Abstract
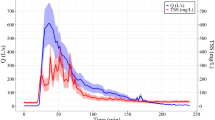
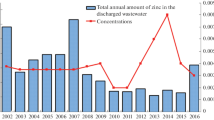
This study investigates the temporal variability of zinc concentrations from zinc roof runoff. The influence of rainfall characteristics and dry period duration is evaluated by combining laboratory experiment on small zinc sheets and in situ measurements under real weather conditions from a 1.6-m2 zinc panel. A reformulation of a commonly used conceptual runoff quality model is introduced and its ability to simulate the evolution of zinc concentrations is evaluated. A systematic and sharp decrease from initially high to relatively low and stable zinc concentrations after 0.5 to 2 mm of rainfall is observed for both experiments, suggesting that highly soluble corrosion products are removed at early stages of runoff. A moderate dependence between antecedent dry period duration and the magnitude of zinc concentrations at the beginning of a rain event is evidenced. Contrariwise, results indicate that concentrations are not significantly influenced by rainfall intensities. Simulated rainfall experiment nonetheless suggests that a slight effect of rainfall intensities may be expected after the initial decrease of concentrations. Finally, this study shows that relatively simple conceptual runoff quality models may be adopted to simulate the variability of zinc concentrations during a rain event and from a rain event to another.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alley WM (1981) Estimation of impervious-area washoff parameters. Water Resour Res. doi:10.1029/WR017i004p01161
Alley WM, Smith PE (1981) Estimation of accumulation parameters for urban runoff quality modeling. Water Resour Res. doi:10.1029/WR017i006p01657
Athanasiadis K, Horn H, Helmreich B (2010) A field study on the first flush effect of copper roof runoff. Corros Sci 52:21–29. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2009.08.048
Bertling S, Odnevall Wallinder I, Leygraf C, Berggren Kleja D (2006) Occurrence and fate of corrosion-induced zinc in runoff water from external structures. Sci Total Environ 367:908–923. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.01.008
Beven K (1993) Prophecy, reality and uncertainty in distributed hydrological modelling. Adv Water Resour 16:41–51. doi:10.1016/0309-1708(93)90028-E
Beven K, Binley A (1992) The future of distributed models: model calibration and uncertainty prediction. Hydrol Process 6:279–298. doi:10.1002/hyp.3360060305
Bielmyer G, Arnold WR, Tomasso J, Isely J, Klaine S (2012) Effects of roof and rainwater characteristics on copper concentrations in roof runoff. Environ Monit Assess 184:2797–2804. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2152-1
Bressy A (2010) Flux de micropolluants dans les eaux de ruissellement urbaines. Effets de différents modes de gestion des eaux pluviales. Université Paris Est, France
Bressy A, Gromaire MC, Lorgeoux C, Saad M, Leroy F, Chebbo G (2012) Towards the determination of an optimal scale for stormwater quality management: micropollutants in a small residential catchment. Water Res 46:6799–6810. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2011.12.017
Chib S, Greenberg E (1995) Understanding the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm. J Am Stat Assoc 49:327–335. doi:10.2307/2684568
Del Giudice D, Honti M, Scheidegger A, Albert C, Reichert P, Rieckermann J (2013) Improving uncertainty estimation in urban hydrological modeling by statistically describing bias. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:4209–4225. doi:10.5194/hess-17-4209-2013
Deletic A, Dotto CBS, McCarthy DT, Kleidorfer M, Freni G, Mannina G, Uhl M, Henrichs M, Fletcher TD, Rauch W, Bertrand-Krajewski JL, Tait S (2012) Assessing uncertainties in urban drainage models. Phys Chem Earth 42–44:3–10. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2011.04.007
Dotto CBS, Kleidorfer M, Deletic A, Rauch W, McCarthy DT, Fletcher TD (2011) Performance and sensitivity analysis of stormwater models using a Bayesian approach and long-term high resolution data. Environ Model Softw 26:1225–1239. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2011.03.013
Dotto CBS, Deletic A, McCarthy DT (2013) Uncertainty analysis in urban drainage modelling: should we break our back for normally distributed residuals? Water Sci Technol 68:1271–1279. doi:10.2166/wst.2013.360
Fallah Shorshani M, Bonhomme C, Petrucci G, André M, Seigneur C (2014) Road traffic impact on urban water quality: a step towards integrated traffic, air and stormwater modelling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:5297–5310. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-2370-x
Fallah Shorshani M, André M, Bonhomme C, Seigneur C (2015) Modelling chain for the effect of road traffic on air and water quality: techniques, current status and future prospects. Environ Model Softw 64:102–123. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.11.020
Förster J (1996) Patterns of roof runoff contamination and their potential implications on practice and regulation of treatment and local infiltration. Water Sci Technol 33:39–48. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(96)00329-0
Freni G, Mannina G, Viviani G (2009) Urban runoff modelling uncertainty: comparison among Bayesian and pseudo-Bayesian methods. Environ Model Softw 24:1100–1111. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2009.03.003
Gnecco I, Berretta C, Lanza LG, La Barbera P (2005) Storm water pollution in the urban environment of Genoa, Italy. Atmos Res 77:60–73. doi:10.1016/j.atmosres.2004.10.017
Gromaire MC, Garnaud S, Saad M, Chebbo G (2001) Contribution of different sources to the pollution of wet weather flows in combined sewers. Water Res 35:521–533. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00261-X
Gromaire M, Robert-Sainte P, Bressy A, Saad M, De Gouvello B, Chebbo G (2011) Zn and Pb emissions from roofing materials—modelling and mass balance attempt at the scale of a small urban catchment. Water Sci Technol 63:2590–2597
Gromaire MC, Van de Voorde A, Lorgeoux C, Chebbo G (2015) Benzalkonium runoff from roofs treated with biocide products—in situ pilot-scale study. Water Res 81:279–287. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.060
Hasting WK (1970) Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57:97–109. doi:10.1093/biomet/57.1.97
He W (2002) Atmospheric corrosion and runoff processes on copper and zinc as roofing materials (Ph.D. Thesis). Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm
He W, Odnevall Wallinder I, Leygraf C (2001) A laboratory study of copper and zinc runoff during first flush and steady-state conditions. Corros Sci. doi:10.1016/S0010-938X(00)00066-4
Kanso A, Tassin B, Chebbo G (2005) A benchmark methodology for managing uncertainties in urban runoff quality models. Water Sci Technol 51:163–170
Kanso A, Chebbo G, Tassin B (2006) Application of MCMC-GSA model calibration method to urban runoff quality modeling. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 91:1398–1405. doi:10.1016/j.ress.2005.11.051
Karlén C, Odnevall Wallinder I, Heijerick D, Leygraf C, Janssen CR (2001) Runoff rates and ecotoxicity of zinc induced by atmospheric corrosion. Sci Total Environ 277:169–180. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00872-X
Lee JG, Selvakumar A, Alvi K, Riverson J, Zhen JX, Shoemaker L, Lai F (2012) A watershed-scale design optimization model for stormwater best management practices. Environ Model Softw 37:6–18. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2012.04.011
Leuenberger-Minger AU, Buchmann B, Faller M, Richner P, Zöbeli M (2002) Dose-response functions for weathering steel, copper and zinc obtained from a four-year exposure programme in Switzerland. Corros Sci 44:675–687. doi:10.1016/S0010-938X(01)00097-X
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Persson D, Kucera V (2001) Release of metals from buildings, constructions and products during atmospheric exposure in Stockholm. Water Air Soil Pollut 1:133–150. doi:10.1023/A:1017556105259
Reiss D, Rihm B, Thöni C, Faller M (2004) Mapping stock at risk and release of zinc and copper in Switzerland—dose response functions for runoff rates derived from corrosion rate data. Water Air Soil Pollut 159:101–113. doi:10.1023/B:WATE.0000049163.18416.ec
Robert-Sainte P (2009) Contribution des matériaux de couverture à la contamination métallique des eaux de ruissellement [contribution of roofing materials to the metal contamination of runoff]. Université Paris-Est (France), Paris
Sage J, Bonhomme C, Al Ali S, Gromaire M-C (2015) Performance assessment of a commonly used “accumulation and wash-off” model from long-term continuous road runoff turbidity measurements. Water Res 78:47–59. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.03.030
Schoups G, Vrugt JA (2010) A formal likelihood function for parameter and predictive inference of hydrologic models with correlated, heteroscedastic, and non-Gaussian errors. Water Resour Res 46. doi:10.1029/2009WR008933
Schriewer A, Horn H, Helmreich B (2008) Time focused measurements of roof runoff quality. Corros Sci 50:384–391. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2007.08.011
Thyer M, Renard B, Kavetski D, Kuczera G, Franks SW, Srikanthan S (2009) Critical evaluation of parameter consistency and predictive uncertainty in hydrological modeling: a case study using Bayesian total error analysis. Water Resour Res 45 doi:10.1029/2008WR006825
Tsihrintzis VA, Hamid R (2001) Modeling and management of urban stormwater runoff quality: a review. Water 11:137–164. doi:10.1023/A:1007903817943
Van de Voorde A (2012) Incidence des pratiques d’entretien des toitures sur la qualité des eaux de ruissellement : cas des traitements par produits biocides [effect of roof maintenance practices on runoff quality : case of biocidal treatments] (Ph.D. Thesis). Université Paris-Est (France)
Vezzaro L, Mikkelsen PS (2012) Application of global sensitivity analysis and uncertainty quantification in dynamic modelling of micropollutants in stormwater runoff. Environ Model Softw 27–28:40–51. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2011.09.012
Vezzaro L, Sharma AK, Ledin A, Mikkelsen PS (2015) Evaluation of stormwater micropollutant source control and end-of-pipe control strategies using an uncertainty-calibrated integrated dynamic simulation model. J Environ Manag 151:56–64. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.12.013
Wang QJ, Shrestha DL, Robertson DE, Pokhrel P (2012) A log-sinh transformation for data normalization and variance stabilization. Water Resour Res 48 doi:10.1029/2011WR010973
Wicke D (2014) Effect of age and rainfall pH on contaminant yields from metal roofs. Water Sci Technol 69:2166–2173. doi:10.2166/wst.2014.124
Yang J, Reichert P, Abbaspour KC (2007) Bayesian uncertainty analysis in distributed hydrologic modeling: a case study in the Thur River basin (Switzerland). Water Resour Res. doi:10.1029/2006WR005497
Yaziz MI, Gunting H, Sapari N, Ghazali AW (1989) Variations in rainwater quality from roof catchments. Water Res. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(89)90211-X
Zhang X, He W, Odnevall Wallinder I, Pan J, Leygraf C (2002) Determination of instantaneous corrosion rates and runoff rates of copper from naturally patinated copper during continuous rain events. Corros Sci 44:2131–2151. doi:10.1016/S0010-938X(02)00015-X
Zobrist J, Müller SR, Ammann A, Bucheli TD, Mottier V, Ochs M, Schoenenberger R, Eugster J, Boller M (2000) Quality of roof runoff for groundwater infiltration. Water Res 34:1455–1462. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00290-0
Acknowledgments
This research has been carried out under the OPUR research program. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Seine-Normandy Water Agency, Val-de-Marne Departmental Council, Seine-Saint-Denis Departmental Council, Hauts-de-Seine Departmental Council, City of Paris, and the Interdepartmental Association for Sewerage Services in the Paris Metropolitan Area (SIAAP), and the French Ministry of Ecology Sustainable Development and Energy for financial support. The authors additionally acknowledge use of the installations of the Scientific and Technical Centre for Building (CSTB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Marcus Schulz
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
A.1—Analysis of the innovations (results shown at the maximum of likelihood for the initial model formulation)—A.1a: autocorrelation plot, A.1b: quantile-quantile plot of innovations (DOCX 73 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sage, J., El Oreibi, E., Saad, M. et al. Modeling the temporal variability of zinc concentrations in zinc roof runoff—experimental study and uncertainty analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 16552–16566 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6827-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6827-6