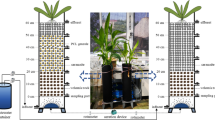
Abstract
We investigated the treatment efficiency of micro-polluted NO3−-dominated river water with low C/N ratio by five parallel pilot-scale IVCWs with different plant and substrate collocation. When the mean concentration was 2.24 and 0.193 mg L−1 in influent, IVCWs achieved an average (mass) removal rate of (0.09 g m−2 day−1) 46.8% and (0.77 g m−2 day−1) 62.3% for TN and TP, respectively, during 1 year of operation. Water quality was significantly improved from grade V to meet the criterion of grade IV of surface water. Through the comparison of removal rate by different IVCWs, we found that lack of carbon sources in influent limited the denitrification in the middle and bottom layers (ML, BL) of IVCW. Zeolites deployed in the upper layer (UL) of IVCW reduced the overall N removal efficiency compared with gravels, due to a stronger nitrification but weaker denitrification. Canna indica (C. indica) was superior to Arundo donax (A. donax) and Thalia dealbata (T. dealbata) for N removal in the UL of IVCW due to higher aboveground biomass accumulation and microbial removal during the first 10 months. Stronger nitrification and denitrification were simultaneously facilitated near the rhizosphere of C. indica. When entered into Dec., A. donax performed higher N removal efficiency than the other two species. The internal replenishment of peats in the ML as carbon sources significantly improved N and P removal efficiency. Zeolites with stronger capacity of ammonium (NH4+) adsorption was more in favor of anammox in the BL, when compared with roseites, but both of them were not conducive to the growth of denitrifiers. However, the deployment of shale ceramisites obtained an opposite result. Gemmata and Pirellula as anammox bacteria were more enriched in the zeolite layer, whereas some anaerobic denitrifiers (Corynebacterium and Paludibacter) and heterotrophic denitrifiers including Bacillus, Geobacter, Pseudomonas, and Lactococcus were more found in shale ceramisite. Supply of peats as carbon sources in the ML was beneficial for the adhesion of anammox bacteria and denitrifiers in the BL of shale ceramisites. An ideal model composed of C. indica + A. donax (DFU)-gravel (UL)-anthracite+peat (ML)-zeolite+shale ceramsite (BL)-Acorus calamus (UFU) was proposed for treating this type of river water to achieve high efficiency.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmagid HM, Tabatabai MA (1987) Nitrate reductase activity of soils. Soil Biol Biochem 19:421–427
Arden S, Ma X (2018) Constructed wetlands for greywater recycle and reuse: a review. Sci Total Environ 630:587–599
Bachand PAM, Horne AJ (2000) Denitrification in constructed free-water surface wetlands: II. Effects of vegetation and temperature. Ecol Eng 14:17–32
Bastviken SK, Weisner SEB, Thiere G, Svensson JM, Ehde PM, Tonderski KS (2009) Effects of vegetation and hydraulic load on seasonal nitrate removal in treatment wetlands. Ecol Eng 35:946–952
Bouali M, Zrafi-Nouira I, Bakhrouf A, Le Paslier D, Chaussonnerie S, Ammar E, Sghir A (2012) The structure and spatio-temporal distribution of the Archaea in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Sci Total Environ 435:465–471
Brdjanovic D, Slamet A, Van Loosdrecht MCM, Hooijmans CM, Alaerts GJ, Heijnen JJ (1998) Impact of excessive aeration on biological phosphorus removal from wastewater. Water Res 32:200–208
Brix H, Arias CA (2005) Danish guidelines for small-scale constructed wetland system for onsite treatment of domestic sewage. Water Sci Technol 51:1–9
Chang JJ, Wu SQ, Dai YR, Liang W, Wu ZB (2012) Treatment performance of integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland plots for domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 44:152–159
Chang JJ, Wu SQ, Dai YR, Liang W, Wu ZB (2013) Nitrogen removal from nitrate-laden wastewater by integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland systems. Ecol Eng 58:192–201
Chen Y, Wen Y, Zhou Q (2014) Effects of plant biomass on nitrogen transformation in subsurface-batch constructed wetlands: a stable isotope and mass balance assessment. Water Res 63:158–167
Du L, xt T, qr C, wang c w h, Xia X, Zhou QH, Xu D, Wu ZB (2018a) Enhancement of microbial nitrogen removal pathway by vegetation in integrated vertical-flow constructed wetlands (IVCWs) for treating reclaimed water. Bioresour Technol 249:644–651
Du L, xt T, qr C, wang c LSY, Liu PP, Zhou QH, Xu D, Wu ZB (2018b) Effect of clinoptilolite on ammonia emissions in integrated vertical-flow constructed wetlands (IVCWs) treating swine wastewater. Ecol Eng 122:153–158
Emily GIP, Tracey P, Ana D, Belinda EH, Perran LMC, Tim DF (2018) Which species? A decision-support tool to guide plant selection in stormwater biofilters. Adv Water Resour 113:86–99
Fang WS, Yan DD, Wang XL, Huang B, Wang XN, Liu J, Liu XM, Li Y, Ouyang CB, Wang QX, Cao AC (2018) Responses of nitrogen-cycling microorganisms to dazomet fumigation. Front Microbiol 9:2529
Ge Y, Zhang CB, Jiang YP, Yue CL, Jiang QS, Min H, Fan HT, Zeng Q, Chang J (2011) Soil microbial abundances and enzyme activities in different rhizospheres in an integrated vertical flow constructed wetland. Clean Soil Air Water 39:206–211
Gebremariam SY, Beutel MW (2008) Nitrate removal and DO levels in batch wetland mesocosms: cattail (Typha spp.) versus bulrush (Scirpus spp.). Ecol Eng 34:1–6
Herrmann M, Saunders AM, Schramm A (2009) Effect of lake trophic status and rooted macrophytes on community composition and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3127–3136
Hou L, Xie XB, Wan XH, Kao SJ, Jiao NZ, Zhang Y (2018) Niche differentiation of ammonia and nitrite oxidizers along a salinity gradient from the Pearl River estuary to the South China Sea. Biogeosciences 15:5169–5187
Hu Y, He F, Ma L, Zhang Y, Wu ZB (2016) Microbial nitrogen removal pathways in integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland systems. Bioresour Technol 207:339–345
Hua YM, Peng L, Zhang SH, Heal KV, Zhao JW, Zhu DW (2017) Effects of plants and temperature on nitrogen removal and microbiology in pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 108:70–77
Jesus JM, Danko AS, Fiúza A, Borges MT (2018) Effect of plants in constructed wetlands for organic carbon and nutrient removal: a review of experimental factors contributing to higher impact and suggestions for future guidelines. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:4149–4164
Ji GD, Wang RJ, Zhi W, Liu XX, Kong YP, Tan YF (2012) Distribution patterns of denitrification functional genes and microbial floras in multimedia constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 44:179–188
Jiang C, Jia LY, Zhang B, He YL, Kirumba G (2014) Comparison of quartzsand, anthracite, shale and biological ceramsite for adsorptive removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 26:466–477
Karpuzcu ME, Stringfellow WT (2012) Kinetics of nitrate removal in wetlands receiving agricultural drainage. Ecol Eng 42:295–303
Kleimeier C, Liu HJ, Rezanezhad F, Lennartz B (2018) Nitrate attenuation in degraded peat soil-based constructed wetlands. Water 10:355
Kouzuma A, Kasai T, Nakagawa G, Yamamuro A, Abe T, Watanabe K (2013) Comparative metagenomics of anode-associated microbiomes developed in rice paddy-field microbial fuel cells. PLoS One 8:e77443
Lai WL, Wang SQ, Peng CL, Chen ZH (2011) Root features related to plant growth and nutrient removal of 35 wetland plants. Water Res 45:3941–3950
Lima MX, Carvalho KQ, Passig FH, Borges AC, Filippe TC, Azevedo JCR, Nagalli A (2018) Performance of different substrates in constructed wetlands planted with E. crassipes treating low-strength sewage under subtropical conditions. Sci Total Environ 630:1365–1373
Ling Z, Hua CL, Ying O, Fen L, Dan T (2011) Kinetic adsorption of ammonium nitrogen by substrate materials for constructed wetlands. Pedosphere 21:454–463
Lovley DR, Fraga JL, Coates JD, Blunt-Harris EL (1999) Humics as an electron donor for anaerobic respiration. Environ Microbiol 1:89–98
Nishimura T, Vertes AA, Shinoda Y, Lnui M, Yukawa H (2007) Anaerobic growth of Corynebacterium glutamicum using nitrate as a terminal electron acceptor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:889–897
Peng L, Hua YM, Cai JB, Zhao JW, Zhou WB (2014) Effects of plants and temperature on nitrogen removal and microbiology in a pilot-scale integrated vertical-flow wetland treating primary domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 64:285–290
Rubaba O, Araki Y, Yamamoto S, Suzuki K, Sakamoto H, Matsuda A, Futamata H (2013) Electricity producing property and bacterial community structure in microbial fuel cell equipped with membrane electrode assembly. J Biosci Bioeng 116:106–113
Saeed T, Sun G (2011) Enhanced denitrification and organics removal in hybrid wetland columns: comparative experiments. Bioresour Technol 102:967–974
Shen JY, Chen Y, Wu SJ, Wu HB, Liu XD, Sun XY, Li JS, Wang LJ (2015) Enhanced pyridine biodegradation under anoxic condition: the key role of nitrate as the electron acceptor. Chem Eng J 277:140–149
Shi PB, Jiang YB, Zhu HT, Sun DZ (2017) Impact of steel slag on the ammonium adsorption by zeolite and a new configuration of zeolite-steel slag substrate for constructed wetlands. Water Sci Technol 76:584–593
State environmental protection Administration of China (2002a) Environmental quality standard for surface water in China. GB383–2002, Beijing
State environmental protection Administration of China (2002b) standard methods for testing water and wastewater, 4th edn. China Environment Science Press, Beijing
Sun HS, Liu F, Xu SJ, Wu SH, Zhuang GQ, Deng Y, Wu JS, Zhuang XL (2017) Myriophyllum aquaticum constructed wetland effectively removes nitrogen in swine wastewater. Front Microbiol 8:1932
Toczylowska-Maminska R, Szymona K, Krol P, Gliniewicz K, Pielech-Przybylska K, Kloch M, Logan BE (2018) Evolving microbial communities in cellulose-fed microbial fuel cell. Energies 11:124
Tu YT, Chiang PC, Yang J, Chen SH, Kao CM (2014) Application of a constructed wetland system for polluted stream remediation. J Hydrol 510:70–78
Valipour A, Ahn YH (2016) Constructed wetlands as sustainable ecotechnologies in decentralization practices: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:180–197
Vesk P, Allaways W (1997) Special variation of copper and lead concentration of water hyacinth plants in a wetland receiving urban run-off. Aquat Bot 59:33–44
Wang Y, Wang J, Zhao X, Song X, Gong J (2016) The inhibition and adaptability of four wetland plant species to high concentration of ammonia wastewater and nitrogen removal efficiency in constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 202:198–205
Wang Z, Dong J, Liu L, Zhu GF, Liu CX (2013) Screening of phosphate-removing substrates for use in constructed wetlands treating swine wastewater. Ecol Eng 54:57–65
Wu SQ, Chang JJ, Dai YR, Wu ZB, Liang W (2013) Treatment performance and microorganism community structure of integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland plots for domestic wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3789–3798
Xiong JB, Mahmood Q (2010) Adsorptive removal of phosphate removal from aqueous media by peat. Desalination 259:59–64
Yang Y, Zhao YQ, Liu RB, Morgan D (2018) Global development of various emerged substrates utilized in constructed wetlands. Bioresour Technol 261:441–452
Zhang XL, Zhang S, He F, Cheng SP, Liang W, Wu ZB (2007) Differentiate performance of eight filter media in vertical flow constructed wetland: removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorus. Fresenius Environ Bull 16:1468–1473
Zhang CB, Wang J, Liu WL, Zhu SX, Liu D, Chang SX, Chang J, Ge Y (2010) Effects of plant diversity on nutrient retention and enzyme activities in a full-scale constructed wetland. Bioresour Technol 101:1686–1692
Zhao HM, Zhao JQ, Li FH, Li XL (2016) Performance of denitrifying microbial fuel cell with biocathode over nitrite. Front Microbiol 7:344
Zhao J, Feng LJ, Dai JC, Yang GF, Mu J (2017) Characteristics of nitrogen removal and microbial community in biofilm system via combination of pretreated lignocellulosic carriers and various conventional fillers. Biodegradation 28:337–349
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Lingwei Kong, Lei Zeng, and Faming Huang for their assistance.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the projects of the National Key Research and Development Plan of China (No. 2016YFC0500403-03) and Science and Technology Service Network Initiative of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KFJ-STS-ZDTP-038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, P., Xiao, E., He, F. et al. High performance of integrated vertical-flow constructed wetland for polishing low C/N ratio river based on a pilot-scale study in Hangzhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 22431–22449 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05508-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05508-0