Abstract
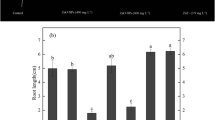
The wide spread of nanoparticles (NPs) has caused tremendous concerns on agricultural ecosystem. Some metallic NPs, such as zinc oxide (ZnO), can be utilized as a nano-fertilizer when used at optimal doses. However, little is known about the responses of plant development and concomitant soil bacteria community to ZnO NPs. The present pot experiment studied the impacts of different doses of ZnO NPs and bulk ZnO (0, 1, 10, 100 mg ZnO/kg), on the growth of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and the associated rhizospheric soil bacterial community. Results showed that at a dose of 10 mg/kg, ZnO NPs and bulk ZnO, enhanced the lettuce biomass and the net photosynthetic rate; whereas, the Zn content in plant tissue was higher in NPs treatment than in their bulk counterpart at 10 mg/kg dose or higher. For the underground observations, 10 mg/kg treatment doses (NPs or bulk) significantly changed the soil bacterial community structure, despite the non-significant variations in alpha diversity. Taxonomic distribution revealed that some lineages within Cyanobacteria and other phyla individually demonstrated similar or different responses to ZnO NPs and bulk ZnO. Moreover, some lineages associated with plant growth promotion were also influenced to different extents by ZnO NPs and bulk ZnO, suggesting the distinct microbial processes occurring in soil. Collectively, this study expanded our understanding of the influence of ZnO NPs on plant performance and the associated soil microorganisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antisari LV, Carbone S, Gatti A, Vianello G, Nannipieri P (2013) Toxicity of metal oxide (CeO2, Fe3O4, SnO2) engineered nanoparticles on soil microbial biomass and their distribution in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 60:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.01.016
Bandyopadhyay S, Plascencia-Villa G, Mukherjee A, Rico CM, Jose-Yacaman M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2015) Comparative phytotoxicity of ZnO NPs, bulk ZnO, and ionic zinc onto the alfalfa plants symbiotically associated with Sinorhizobium meliloti in soil. Sci Total Environ 515:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.014
Biddle JF, Fitz-Gibbon S, Schuster SC, Brenchley JE, House CH (2008) Metagenomic signatures of the Peru margin subseafloor biosphere show a genetically distinct environment. P Natl Acad Sci USA 105(30):10583–10588. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709942105
Campbell BJ, Polson SW, Hanson TE, Mack MC, Schuur EA (2010) The effect of nutrient deposition on bacterial communities in Arctic tundra soil. Environ Microbiol 12(7):1842–1854. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02189.x
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Chai H, Yao J, Sun J, Zhang C, Liu W, Zhu M, Ceccanti B (2015) The effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on functional bacteria and metabolic profiles in agricultural soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94(4):490–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1485-9
Dimkpa CO (2014) Can nanotechnology deliver the promised benefits without negatively impacting soil microbial life? J Basic Microbiol 54(9):889–904. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201400298
Dimkpa CO, Latta DE, McLean JE, Britt DW, Boyanov MI, Anderson AJ (2013) Fate of CuO and ZnO nano- and microparticles in the plant environment. Environ Sci Technol 47(9):4734–4742. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304736y
Dimkpa CO, Hansen T, Stewart J, McLean JE, Britt DW, Anderson AJ (2015) ZnO nanoparticles and root colonization by a beneficial pseudomonad influence essential metal responses in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Nanotoxicology 9(3):271–278. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2014.900583
Ditta A, Arshad M (2016) Applications and perspectives of using nanomaterials for sustainable plant nutrition. Nanotechnol Rev 5:209–229. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2015-0060
Edgar RC (2017) SEARCH_16S: a new algorithm for identifying 16S ribosomal RNA genes in contigs and chromosomes. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/124131
Frassinetti S, Bronzetti G, Caltavuturo L, Cini M, Della Croce C (2006) The role of zinc in life: a review. J Environ Pathol Toxicol 25(3):597–610. https://doi.org/10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.v25.i3.40
Frenk S, Ben-Moshe T, Dror I, Berkowitz B, Minz D (2013) Effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on microbial community structure and function in two different soil types. PLoS One 8(12):e84441. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084441
Garcia-Gomez C, Obrador A, Gonzalez D, Babin M, Fernandez MD (2017) Comparative effect of ZnO NPs, ZnO bulk and ZnSO4 in the antioxidant defences of two plant species growing in two agricultural soils under greenhouse conditions. Sci Total Environ 589:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.153
Ge YG, Schimel JP, Holden PA (2011) Evidence for negative effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on soil bacterial communities. Environ Sci Technol 45(4):1659–1664. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103040t
Heggelund LR, Diez-Ortiz M, Lofts S, Lahive E, Jurkschat K, Wojnarowicz J, Cedergreen N, Spurgeon D, Svendsen C (2014) Soil pH effects on the comparative toxicity of dissolved zinc, non-nano and nano ZnO to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Nanotoxicology 8(5):559–572. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2013.809808
Jangid K, Williams MA, Franzluebbers AJ, Sanderlin JS, Reeves JH, Jenkins MB (2008) Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil microbial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biol Biochem 40(11):2843–2853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.07.030
Kasemets K, Ivask A, Dubourguier HC, Kahru A (2009) Toxicity of nanoparticles of ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicol In Vitro 23(6):1116–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.05.015
Kennedy IR, Choudhury ATMA, Kecskés ML, Roughley RJ, Hien NT (2005) Non-symbiotic bacterial diazotrophs in crop-farming systems: can their potential for plant growth promotion be better exploited? In: Wang Y-P, Lin M, Tian Z-X, Elmerich C, Newton WE (eds) Biological nitrogen fixation, sustainable agriculture and the environment: proceedings of the 14th international nitrogen fixation congress. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 271–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3570-5_66
Lin D, Xing B (2007) Phytotoxicity of nanoparticles: inhibition of seed germination and root growth. Environ Pollut 150(2):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.01.016
Liu R, Lal R (2015) Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci Total Environ 514:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.104
Liu X, Wang F, Shi Z, Tong R, Shi X (2015) Bioavailability of Zn in ZnO nanoparticle-spiked soil and the implications to maize plants. J Nanopart Res 17(4) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2989-2
Luo YQ, Hui DF, Zhang DQ (2006) Elevated CO2 stimulates net accumulations of carbon and nitrogen in land ecosystems: a meta-analysis. Ecology 87(1):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1890/04-1724
Ma X, Geiser-Lee J, Deng Y, Kolmakov A (2010) Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: phytotoxicity, uptake and accumulation. Sci Total Environ 408(16):3053–3061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.03.031
Mohd Omar F, Abdul Aziz H, Stoll S (2014) Aggregation and disaggregation of ZnO nanoparticles: influence of pH and adsorption of Suwannee River humic acid. Sci Total Environ 468-469:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.044
Monreal CM, DeRosa M, Mallubhotla SC, Bindraban PS, Dimkpa C (2016) Nanotechnologies for increasing the crop use efficiency of fertilizer-micronutrients. Biol Fertil Soils 52(3):423–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-015-1073-5
Mousavi Kouhi SM, Lahouti M, Ganjeali A, Entezari MH (2015) Comparative effects of ZnO nanoparticles, ZnO bulk particles, and Zn2+ on Brassica napus after long-term exposure: changes in growth, biochemical compounds, antioxidant enzyme activities, and Zn bioaccumulation. Water Air Soil Poll 226(11):364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2628-7
Oksanen J et al. (2013) Vegan: Community ecology package. R package version 2.0-7. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Prasad TNVKV, Sudhakar P, Sreenivasulu Y, Latha P, Munaswamy V, Reddy KR, Sreeprasad TS, Sajanlal PR, Pradeep T (2012) Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J Plant Nutr 35(6):905–927. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2012.663443
R Core Team (2017) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Australia. http://www.R-project.org/
Raguvaran R, Anju M, Balvinder KM (2015) Zinc oxide nanoparticles: opportunities and challenges in veterinary sciences. Immunome Res 11:95. https://doi.org/10.4172/1745-7580.1000095
Reddy KJ, Haskell JB, Sherman DM, Sherman LA (1993) Unicellular, aerobic nitrogen-fixing Cyanobacteria of the genus Cyanothece. J Bacteriol 175(5):1284–1292. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.175.5.1284-1292.1993
Reddy PVL, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2016) Lessons learned: are engineered nanomaterials toxic to terrestrial plants? Sci Total Environ 568:470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.042
Rico CM, Majumdar S, Duarte-Gardea M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2011) Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. J Agric Food Chem 59(8):3485–3498. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf104517j
Savoly Z, Hracs K, Pemmer B, Streli C, Zaray G, Nagy PI (2016) Uptake and toxicity of nano-ZnO in the plant-feeding nematode, Xiphinema vuittenezi: the role of dissolved zinc and nanoparticle-specific effects. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(10):9669–9678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5983-4
Sciuto K, Moro I (2015) Cyanobacteria: the bright and dark sides of a charming group. Biodivers Conserv 24(4):711–738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-015-0898-4
Servin A, Elmer W, Mukherjee A, de la Torre-Roche R, Hamdi H, White JC, Bindraban P, Dimkpa C (2015) A review of the use of engineered nanomaterials to suppress plant disease and enhance crop yield. J Nanopart Res 17(2):92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2907-7
Shaymurat T, JX G, CS X, Yang ZK, Zhao Q, Liu YX, Liu YC (2012) Phytotoxic and genotoxic effects of ZnO nanoparticles on garlic (Allium sativum L.): a morphological study. Nanotoxicology 6(3):241–248. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.570462
Shen Z, Chen Z, Hou Z, Li T, Lu X (2015) Ecotoxicological effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on soil microorganisms. Front Env. Sci Eng 9:912–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-015-0789-7
Simonin M, Richaume A (2015) Impact of engineered nanoparticles on the activity, abundance, and diversity of soil microbial communities: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(18):13710–13723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4171-x
Simonin M, Martins JMF, Le Roux X, Uzu G, Calas A, Richaume A (2017) Toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles on soil nitrification at environmentally relevant concentrations: lack of classical dose-response relationships. Nanotoxicology 11(2):247–255. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2017.1290845
Trujillo-Reyes J, Majumdar S, Botez CE, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2014) Exposure studies of core-shell Fe/Fe3O4 and cu/CuO NPs to lettuce (Lactuca sativa) plants: are they a potential physiological and nutritional hazard? J Hazard Mater 267:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.067
Wen X, Wang M, Ti JS, Wu Y, Chen F (2017) Bacterial community composition in the rhizosphere of maize cultivars widely grown in different decades. Biol Fertil Soils 53(2):221–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-016-1169-6
WHO/FAO (2011) Joint FAO/WHO food standard programme-codex committee on contaminants in foods. Hague Netherlands
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Mädler L, Gilbert B, Shi H, Yeh JI, Zink JI, Nel AE (2008) Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano 2(10):2121–2134. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn800511k
Xu K, Juneau P (2016) Different physiological and photosynthetic responses of three cyanobacterial strains to light and zinc. Aquat Toxicol 170:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.11.015
Yan Y, Kuramae EE, de Hollander M, Klinkhamer PGL, van Veen JA (2017) Functional traits dominate the diversity-related selection of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere. Isme J 11(1):56–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2016.108
Yoon SJ, Kwak JI, Lee WM, Holden PA, An YJ (2014) Zinc oxide nanoparticles delay soybean development: a standard soil microcosm study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 100:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.10.014
Zhai Y, Hunting ER, Wouterse M, Peijnenburg W, Vijver MG (2017) Importance of exposure dynamics of metal-based nano-ZnO, -Cu and -Pb governing the metabolic potential of soil bacterial communities. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:349–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.031
Zhang BC, Kong WD, Wu N, Zhang YM (2016) Bacterial diversity and community along the succession of biological soil crusts in the Gurbantunggut Desert, Northern China. J Basic Microbiol 56(6):670–679. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201500751
Zhao L, Sun Y, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Hong J, Majumdar S, Niu G, Duarte-Gardea M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2015) Monitoring the environmental effects of CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles through the life cycle of corn (Zea mays) plants and in situ m-XRF mapping of nutrients in kernels. Environ Sci Technol 49(5):2921–2928. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5060226
Zhao LJ et al (2013) Influence of CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on cucumber physiological markers and bioaccumulation of Ce and Zn: a life cycle study. J Agric Food Chem 61(49):11945–11951. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404328e
Acknowledgements
We thank Lisa A. Boughner from the Center for Microbial Ecology, Michigan State University, for polishing the manuscript and improving the points of view of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41501264), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20140991), the CAS Strategic Priority Research Program Grant (XDB15020103), the Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture, Nanjing Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Science (Y412201441), the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, and the foundation from the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Thomas D. Bucheli
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Luo, X., Wang, Y. et al. Evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles on lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth and soil bacterial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 6026–6035 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0953-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0953-7