Abstract
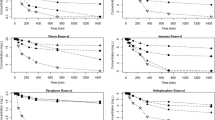
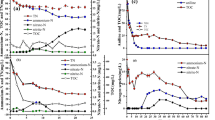
Aerobic denitrifiers coupled with a denitrification agent were applied in the sediment of an urban river for the bioremediation of nitrogen pollution. The results revealed that 14.7% of the total nitrogen in the sediment was removed after 115 days of treatment and the nitrate nitrogen concentration removal rate was enhanced in the overlying water. Compared with the control, the total transferable nitrogen in the sediment increased from 0.097 to 0.166 mg/g, indicating that more nitrogen is likely to be involved in the biogeochemical cycling of nitrogen. Increased urease activity indicated the possible further potential of nitrogen biodegradation, while the decreased protease pointed to the low concentration of protein remaining in the sediment. Sequencing revealed that the bacterial community diversity in the sediment increased significantly after 43 days of treatment and that the effect persisted. Compared with other microcosms, the dominant phyla in the sediment after 43 days were Firmicutes, Elusimicrobia, Spirochaetae and Fibrobacteres; whereas, after 115 of treatment, the dominant bacteria were Nitrospirae, Deferribacteres and Chloroflexi. The dominant bacteria in the sediment are mainly associated with nitrogen cycling and thus contributed considerably to nitrogen removal in the sediment. Overall, the direction of species succession was similar to natural succession; namely, there were no undesirable ecological risks involved. This study highlights the possible benefits and feasibility of using bioaugmentation technology coupled with biostimulation to remediate nitrogen-polluted sediments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burns RG, Forest JLD, Marxsen J, Sinsabaugh RL, Stromberger ME, Wallenstein MD, Weintraub MN, Zoppini A (2013) Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol Biochem 58:216–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.11.009
Camargo JA, Alonso A (2006) Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: a global assessment. Environ Int 32(6):831–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.002
Chang BV, Yuan SY, Ren YL (2012) Aerobic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol-a by microbes in river sediment. Chemosphere 87(5):535–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.057
Chen F, Ke Z, Zhou J, Yang J, Peng W (2007) Control of Lake Eutrophication by compound bacterium. China. Environ Sci Technol 30(5):29–32
Chen Q, Ni J, Ma T, Liu T, Zheng M (2015) Bioaugmentation treatment of municipal wastewater with heterotrophic-aerobic nitrogen removal bacteria in a pilot-scale SBR. Bioresour Technol 183:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.022
Chen C, Xu X, Xie P, Yuan Y, Zhou X, Wang A, Lee D, Ren N (2017) Pyrosequencing reveals microbial community dynamics in integrated simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification process at different influent nitrate concentrations. Chemosphere 171:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.159
Dick RP (1994) Soil enzyme activities as indicators of soil quality. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:107–124
Farhadian M, Vachelard C, Duchez D, Larroche C (2008) In situ bioremediation of monoaromatic pollutants in groundwater: a review. Bioresour Technol 99(13):5296–5308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.025
Garcia-Blanco S, Venosa AD, Suidan MT, Lee K, Cobanli S, Haines JR (2007) Biostimulation for the treatment of an oil-contaminated coastal salt marsh. Biodegradation 18(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-9029-3
Gittel A, Kofoed MVW, Sorensen KB, Ingvorsen K, Schramm A (2012) Succession of Deferribacteres and Epsilonproteobacteria through a nitrate-treated high-temperature oil production facility. Syst Appl Microbiol 35(3):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2012.01.003
Guan S (1986) Soil enzyme and its research methods, 1st edn. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Guo L, Chen Q, Fang F, Hu Z, Wu J, Miao A, Xiao L, Chen X, Yang L (2013) Application potential of a newly isolated indigenous aerobic denitrifier for nitrate and ammonium removal of eutrophic lake water. Bioresour Technol 142(4):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.05.021
He T, Guan W, Luan Z, Xie S (2016) Spatiotemporal variation of bacterial and archaeal communities in a pilot-scale constructed wetland for surface water treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:479–1488
Herlemann DPR, Geissinger O, Ikeda-Ohtsubo W, Kunin V, Sun H, Lapidus A, Hugenholtz P, Brune A (2009) Genomic analysis of “Elusimicrobium minutum,” the first cultivated representative of the phylum “Elusimicrobia”. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(9):2841–2849. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02698-08
Huang C, Shi Y, El-Din MG, Liu Y (2016) Optimization of ozonation combined with integrated fixed-film activated sludge (IFAS) in the treatment of oil sands process-affected water (OSPW). Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 112:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.037
Jiang X, Wang W, Wang S, Jin X (2012) Calculation of environmental dredging depth of heavy metal polluted sediments in Zhushan Bay of Taihu Lake. Environ Sci 33(4):1189–1197
Jiao Y, Zhao Q, Jin W, Hao X, You S (2011) Bioaugmentation of a biological contact oxidation ditch with indigenous nitrifying bacteria for in situ remediation of nitrogen-rich stream water. Bioresour Technol 102(2):990–995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.061
Kampmann K, Ratering S, Kramer I, Schmidt M, Zerr W, Schnell S (2012) Unexpected stability of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes communities in laboratory biogas reactors fed with different defined substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(7):2106–2119. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06394-11
Knowles R (1982) Denitrification. Microbiol Rev 46(1):43–70
Lang FS, Destain J, Delvigne F, Druart P, Ongena M, Thonart P (2016) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in mangrove sediments under different strategies: natural attenuation, biostimulation, and bioaugmentation with Rhodococcus erythropolis T902.1. Water Air Soil Pollut 227(9):297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2999-4
Lee S, Park J, Kang H, Lee Y, Lee T, Park H (2013) Distribution and abundance of Spirochaetes in full-scale anaerobic digesters. Bioresour Technol 145:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.070
Li D, Huang Y, Li W (2007) Study on remediation of city river water body by technology of aerating sediments. China Water Wastewater 23(5):22–25
Li X, Wu S, Shen Y, Ning Y, Zhang X, Sun X, Zhang B, Chen J (2015) Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by four novel isolated bacteria. Pol J Environ Stud 24(4):1677–1682. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/35392
Lin X (2010) Soil microbial research principles and methods, 1st edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Liu J, Zhang S, Yang Z, He L, Zhou N, Zhang Q (2015) Effect of drought and subsequent re-wetting cycles on transferable nitrogen and its form distribution in the sediment of water level fluctuating zone in the tributary of three gorge reservoir areas. Environ Sci 36(7):2459–2464
Lv M (2016) Effect and mechanism of chemical and biological collaborative remediation to river sediment. Dissertation, Tianjin University
Lv X, Song J, Yuan H, Li X, Zhan T, Li N, Gao X (2004) The potential ecological roles of nitrogen in the surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea. Acta Ecol Sin 24(8):1635–1643
Ma H, Song J, Lv X (2002) Nitrogen forms and decomposition of organic carbon in the southern Bohai Sea core sediments. Acta Oceanol Sin 24(5):64–70
Miura Y, Watanabe Y, Okabe S (2007) Significance of Chloroflexi in performance of submerged membrane bioreactors (MBR) treating municipal wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 41(22):7787–7794. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071263x
Moreno JL, Garcia C, Hernandez T (2003) Toxic effect of cadmium and nickel on soil enzymes and the influence of adding sewage sludge. Eur J Soil Sci 54(2):377–386. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.00533.x
Morgante V, López-López A, Flores C, González M, González B, Vásquez M, Rosselló-Mora R, Seeger M (2010) Bioaugmentation with Pseudomonas sp. strain MHP41 promotes simazine attenuation and bacterial community changes in agricultural soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72(1):152–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00834.x
National Environment Protection Agency of China (NEPAC) (2002) Standard analysis methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 4th version. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing
Pai S, Chong N, Chen C (1999) Potential applications of aerobic denitrifying bacteria as bioagents in wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 68(2):179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(98)00140-0
Pan Q, Luo Z, Qiu Z, Yan C (2011) Distribution characteristics of nitrogen forms in surface sediments of Jiulongjiang Estuary Wetland. Res Environ Sci 24(6):673–678
Park J, Krumins V, Kjellerup BV, Fennell DE, Rodenburg LA, Sowers KR, Kerkhof LJ, Haggblom MM (2011) The effect of co-substrate activation on indigenous and bioaugmented PCB dechlorinating bacterial communities in sediment microcosms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(6):2005–2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2958-8
Pei L, Peng D, Wei J, Wang B, Zhang X, Yu L (2014) Nitrogen removal from an AAO pilot plant with nitrifier bioaugmentation after seasonal deterioration. Desalin Water Treat 55(6):1–8
Pourabadehei M, Mulligan CN (2016) Resuspension of sediment, a new approach for remediation of contaminated sediment. Environ Pollut 213:63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.01.082
Ransom-Jones E, Jones DL, Edwards A, Donald JEM (2014) Distribution and diversity of members of the bacterial phylum Fibrobacteres in environments where cellulose degradation occurs. Syst Appl Microbiol 37(7):502–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2014.06.001
Reynolds CM, Wolf DC, Armbruster JA (1985) Factors related to urea hydrolysis in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49(1):104–108. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900010021x
Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1983) Thiosphaera pantotropha gen. nov. sp. nov., a facultatively anaerobic, facultatively autotrophic sulphur bacterium. J Gen Microbiol 129(9):2847–2855
Sarnaik SS, Phalke VV, Kanekar PP (2015) Removal of ammoniacal nitrogen from fish processing wastewater using bioaugmentation technique. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 6(1):1021–1029
SØndergaard M, Jeppesen E, Lauridsen TL, Skov C, Nes EHV, Roijackers R, Lammens E, Portielje R (2007) Lake restoration: successes, failures and long-term effects. J Appl Ecol 44(6):1095–1105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01363.x
Standardization Administration of China (SAC) (2009) Water quality—determination of total organic carbon-combustion oxidation nondispersive infrared absorption method. Standards press of china, Beijing
Standardization Administration of China (SAC) (2014) Method for the determination of soli total nitrogen (modified Kjeldahl method). Standards press of china, Beijing
Subha B, Song YC, Woo JH (2017) Bioremediation of contaminated coastal sediment: optimization of slow release biostimulant ball using response surface methodology (RSM) and stabilization of metals from contaminated sediment. Mar Pollut Bull 114(1):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.034
Sun L, Feng C, Liu Y, Jin H (2009) Nitrogen removal from Pearl River by enhanced ecological floating bed system. Acta Sci Nat Univ Sunyatseni 48(1):93–97
Tyagi M, Fonseca MMRD, Carvalho CCCRD (2011) Bioaugmentation and biostimulation strategies to improve the effectiveness of bioremediation processes. Biodegradation 22(2):231–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9394-4
Wang X (2011) Biochemical collaborative remediation and optimization of polluted sediment. Dissertation, Tianjin University
Wang S (2013) Sediment-water interface process of lakes: nitrogen and phosphorus biogeochemistry, 1st edn. Science Press, Beijing
Wang S, Jin X, Jiao L, Wu F (2008) Nitrogen fractions and release in the sediments from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River area, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 187:5–14
Wang M, Liu Y, Zheng B, Zhou J, Jiang Q (2014) Nitrogen forms in surface sediments of urban river and their influence factors: a case study of Qingyi River in Xuchang City. China Environ Sci 34(3):720–726
Wilczek S, Fischer H, Pusch MT (2004) Regulation and seasonal dynamics of extracellular enzyme activities in the sediments of a large lowland river. Microb Ecol 50:253–267
Xiong J, Li G, An T (2017) The microbial degradation of 2,4,6-tribromophenol (TBP) in water/sediments interface: investigating bioaugmentation using Bacillus sp. GZT. Sci Total Environ 575:573–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.017
Yang L, Lin F, Xu Z, Zhang M, Gao Y (2007) Effect of temperature on the activities of microorganism and the pollutants release in the bioremediation of the sediment. Environ Pollut Cont 29(1):22–29
Zhang B, Chen Y, Fang F, Li Z, Guo J, Wang Z (2012a) Nitrogen forms and their distribution characteristics in the soils of water-level—luctuationg zone in the central Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Sci Circumst 32(5):1126–1133
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Ai G, Miao L, Zheng H, Liu Z (2012b) The characteristics of a novel heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium, Bacillus methylotrophicus strain L7. Bioresour Technol 108:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.139
Zheng H, Dietrich C, Radek R, Brune A (2016) Endomicrobium proavitum, the first isolate of Endomicrobia class. nov. (phylum Elusimicrobia)—an ultramicrobacterium with an unusual cell cycle that fixes nitrogen with a group IV nitrogenase. Environ Microbiol 18(1):191–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12960
Zhou S, Huang T, Ngo HH, Zhang H, Liu F, Zeng M, Shi J, Qiu X (2016) Nitrogen removal characteristics of indigenous aerobic denitrifiers and changes in the microbial community of a reservoir enclosure system via in situ oxygen enhancement using water lifting and aeration technology. Bioresour Technol 214:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.04.071
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the National Nature Science Foundation of China (51378339) and Ministry of Water Resources’ special funds for scientific research on public causes (201401047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification abilities of aerobic denitrifiers under aeration condition. a Ability of aerobic denitrification. b Ability of heterotrophic nitrification. (PDF 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Li, M., Xu, D. et al. Application potential of aerobic denitrifiers coupled with a biostimulant for nitrogen removal from urban river sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 5980–5993 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0903-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0903-4