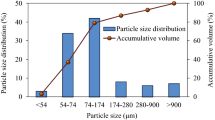
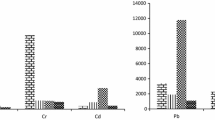
Abstract
Coal combustion is one of the most significant anthropogenic sources of thallium in the environment. This study presents the results of determination of thallium and some toxic elements (Pb, Cd, As, Ni, Zn, and Cu) concentration in fly ash produced in the coal combustion in conventional furnaces (pulverized coal furnace and grate furnace), in a fluidized-bed furnace with circulation bed, and in a home furnace. The high content of thallium was determined in ash produced in the grate furnace (on average 10.7 mg/kg) and fluidized-bed furnace with circulation bed (6.6 mg/kg). The average content of Tl in the fly ash of the pulverized coal furnace and in the home furnace is 1.7 and 2.4 mg/kg, respectively. There was a strong relationship between the occurrence of Tl and As, Cd, Pb, Cu, and Zn in ash from grate and pulverized coal furnace.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari B, Dahal KR, Khanal SN (2014) A review of factor affecting the composition of municipal solid waste landfill leachate. Int J Eng Sci Innov Technol 3(5):272–281
Alastuey A, Jimenez A, Plana F, Querol X, Suárez-Ruiz I (2001) Geochemistry, mineralogy, and technological properties of the main stephanian carboniferous coal seams. Int J Coal Geol 45(40):247–265
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Diseases Registry) (1991) Toxicological profile for thallium (draft). U.S. Department of Public Health, Washington, DC
Den Boer E, Jędrczak A, Kowalski Z, Kulczycka J, Szpadt R (2010) A review of municipal solid waste composition and quantities in Poland. Waste Manag 30:369–377
Duffy SJ, Van Loon G (2007) Environmental chemistry: a part perspective. PWN, Warszawa
Ensafi AA, Rezaei B (1998) Speciation of thallium by flow injection analysis with spectrofluorimetric detection. Microchem J 60:75–83
GUS: Główny Urząd Statystyczny (2015) Zużycie paliw i nośników energii w 2014 r., Warszawa
Hršak J., Škrbec A., Balago vić I., Šega K. (2003) Thallium content in Zagreb Air
Jian-guo J, Xin XU, Jun W, Shi-jian Y, Yan Z (2007) Investigation of basic properties of fly ash from urban waste incinerators in China. J Environ Sci 19:458–463
Jinghai L, Chang S (2016) Evaluation of the migration of thallium, cadmium, vanadium, and chromium from a thermal power plant. Environ Earth Sci 75:388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5159-z
Kabata-Pendias A, Szteke B (2012) Pierwiastki śladowe w geo- i biosferze. PWN, Warszawa
Ketris MP, Yudovich YAE (2009) Estimations of Clarkes for carbonaceous biolithes: world averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. Int J Coal Geol 78:135–148
Lin T, Nriagu JO (1998) Thallium in the environment. Wiley, New York
Lis J, Pasieczna A, Karbowska B, Zembrzuski W, Lukaszewski Z (2003) Thallium in soil and stream sediments of a Zn-Pb mining and smelting area. Environ Sci Technol 37(20):4569–4572
López Antón MA, Spears DA, Díaz-Smoano M, Diaz L, Martínez-Tarazona MR (2013) Thallium in coal: analysis and environmental implications. Fuel 105:13–18
López Antón MA, Spears DA, Díaz-Smoano M, Diaz L, Martínez-Tarazona MR (2015) Enrichment of thallium in fly ash in a Spanish circulating fluidized-bed combustion plant. Fuel 146:51–55
Lukaszewski Z, Jakubowska M, Zembrzuski W, Pasieczna A, Karbowska B (2010) Flow injection differential-pulse anodic stripping voltammetry as a tool for thallium monitoring in the environment. Electroanalysis 22:1963–1966
Muszyńska B, Rojowski J, Dobosz K, Opoka W (2015) Biological and physico-chemical properties of thallium. Medicina Internacia Revuo 26(4):180–185
Natush DFS, Wallace JR, Evans CR (1974) Toxic trace elements: preferential concentration in respirable particles. Science 183:202–204
Parzentny H, Lewińska-Preis L (2006) The role of sulphide and carbonate minerals in the concentration of chalcophile elements in the bituminous coal seams of a paralic series (upper carboniferous) in the upper Silesian Coal Basin (USCB), Poland. Chem Erde 66:227–247
Peter JAL, Viraraghavan T (2005) Thallium: a review of public health and environmental concerns. Environ Int 31:493–501
Querol X, Fernández_Turiel JL, López-Soler A (1995) Trace elements in coal and their behaviour during combustion in a large power station. Fuel 74:331–343
Smołka-Danielowska D. (2015) Trace elements and mineral composition of waste produced in the process of combustion of solid fuels in individual household furnaces in the Upper Silesian Industrial Region (Poland). Environ Socio-Econ Stud 3(4):30–38
Suárez-Ruiz I, Flores D, Marques MM, Martinez-Tarazona MR, Pis J, Rubiera F (2006) Geochemistry, mineralogy and technological properties of coal from Rio Maior (Portugal) and Peñarroya (Spain) basins. Int J Coal Geol 67:171–190
Testoff A. (2013) Estimating the potential release of thallium from fly ash under different environmental scenarios. The Ohio State University
Wang W, Qin Y, Sang S, Jiang B, Guo Y, Zhu Y, Fu X (2006) Partitioning of minerals and during preparation of Taixi coal, China. Fuel 85(1):57–67
Xiao T, Guha J, Boyle D, Liu CO, Jingan Chen J (2004) Environmental concerns related to high thallium levels in soils and thallium uptake by plants in Southwest Guizhou, China. Sci Total Environ 318:223–244
Zhang G, Liu CQ, Yang Y, Wu P (2004) Characterization of heavy metals and sulphur isotope in water and sediments of a mine-tailing area rich in carbonate. Water Air Soil Pollut 155(1–4):51–62
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smolka-Danielowska, D., Fiedor, D. Potentially toxic elements in fly ash dependently of applied technology of hard coal combustion. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 25091–25097 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2548-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2548-3