Abstract
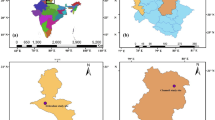
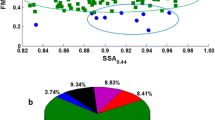
Optical and micro-physical features of aerosol are reported using Skyradiometer (POM-01L, Prede, Japan) observations taken from a high-altitude station Merak, located in north-eastern Ladakh of the western trans-Himalayas region during January 2011 to December 2013. The observed daily mean aerosol optical depth (AOD, at 500 nm) at the site varied from 0.01 to 0.14. However, 75 % of the observed AOD lies below 0.05 during the study period. Seasonal peaks of AOD occurred in spring as 0.06 and minimum in winter as 0.03 which represents the aged background aerosols at the site. Yearly mean AOD at 500 nm is found to be around 0.04 and inter-annual variations of AOD is very small (nearly ±0.01). Angstrom exponent (a) varied seasonally from 0.73 in spring to 1.5 in autumn. About 30 % of the observed a lies below 0.8 which are the indicative for the presence of coarse-mode aerosols at the site. The station exhibits absorbing aerosol features which prominently occurred during spring and that may be attributed by the transported anthropogenic aerosol from Indo-Gangatic Plain (IGP). Results were well substantiated with the air mass back-trajectory analysis. Furthermore, seasonal mean of single scattering albedo (SSA at 500 nm) varied from of 0.94 to 0.98 and a general increasing trend is noticed from 400 to 870 nm wavelengths. These features are apparently regional characteristics of the site. Aerosol asymmetry factor (AS) decreases gradually from 400 to 870 nm and varied from 0.66 to 0.69 at 500 nm across the seasons. Dominance of desert-dust aerosols, associated by coarse mode, is indicated by tri-modal features of aerosol volume size distribution over the station during the entire seasons.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bokoye AI, Royer A, ONeill NT, Cliche P, Fedosejevs G, Teillet PM, McArthur LJB (2001) Characterization of atmospheric aerosols across Canada from a ground-based sunphotometer network. Aerocan Atmosphere-Ocean 39:429–456
Campanelli M, Estells V, Tomasi C, Nakajima T, Malvestuto V, Martnez-Lozano JA (2007) Application of the SKYRAD improved Langley plot method for the in situ calibration of CIMEL sun-skphotometers, vol 46. No. 14 May
Che H, Shi G, Uchiyama A, Yamazaki A, Chen H, Goloub P, Zhang X (2008) Intercomparison between aerosol optical properties by a PREDE skyradiometer and CIMEL sunphotometer over Beijing, China. Atmos Chem Phys 8:3199–3214
Che H, Zhang X, Chen H, Damiri B, Goloub P, Li Z, Zhang X, Wei Y, Zhou H, Dong F, Li D, Zhou T (2009) Instrument calibration and aerosol optical depth (AOD) validation of the China aerosol remote sensing network (CARSNET). Journal of Geophys Res 114. doi:10.1029/2008JD011030
Che H, Yaqiang W, Junying S (2011) Aerosol optical properties at Mt. Waliguan Observatory, China. Atmos Env 45:6004–6009
Cong Z, Shichang K, Alexander S, Brent H (2009) Aerosol Optical properties at Nam Co, a remote site in central Tibetan Plateau. Atmos Res 92:42–48
Chatterjee A, Ghosh SK, Adak A, Singh AK, Devara PCS, Raha S (2012) Effect of dust and anthropogenic aerosols on columnar aerosol optical properties over Darjeeling (2200 m asl), Eastern Himalayas. India. PLoS ONE 7(7):e40286. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040286
Dubovik O, Holben B, Eck TF, Smirnov A, Kaufman YJ, King MD, Tanré D, Slutsker I (2002) Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J Atmos Sci 59:590–608
Eck TF, Holben BN, Reid JS, Dubovik O, Smirnov A, O’Neill NT, Slutsker I, Kinne S (1999) Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J.Geophy. Res 104 (D24):31333–31349
Gautam R, Hsu NC, Lau KM, Tsay SC, Kafatos M (2009) Enhanced pre-monsoon warming over the Himalayan-Gangetic region from 1979 to 2007. Geophys Res Letts 36:L07704. doi:10.1029/2009GL037641
Goloub P, Li Z, Dubovik O, Blarel L, Podvin T, Jankowiak I, Lecoq R, Deroo C, Chatenet B, Morel JP, Cuevas E, Ramos R (2008) PHOTONS/AERONET sunphotometer network overview: description, activities, results. In: Proceedings SPIE 6936, Fourteenth International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics/Atmospheric Physics 69360V, doi:10.1117/12.783171, (to appear in print)
Guleria RP, Kuniyal JC, Rawat PS, Thakur HK, Sharma M, Sharma NL, Singh M, Chand K, Sharma P, Thakur AK, Dhyani PP, Bhuyan PK (2011) Aerosols optical properties in dynamic atmosphere in the northwestern part of the Indian Himalaya: a comparative study from ground and satellite based observations. Atmos Res 101:726–738
Hegde P, Pant P, Naja M, Dumka UC, Sagar R (2007) South Asian dust episode in June 2006: aerosol observations in the central Himalayas. Geophy. Res. Letters 34:L23802. doi:10.1029/2007GRL030692
Holben BN, et al. (2001) An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J Geophys Res 106(11):12067–12097
Hyvarinen AP, Lihavainen H, Komppula M, Sharma VP, Kerminen V-M, Panwar TS, Viisanen Y (2009) Continuous measurements of optical properties of atmospheric aerosols in Mukteshwar, northern India. J Geophys Res 114:D08207. doi:10.1029/2008JD011489
Khatri P, Takamura T (2009) An algorithm to screen cloud-affected data for sky radiometer data analysis. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 87:189–204
Kim DH, BJ Sohn, Nakajima T, Takamura T (2005) Aerosol radiative forcing over east Asia determined from ground-based solar radiation measurements. J Geophy Res 110. doi:10.1029/2004JD0046786
Kumar R, Naja M, Satheesh SK, Ojha N, Joshi H, Sarangi T, Pant P, Dumka UC, Hegde P, Venkataramani S (2011) Influences of the springtime northern Indian biomass burning over the central Himalayas. J Geophys Res 116(Issue D19). doi:10.1029/2010JD015509
Kuniyal JC, Thakur A, Thakur HH, Sharma S, Pant P, Rawat PS, Moorthy KK (2009) Aerosol optical depth at Mohal-Kullu in the northwestern Indian Himalayan high altitude station during ICARB. J Earth Syst Sci 118(1):41–48
Lelieveld J, Crutzen PJ, Ramanathan, et al. (2001) The Indian Ocean Experiment: widespread air pollution from South and Southeast Asia. Science 291:1031–1036
Levelt PF, et al. (2006) The ozone monitoring instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci Remote Sens 44:1093–1101
Marinoni A, Cristofanelli P, Laj P, Duchi R, Calzolari F, Decesari S , Sellegri K, Vuillermoz E, Verza G P, Villani P, Bonasoni P, (2010) Aerosol mass and black carbon concentrations, a two year record at NCO-P (5079 m, Southern Himalayas). Atmos Chem Phys 10:8551–8562
Nakajima T, Tonna G, Rao R, Boi P, Kaufman Y, Holben BN (1996) Use of sky brightness measurements from ground for remote sensing of particulate polydispersions. App Opt 35:2672– 2786
Nakajima, et al. (2007) Overview of the atmospheric Brown Cloud East Asian Regional Experiment 2005 and a study of the aerosol direct radiative forcing in east Asia. J Geophys Res 112:D24S91. doi:10.1029/2007JD009009
Ningombam SS, Bagare SP, Sinha N, Singh RB, Srivastava AK, Larson E, Kanawade VP (2014a) Characterization of aerosol optical properties over the high-altitude station Hanle, in the trans-Himalayan region. Atmos Res 138:308–323
Ningombam SS, Bagare SP, Srivastava AK, Sohn BJ, Song H-J, Larson E (2014b) Aerosol radiative forcing over a high-altitude station Merak, in the trans-Himalayan region during advection of anthropogenic events from the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos Env 98:253–259
Ningombam SS, Bagare SP, Singh RB, Campanelli M, Khatri P, Dorjey N (2014c) Calibration of a Sky radiometer (Prede) using observations obtained from Hanle and Merak high-altitude stations in Ladakh. Atmos Res 143:118–128
ONeill NT, Ignatov A, Holben BN, Eck TF (2000) The lognormal distribution as a reference for reporting aerosol optical depth statistics: empirical tests using multi-year, multi-site AERONET sunphotometer data. Geophys Res Lett 27(20):3333–3336
Ramanathan V, Ramana MV, Roberts G, Kim D, Corrigan C, Chung C, Winker D (2007) Warming trends in Asia amplified by brown cloud solar absorption. Nature 448:575–578. doi:10.1038/nature06019
Srivastava AK, Pant P, Hegde P, Singh S , Dumka UC, Naja M, Singh N, Bhavanikumar Y (2011) The influence of a south Asian dust storm on aerosol radiative forcing at a high-altitude station in central Himalayas. Int J Remote Sens 32(22):7827–7845
Srivastava AK, Sachchidanand Singh, Tiwari S, Bisht DS (2012) Contribution of anthropogenic aerosols in direct radiative forcing and atmospheric heating rate over Delhi in the Indo-Gangatic Basin. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 19:1144–1158. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0633
Srivastava AK, Ram K, Singh S, Kumar S, Tiwari S (2015) Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects over Manora Peak in the Himalayan foothills: seasonal variability and role of transported aerosols. Science of the Total Environment 502:287–295
Takamura T, Nakajima T (2004) Overview of SKYNET and its activities. Opt Pura Apl 37:3303–3308
Uchiyama A, Yamazaki A, Togawa H, Asano J (2005) Characteristics of Aeolian Dust Observed by Sky-Radiometer in the Intensive Observation Period 1 (IOP1). J Meteorol Soc Jpn 83:291–305
Vadrevu KP, Ellicott E, Giglio L, Badarinath KVS, Vermote E, Justice C, Lau WKM (2012) Vegetation fires in the Himalayan region: aerosol load, black carbon emissions and smoke plume heights. Atmos Environ 47:241–251
Verma N, Bagare SP, Ningombam SS, Singh RB (2010) Aerosol optical properties retrieved using Skyradiometer at handle in western Himalayas. J Atmos Solar-Terrestrial Phys 72:115–124
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the Director (IIA) for his support and encouragement. Furthermore, the authors are very grateful to the entire staff of the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO)-Hanle and Merak stations for their invaluable assistance during the observations. One of the authors A. K. Srivastava would like to thank Director, IITM for his encouragements and supports. The Skyradiometer data were analyzed using the Skyrad.pack software, version 4.2 and the authors thank Prof. T. Nakajima for providing the code. The authors gratefully acknowledge the NOAA Air Resources Laboratory (ARL) for providing airmass trajectory calculations (http://www.ready.noaa.gov). Finally, the authors are thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerhard Lamme
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ningombam, S.S., Srivastava, A.K., Bagare, S.P. et al. Assessment of aerosol optical and micro-physical features retrieved from direct and diffuse solar irradiance measurements from Skyradiometer at a high altitude station at Merak. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 16610–16619 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4788-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4788-9