Abstract
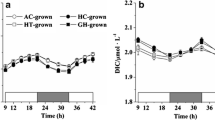
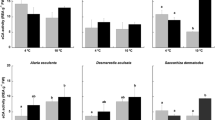
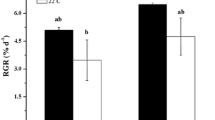
To estimate the combined effects of elevated CO2 and temperature on microalgae, three typical and worldwide freshwater species, the green alga Scenedesmus acuminatus, the diatom Cyclotella meneghiniana, and the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa, as well as mixes of these three species were continuously cultured in controlled environment chambers with CO2 at 390 and 1000 ppm and temperatures of 20, 25, and 30 °C. CO2 and temperature significantly affected the production of microalgae. The cell productivity increased under elevated CO2 and temperature. Although the green alga dominated in the mixed culture within all CO2 and temperature conditions, rising temperature and CO2 intensified the competition of the cyanobacterium with other microalgae. CO2 affected the extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) characteristics of the green alga and the cyanobacterium. Elevated CO2 induced the generation of humic substances in the EPS fractions of the green alga, the cyanobacterium, and the mixed culture. The extracellular carbohydrates of the diatom and the extracellular proteins of the cyanobacterium increased with elevated CO2 and temperature, while the extracellular carbohydrates and proteins of the green alga and the mixes increased under elevated CO2 and temperature. There were synergistic effects of CO2 and temperature on the productivity and the EPS of microalgae. Climate change related CO2 and temperature increases will promote autochthonous organic carbon production in aquatic ecosystems and facilitate the proliferation of cyanobacteria, which potentially changes the carbon cycling and undermines the functioning of ecosystems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo-Trejos E, Brandt G, Bruggeman J, Merico A (2015) Mechanisms shaping size structure and functional diversity of phytoplankton communities in the ocean. Sci Rep 5:8918
Attermeyer K, Premke K, Hornick T, Hilt S, Grossart HP (2013) Ecosystem-level studies of terrestrial carbon reveal contrasting bacterial metabolism in different aquatic habitats. Ecology 94:2754–2766
Bade DL, Carpenter SR, Cole JJ, Pace ML, Kritzberg E, Van de Bogert MC, Cory RM, McKnight DM (2007) Sources and fates of dissolved organic carbon in lakes as determined by whole-lake carbon isotope additions. Biogeochemistry 84:115–129
Badger MR, Price GD, Long BM, Woodger FJ (2006) The environmental plasticity and ecological genomics of the cyanobacteriuml CO2 concentrating mechanism. J Exp Bot 57:249–265
Beardall J, Young E, Roberts S (2001) Approaches for determining phytoplankton nutrient limitation. Aquat Sci 63:44–69
Bennett EM, Carpenter SR, Caraco NF (2001) Human impact on erodable phosphorus and eutrophication: a global perspective. Bioscience 51:227–234
Brönmark C, Hannson LA (2005) The biology of lakes and ponds. Oxford University Press, Oxford Chapter 3
Butterwick C, Heaney SI, Talling JF (2005) Diversity in the influence of temperature on the growth rates of freshwater algae, and its ecological relevance. Freshw Biol 50:291–300
Caceres CE, Schwalbach MS (2001) How well do labo- ratory experiments explain field patterns of zooplankton emergence? Freshw Biol 46:1179–1189
Carpenter SR (1996) Microcosm experiments have limited relevance for community and ecosystem ecology. Ecology 77:677–680
Dodds WK, Bouska WW, Eitzmann JL, Pilger TJ, Pitts KL, Riley AJ, Schloesser JT, Thornbrugh DJ (2009) Eutrophication of US freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environ Sci Technol 43:12–19
Falkowski PG, Greene RM, Geider RJ (1992) Physiological limitations on phytoplankton productivity in the ocean. Oceanography 5:84–91
Fajon C, Cauwet C, Lebaron P, Terzic S, Ahel M, Malej A, Mozetic P, Turk V (1999) The accumulation and release of polysaccharides by planktonic cells and the subsequent bacterial response during a controlled experiment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 29:351–363
Fowler D, Coyle M, Skiba U, Sutton MA, Cape JN, Reis S, Sheppard LJ, Jenkins A, Grizzetti B, Galloway JN, Vitousek P, Leach A, Bouwman AF, Butterbach-Bahl K, Dentener F, Stevenson D, Amann M, Voss M (2013) The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Philos Trans R Soc B-Biol Sci 368:20130164
Frølund B, Griebe T, Nielsen PH (1995) Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:755–761
Hanson PC, Hamilton DP, Stanley EH, Preston N, Langman OC, Kara EL (2011) Fate of allochthonous dissolved organic carbon in lakes: a quantitative approach. PLoS One 6:e21884
Hasler CT, Butman D, Jeffrey JD, Suski CD (2016) Freshwater biota and rising pCO2? Ecol Lett 19:98–108
Hodaifa G, Martinez ME, Sanchez S (2010) Influence of temperature on growth of Scenedesmus obliquus in diluted olive mill wastewater as culture medium. Eng Life Sci 10:257–264
Horner-Devine MC, Leibold MA, Smith VH, Bohannan BJM (2003) Bacterial diversity patterns along a gradient of primary productivity. Ecol Lett 6:613–622
Ibelings BW, Gsell AS, Mooij WM, van Donk E, van den Wyngaert S, Domis LND (2011) Chytrid infections and diatom spring blooms: paradoxical effects of climate warming on fungal epidemics in lakes. Freshw Biol 56:754–766
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2013. Fifth assessment report: Climate change 2013: the physical science basis: Chapter 11
Kilham SS, Kreeger DA, Lynn SG, Goulden CE, Herrera L (1998) COMBO: a defined freshwater culture medium for algae and zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 377:147–159
Kingsolver JG (2009) The well-temperatured biologist. Am Nat 174:755–768
Kruk C, Segura AM (2012) The habitat template of phytoplankton morphology-based functional groups. Hydrobiologia 698:191–202
Low-Décarie E, Fussmann GF, Bell G (2011) The effect of elevated CO2 on growth and competition in experimental phytoplankton communities. Glob Chang Biol 17:2525–2535
Low-Décarie E, Jewell MD, Fussmann GF, Bell G (2013) Long-term culture at elevated atmospheric CO2 fails to evoke specific adaptation in seven freshwater phytoplankton species. Proc R Soc B 280:20122598
Low-Décarie E, Fussmann GF, Bell G (2014) Aquatic primary production in a high-CO2 world. Trends Ecol Evol 29:223–232
Low-Décarie E, Bell G, Fussmann GF (2015) CO2 alters community composition and response to nutrient enrichment of freshwater phytoplankton. Oecologia 177:875–883
Lürling M, Eshetu F, Faassen EJ, Kosten S, Huszar VL (2013) Comparison of cyanobacteriuml and green algal growth rates at different temperatures. Freshw Biol 58:552–559
Maberly SC (1985) Photosynthesis by Fontinalis antipyretica. I. Interaction between photon irradiance, concentration of carbon and temperature. New Phytol 100:127–140
Maksimova IV, Bratkovskaya LB, Plekhanov SE (2004) Extracellular carbohydrates and polysaccharides of the alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa Chick S-39. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 31:175–181
Müller-Navarra DC, Brett MT, Liston AM, Goldman CR (2000) A highly unsaturated fatty acid predicts carbon transfer between primary producers and consumers. Nature 403:74–77
Müller-Navarra DC, Brett MT, Park S, Chandra S, Ballantyne AP, Zorita E, Goldman CR (2003) Unsaturated fatty acid content in seston and tropho-dynamic coupling in lakes. Nature 427:69–72
O’Neil JM, Davis TW, Burford MA, Gobler CJ (2012) The rise of harmful cyanobacterium blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14:313–334
Paerl HW, Huisman J (2009) Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacteriuml blooms. Environ Microbiol Rep 1:27–37
Paerl HW, Otten TG (2013) Blooms bite the hand that feeds them. Science 342:433–434
Paerl HW, Paul VJ (2012) Climate change: links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacterium. Water Res 46:1349–1363
Pagani M, Huber M, Liu ZH, Bohaty SM, Henderiks J, Sijp W, Krishnan S, DeConto RM (2011) The role of carbon dioxide during the onset of Antarctic glaciation. Science 334:1261–1264
Petrin Z, Englund G, Malmqvist B (2008) Contrasting effects of anthropogenic and natural acidity in streams: a meta-analysis. Proc R Soc B-Biol Sci 275:1143–1148
Potts M (1994) Desiccation tolerance of prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev 58:755–805
Reynolds C, Huszar V, Kruk C, Naselli-Flores L, Melo S (2002) Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J Plankton Res 24:417–428
Reynolds CS (2006) Ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Oxford, UK Chapter 3-6
Royer DL (2006) CO2-forced climate thresholds during the Phanerozoic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:5665–5675
Song XL, Liu ZW, Pan HK, Yang GJ, Chen YW (2007) Phytoplankton community structure in Meiliang Bay and Lake Wuli of Lake Taihu. J Lake Sci 19:643–651
Shafik HM, Herodek S, Voros L, Presing M, Kiss KT (1997) Growth of Cyclotella meneghiniana Kutz. 1. Effects of temperature, light and low rate of nutrient supply. Ann De Limnol Int J Limnol 33:139–147
Shiraiwa Y, Miyachi S (1985) Effects of temperature and CO2 concentration on induction of carbonic anhydrase and changes in efficiency of photosynthesis in Chlorella vulgaris 11 h. Plant Cell Physiol 26:543–549
Smil V (2000) Phosphorus in the environment: natural flows and human interferences. Annu Rev Energy Environ 25:53–88
Smith, V. H. 2009. Eutrophication. In: Likens GE (ed) Encyclopedia of inland waters, Elsevier: Chapter 2
Sterner RW, Hessen DO (1994) Algal nutrient limitation and the nutrition of aquatic herbivores. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 25:1–29
Tortell PD (2000) Evolutionary and ecological perspectives on carbon acquisition in phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 45:744–750
Tilman D, Kiesling R, Sterner R, Tilman S (1986) Green, blue-green and diatom algae: taxonomic differences in competitive ability for phosphorus, silicon, and nitrogen. Arch Hydrobiol 106:473–485
Urabe J, Watanabe Y (1992) Possibility of N or P limitation for planktonic cladocerans: an experimental test. Limnol Oceanogr 37:244–251
Urabe J, Waki N (2009) Mitigation of adverse effects of rising CO2 on a planktonic herbivore by mixed algal diets. Glob Chang Biol 15:523–531
Verschoor AM, Van Dijk MA, Huisman JEF, Van Donk E (2013) Elevated CO2 concentrations affect the elemental stoichiometry and species composition of an experimental phytoplankton community. Freshw Biol 58:597–611
Wang X, Zhang YL (2007) Experimental study on spectral absorption and scattering properties of Microcystis and Scenedesmus. Trans in Oceanol Limnol S:82–90
Watt WD (1966) Release of dissolved organic material from cells of phytoplankton populations. Proc R Soc Ser B-Biol Sci 164:521
Webb BW, Hannah DM, Moore RD, Brown LE, Nobilis F (2008) Recent advances in stream and river temperature research. Hydrol Process 22:902–918
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lake and river ecosystems, 3rd edn. Academic, San Diego Chapter 3
Winder M, Reuter JE, Schladow SG (2009) Lake warming favours small-sized planktonic diatom species. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 276:427–435
Woodward G, Friberg N, Hildrew AG (2009) The need for scientific rigour in biomonitoring and conservation of freshwaters. Freshwater ecosystems: biodiversity, management and conservation. Nova, Hauppage, NY Chapter 4
Wu XH, Wu ZX, Song LR (2011) Phenotype and temperature affect the affinity for dissolved inorganic carbon in a cyanobacterium Microcystis. Hydrobiologia 675:175–186
Xu X, Li W, Fujibayashi M, Nomura M, Sakamaki T, Nishimura O, Li X (2014) Feedback of threshold via estimating sources and composition of sedimentary organic matter across trophic gradients in freshwater lakes. Sci Total Environ:500–501 373–382
Zhang XQ, Bishop PL, Kinkle BK (1999) Comparison of extraction methods for quantifying extracellular polymers in biofilms. Water Sci Technol 39:211–218
Ziegmann M, Abert M, Muller M, Frimmel FH (2010) Use of fluorescence fingerprints for the estimation of bloom formation and toxin production of Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res 44:195–204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 161 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Xu, X., Fujibayashi, M. et al. Response of microalgae to elevated CO2 and temperature: impact of climate change on freshwater ecosystems. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 19847–19860 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7180-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7180-5