Abstract
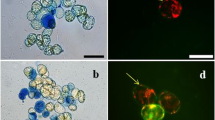
Effect of cadmium cations and their interaction with silicon cations was determined in poplar calli and expressed as changes in callus growth, cell viability and cadmium cation accumulation. Cell viability throughout culture versus cadmium cation accumulation in cells is discussed. At the same time, the study sought appropriate methods for cadmium cation detection in callus cells and also in experiments with low plant material (e.g. protoplasts). Cadmium cations were determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy and using fluorescence microscopy with a specific cadmium cation fluorescent dye. The detection of cadmium cations in callus cells by the latter method appears suitable because the callus cells are surrounded by primary cell walls without auto-fluorescence and these values fit well with atomic absorption spectroscopy quantification. However, the visualisation method has some limits discussed below.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAS:
-
Atomic absorption spectroscopy
- Cd:
-
Cadmium cations
- LOD:
-
Detection limit
- LOQ:
-
Quantitation limit
- Si:
-
Silicon cations
References
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Qayyum MF (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: a review. Ecotox Environ Safe 119:186–197. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.05.011
Asgher M, Khan MIR, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants—of plant growth regulators. Protoplasma 252:399–413. doi:10.1007/s00709-014-0710-4
Cabot C, Gallego B, Martos S, Barceló J, Poschenrieder C (2013) Signal cross talk in Arabidopsis exposed to cadmium, silicon, and Botrytis cinerea. Planta 237:337–349. doi:10.1007/s00425-012-1779-7
Chaiyo S, Apiluk A, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O (2016) High sensitivity and specificity simultaneous determination of lead, cadmium and copper using μPAD with dual electrochemical and colorimetric detection. Sens Actuators B-Chem 233:540–549. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2016.04.109
Chen Z, Feng Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Liu Q, Xu S, Guan W (2015) Study on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of wheat seedlings under [C4mim][OAc] (1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium acetate) with Cd2+ stress. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94:627–632. doi:10.1007/s00128-015-1519-3
Cooke J, Leishman MR (2011) Is plant ecology more siliceous than we realise? Trends Plant Sci 16:61–68. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2010.10.003
Di Baccio D, Castagna A, Tognetti R, Ranieri A, Sebastiani L (2014) Early responses to cadmium of two poplar clones that differ in stress tolerance. J Plant Physiol 171:1693–1705. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2014.08.007
Di Lonardo S, Capuana M, Arnetoli M, Gabbrielli R, Gonnelli C (2011) (2011) Exploring the metal phytoremediation potential of three Populus alba L. clones using an in vitro screening. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:82–90. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0354-7
Diaz-Colon JD, Bonny RW, Dawis FS, Bauer JR (1972) Comparative effects and concentrations of Picloran, 2,4,5-T and Dicamba in tissues culture. Physiol Plant 27:60–64. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1972.tb01137.x
Donaldson LA, Radotić K (2013) Fluorescence lifetime imaging of lignin autofluorescence in normal and compression wood. J Microsc 251:178–187. doi:10.1111/jmi.12059
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Ishaque W, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2013) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. Ecotox Environ Safe 96:242–249. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.07.006
Garbisu C, Alkorta I (2001) Phytoextraction: a cost-effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresour Technol 77:229–236. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00108-5
Greger M, Landberg T (2015) Novel field data on phytoextraction: pre-cultivation with salix reduces cadmium in wheat grains. Int J Phytoremediat 17:917–924. doi:10.1080/15226514.2014.1003785
Greger M, Kabir AH, Landberg T, Maity PJ, Lindberg S (2016) Silicate reduces cadmium uptake into cells of wheat. Environ Pollut 211:90–97. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2015.12.027
Guo B, Liu C, Ding N, Fu Q, Lin Y, Li H, Li N (2016) Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in two cypress varieties by strengthening the exodermis tissues and stimulating phenolic exudation of roots. J Plant Growth Regul 35:420–429. doi:10.1007/s00344-015-9549-y
Keller C, Rizwan M, Davidian JC, Pokrovsky OS, Bovet N, Chaurand P, Meunier JD (2015) Effect of silicon on wheat seedlings (Triticum turgidum L.) grown in hydroponics and exposed to 0 to 30 μM Cu. Planta 241:847–860. doi:10.1007/s00425-014-2220-1
Kollárová K, Vatehová Z, Zelko I, Kučerová D, Lišková D (2015) Physiological characteristics in poplar callus under antimony, arsenic and silicon treatment. Book of abstracts. 14th Conference of Experimental Plant Physiology, Brno, p 80
Kováčik J, Babula P, Klejdus B, Hedbavný J (2014) Comparison of oxidative stress in four Tillandsia species exposed to cadmium. Plant Physiol Biochem 80:33–40. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.03.015
Küpper H, Andresen E (2016) Mechanisms of metal toxicity in plants. Metallomics 8:269–285. doi:10.1039/c5mt00244c
Liang YC, Wong JWC, Wei L (2005) Silicon-mediated enhancement of cadmium tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium contaminated soil. Chemosphere 58:475–483. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.034
Liang YC, Sun WC, Zhu YG, Christie P (2007) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: a review. Environ Pollut 147:422–428. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.06.008
Lukačová Z, Švubová R, Kohanová J, Lux A (2013) Silicon mitigates the Cd toxicity in maize in relation to cadmium translocation, cell distribution, antioxidant enzymes stimulation and enhanced endodermal apoplasmic barrier development. Plant Growth Regul 70:89–103. doi:10.1007/s10725-012-9781-4
Ma JF (2004) Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plants to biotic and abiotic stresses. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50:11–18. doi:10.1080/00380768.2004.10408447
Madejón P, Marañón T, Murillo JM, Robinson B (2004) White poplar (Populus alba) as a biomonitor of trace elements in contaminated riparian forests. Environ Pollut 132:145–155. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.03.015
Morel M, Crouzet J, Gravot A, Auroy P, Leonhardt N, Vavasseur A, Richaud P (2009) AtHMA3, a P1B-ATPase allowing Cd/Zn/Co/Pb vacuolar storage in Arabidopsis1[W]. Plant Physiol 149:894–904. doi:10.1104/pp.108.130294
Najmanova J, Neumannova E, Leonhardt T, Zitka O, Rene Kizek R, Macek T, Mackova M, Kotrba P (2012) Cadmium-induced production of phytochelatins and speciation of intracellular cadmium in organs of Linum usitatissimum seedlings. Ind Crop Prod 36:536–542. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.11.008
Nwugo CC, Huerta AJ (2008) Effects of silicon nutrition on cadmium uptake, growth and photosynthesis of rice plants exposed to low-level cadmium. Plant Soil 311:73–86. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9659-4
Parrotta L, Guerriero G, Sergeant K, Cai G, Hausman JF (2015) Target or barrier? The cell wall of early- and later-diverging plants vs cadmium toxicity: differences in the response mechanisms. Front Plant Sci 6:133. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00133
Polle A, Douglas C (2010) The molecular physiology of poplars: paving the way for knowledge-based biomass production. Plant Biol 12:239–241. doi:10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00318.x
Romeo S, Francini A, Sebastiani L, Morabito D (2015) High Zn concentration does not impair biomass, cutting radial growth, and photosynthetic activity traits in Populus alba L. J Soils Sediments (in press). doi:10.1007/s11368-015-1251-y
Shi Q, Wang J, Zou J, Jiang Z, Wu H, Wang J, Jiang W, Liu D (2016) Cadmium localization and its toxic effects on root tips of barley. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture 103:151–158. doi:10.13080/z-a.2016.103.020
Shingles R, Wimmers LE, McCarty RE (2004) Copper transport across pea thylakoid membranes. Plant Physiol 135:145–151. doi:10.1104/pp.103.037895
Song A, Li ZJ, Xue GF, Fan FL, Liang YC (2009) Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. J Hazard Mater 172:74–83. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.143
Song A, Li P, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Nikolic M, Liang YC (2011) The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant Soil 344:319–333. doi:10.1007/s11104-011-0749-3
Vaculík M, Landberg T, Greger M, Luxová M, Stoláriková M, Lux A (2012) Silicon modifies root anatomy, and uptake and subcellular distribution of cadmium in young maize plants. Ann Bot 110:433–443. doi:10.1093/aob/mcs039
Vaculík M, Pavlovič A, Lux A (2015) Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity by enhanced photosynthetic rate and modified bundle sheath’s cell chloroplasts ultrastructure in maize. Ecotox Environ Safe 120:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.05.026
Van de Mortel JE, Villanueva LA, Schat H, Kwekkeboom J, Coughlan S, Moerland PD, van Themaat EVL, Koornneef M, Aarts MGM (2006) Large expression differences in genes for iron and zinc homeostasis, stress response, and lignin biosynthesis distinguish roots of Arabidopsis thaliana and the related metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Physiol 142:1127–1147. doi:10.1104/pp.106.082073
Vatehová Z, Kollárová K, Zelko I, Richterová-Kučerová D, Bujdoš M, Lišková D (2012) Interaction of silicon and cadmium in Brassica juncea and Brassica napus. Biologia 67:498–504. doi:10.2478/s11756-012-0034-9
Verkleij JAC, Golan-Goldhirsh A, Antosiewisz DM, Schwitzguébel JP, Schröder P (2009) Dualities in plant tolerance to pollutants and their uptake and translocation to the upper plant parts. Environ Exp Bot 67:10–22. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.05.009
Zelko I, Kollárová K, Vatehová Z, Lišková D (2014) Silicon effect on growth dynamics, macro and microelements content in cadmium and arsenic treated poplar calli. Book of abstracts. 6th Int. Conference on Silicon in Agriculture, Stockholm, p 182
Zeng Y, Zhao S, Wei H, Tucker MP, Himmel ME, Mosier NS, Meilan R, Ding SY (2015) In situ micro-spectroscopic investigation of lignin in poplar cell walls pretreated by maleic acid. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:126. doi:10.1186/s13068-015-0312-1
Zhang C, Wang L, Nie Q, Zhang W, Zhang F (2008) Long-term effects of exogenous silicon on cadmium translocation and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Environ Exp Bot 62:300–307. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.10.024
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education of the Slovak Republic and the Academy of Sciences VEGA no. 2/0083/14 and the Slovak Research and Development Agency, grant no. APVV-0140-10. The authors thank Dr. Marek Bujdoš for providing the expertise on Cd and Si determination by AAS analysis in plant material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kollárová, K., Vatehová, Z., Kučerová, D. et al. Cadmium impact, accumulation and detection in poplar callus cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 15340–15346 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9158-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9158-3