 184:253–260
Yuan Y, Zhao D, Li J, Wu F, Brigante M, Mailhot G (2018) Rapid oxidation of paracetamol by cobalt(II) catalyzed sulfite at alkaline pH. Catal Today 313:155–160
Zhang J, Ma J, Song H, Sun S, Zhang Z, Yang T (2018a) Organic contaminants degradation from the S(IV) autoxidation process catalyzed by ferrous-manganous ions: a noticeable Mn(III) oxidation process. Water Res 133:227–235
Zhang R, Wang X, Zhou L, Liu Z, Crump D (2018b) The impact of dissolved oxygen on sulfate radical-induced oxidation of organic micro-pollutants: a theoretical study. Water Res 135:144–154
Zhou D, Chen L, Zhang H (2015a) Sulfur-replaced Fenton systems: can sulfate radical substitute hydroxyl radical for advanced oxidation technologies? J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:775–779
Zhou D, Yuan Y, Yang S, Gao H, Chen L (2015b) Roles of oxysulfur radicals in the oxidation of acid orange 7 in the Fe(III)–sulfite system. J Sulfur Chem 36:373–384
Zhou L, Ferronato C, Chovelon JM, Sleiman M, Richard C (2017) Investigations of diatrizoate degradation by photo-activated persulfate. Chem Engin J 311:28–36
Zhou D, Chen L, Li J, Wu F (2018) Transition metal catalyzed sulfite auto-oxidation systems for oxidative decontamination in waters: a state-of-the-art minireview. Chem Eng J 346:726–738
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51808233) and the Scientific Research Funds of Huaqiao University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Vítor Pais Vilar
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Co(II) and Cu(II) exhibit excellent catalytic activity for sulfite autoxidation.
• Co(II)/sulfite or Cu(II)/sulfite achieve rapid abatement of iohexol at neutral pH.
• Sulfate radical is identified as the main active species for iohexol degradation.
• Bicarbonate facilitates iohexol abatement in Co(II)/sulfite process.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 124 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Wu, W. & Yan, Y. Efficient abatement of an iodinated X-ray contrast media iohexol by Co(II) or Cu(II) activated sulfite autoxidation process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 24707–24719 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05601-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05601-4