Abstract
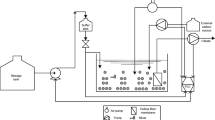
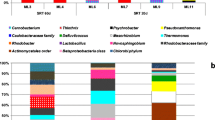
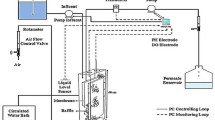
The study tested the performance of super fast membrane bioreactor (SFMBR) using starch as a slowly biodegradable substrate, exploring the fate of starch, and the response of the microbial community. SFMBR was operated at extremely low sludge ages of 0.5–2.0 days, with a hydraulic retention time of 1.0 h. Average values for permeate chemical oxygen demand (COD) always remained in the narrow range between 14 and 18 mg/L, regardless of the selected mode of MBR operation at different sludge ages. Soluble COD levels in the reactor were consistently higher than the corresponding permeate COD. Parameters defining process kinetics, determined by model calibration of oxygen uptake rate (OUR) profiles, varied as a function of sludge age. Model simulation of SFMBR performance indicated total removal of hydrolysis products so that permeate COD consisted of residual microbial products. PCR-DGGE experiments revealed significant shifts in the composition of the microbial community imposed by variations in the sludge age, reflecting on corresponding process kinetics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st edn, American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC. USA.
Chang S (2011) Application of submerged hollow fiber membrane in membrane bioreactors: filtration principles, operation, and membrane fouling. Desalination 283:31–39
Ciggin AS, Rosetti S, Majone M (2013) Extent of intracellular storage in single and dual substrate systems under pulse feeding. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1225–1238
Daigger GT, Grady CPL (1977) Model for bio-oxidation process based on product formation concepts. Water Res 11:1049–1057
Dricks K, Henze M, van Loosdrecht MCM, Mosbæk H, Aspegren H (2001) Storage and degradation of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in activated sludge under aerobic conditions. Water Res 35:2277–2285
Duan L, Song YH, Yu HB, Xia SQ, Hermanowicz SW (2014) The effect of solids retention times on the characterization of extracellular polymeric substances and soluble microbial products in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 163:395–398
Dulekgurgen E, Dogruel S, Karahan O, Orhon D (2006) Size distribution of wastewater COD fractions as an index for biodegradability. Water Res 40:273–282
Garrido JM, Fdz-Polanco M, Fdz-Polanco F (2013) Working with energy and mass balances: a conceptual framework to understand the limits of municipal wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 64:2294–2301
Goel R, Mino T, Satoh H, Matsuo T (1999) Modeling hydrolysis processes considering intracellular storage. Water Sci Technol 39:97–105
Gujer W, Henze M, Mino T, Matsuo T, Mentzel MC, Vonmarais G (1995) The activated sludge model no.2-biological phosphorous removal. Water Sci Technol 31:1–11
Henze M, Grady CPL Jr, Gujer W, Marais GR, Matsuo T (1987) Activated Sludge Model no.1, IAWPRC Sci. Technol Report no.1. IAWPRC, London
Henze M (1992) Characterization of waste-water for modeling of activated-sludge processes. Water Sci Technol 25:1–15
Hocaoglu SM, Orhon D (2010) Fate of soluble residual organics in membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 364:65–74
Hocaoglu SM, Insel G, Ubay-Cokgor E, Orhon D (2011) Effect of low dissolved oxygen on simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a membrane bioreactor treating black water. Bioresour Technol 102:4333–4340
Huang LY, Lee DJ (2015) Membrane bioreactor: a mini review on recent R&D works. Bioresour Technol 194:383–388
Jenkins D, Wanner J (2014) Activated sludge—100 years and counting. IWA Publishing, London
Karahan O, Martins A, Orhon D, van Loosdrecht MCM (2006a) Experimental evaluation of starch utilization mechanism by activated sludge. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:964–970
Karahan O, van Loosdrecht MCM, Orhon D (2006b) Modelling the utilization of starch by activated sludge for simultaneous substrate storage and microbial growth. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:43–53
LaPara TM, Klatt CG, Chen R (2006) Adaptations in bacterial catabolic enzyme activity and community structure in membrane-coupled bioreactors fed simple synthetic wastewater. J Biotechnol 121:368–380
Luo WH, Hai FI, Price WE, Guo WS, Ngo HH, Yamamoto K, Nghiem LD (2014) High retention membrane bioreactors: challenges and opportunities. Bioresour Technol 167:539–546
Matin A (1979) Microbial regulatory mechanisms at low nutrient concentrations as studied in chemostat. In: Shilo M (ed) Strategies of microbial life in extreme environments. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 323–339
McCarty PL, Bae J, Kim J (2011) Domestic wastewater treatment as a net energy producer—can this be achieved? Environ Sci Technol 45:7100–7106
Orhon D, Artan N, Cimsit Y (1989) The concept of soluble residual product formation in the modeling of activated-sludge. Water Sci Technol 21:339–350
Orhon D, Ubay-Cokgor E, Sözen S (1998) Dual hydrolysis model of the slowly biodegradable substrate in activated sludge systems. Biotechnol Tech 12:737–741
Orhon D, Okutman D, Insel G (2002) Characterisation and biodegradation of settleable organic matter for domestic wastewater. Water SA 28:299–305
Pala-Ozkok I, Rehman A, Yagci N, Ubay-Cokgor E, Jonas D, Orhon D (2012) Characteristics of mixed microbial culture at different sludge ages: effect on variable kinetics for substrate utilization. Bioresour Technol 126:274–282
Pala-Ozkok I, Rehmann A, Ubay-Çokgor E, Jonas D, Orhon D (2014) Pyrosequencing reveals the inhibitory impact of chronic exposure to erythromycin on activated sludge bacterial community structure. Biochem Eng J 90:195–205
Razbonyalı C (2013) Determination of the process performance of high rate membrane bioreactors treating domestic wastewater, MSc Thesis. Department of Environmental Engineering, ITU Graduate School of Science Engineering and Technology, Istanbul
Riechert P (1998) AQUASIM-2.0—user manual. Swiss Federal Institute for Environmental Science and Technology (EAWAG), Duebendorf
Sözen S, Ubay-Cokgor E, Teksoy-Basaran S, Aysel M, Akarsubaşı A, Ergal I, Kurt H, Pala-Ozkok I, Orhon D (2014) Effect of high loading on substrate utilization kinetics and microbial community structure in super fast submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 159:118–127
Sözen S, Pala-Ozkok I, Aysel M, Teksoy Basaran S, Akarsubaşı A, Ergal I, Kurt H, Ubay-Cokgor E (2015) Performance and microbial behavior of submerged membrane bioreactor at extremely low sludge ages. Desalin. Water Treat 56:862–874
Tan TW, Ng HY, Ong SL (2008) Effect of mean cell residence time on the performance and microbial diversity of pre-denitrification submerged membrane bioreactors. Chemosphere 70:387–396
Teksoy-Başaran S, Aysel M, Kurt H, Ergal I, Kumru M, Akarsubaşı A, Sözen S, Orhon D (2012) Removal of readily biodegradable substrate in super fast membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 423:477–486
Teksoy-Başaran S, Aysel M, Kurt H, Ergal I, Akarsubaşı A, Yagci N, Dogruel S, Ubay-Cokgor E, Sözen S, Orhon D (2014) Kinetic characterization of acetate utilization and response of microbial population in super fast membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 455:392–404
Ubukata Y (1998) Kinetics and fundamental mechanisms of protein removal by activated sludge: hydrolysis of peptone to amino acids is the rate-determining step. Water Sci Technol 38:121–128
Vanrolleghem PA (2002) Principles of respirometry in activated sludge wastewater treatment. In: Proceedings international workshop on recent development in respirometry for wastewater treatment plant monitoring and control. Taipei, Taiwan, pp 2/1–20
Vyrides I, Stuckey DC (2011) Fouling cake layer in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating wastewaters: curse or a blessing? Water Sci Technol 63:2902–2908
Zangi-Kotler M, Ben-Dov E, Tiehm A, Kushmaro A (2015) Microbial community structure and dynamics in a membrane bioreactor supplemented with the flame retardant dibromoneopentyl glycol. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17615–17624
Zhang JS, Chuan CH, Zhou JT, Fane AG (2006) Effect of sludge retention time on membrane bio-fouling intensity in a submerged membrane bioreactor Sep. Sci Technol 41:1313–1329
Zonoozi MH, Moghaddam MRA, Maknoon R (2015) Operation of integrated sequencing batch membrane bioreactor treating dye-containing wastewater at different SRTs: study of overall performance and fouling behavior. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:5931–5942
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted as part of a research and development project funded by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (Project No. 109Y261). TUBITAK is kindly acknowledged for its financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sözen, S., Teksoy Başaran, S., Akarsubaşı, A. et al. Toward a novel membrane process for organic carbon removal—fate of slowly biodegradable substrate in super fast membrane bioreactor. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 16230–16240 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6795-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6795-x