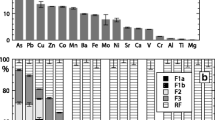
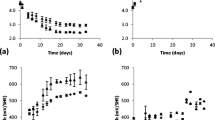
Abstract
Contaminated dredged sediments are often considered hazardous wastes, so they have to be adequately managed to avoid leaching of pollutants. The mobility of inorganic contaminants is a major concern. Metal sulfides (mainly framboïdal pyrite, copper, and zinc sulfides) have been investigated in this study as an important reactive metal-bearing phase sensitive to atmospheric oxygen action. An oxygen consumption test (OC-Test) has been adapted to assess the reactivity of dredged sediments when exposed to atmospheric oxygen. An experimental column set-up has been developed allowing the coupling between leaching and oxygen consumption test to investigate the reactivity of the sediment. This reactivity, which consisted of sulfide oxidation, was found to occur for saturation degree between 60 and 90 % and until the 20th testing week, through significant sulfates releases. These latter were assumed to come from sulfide oxidation in the first step of the test, then probably from gypsum dissolution. Confrontation results of OC-Test and leachate quality shows that Cu was well correlated to sulfates releases, which in turn, leads to Ca and Mg dissolution (buffer effect). Cu, and mostly Zn, was associated to organic matter, phyllosilicates, and other minerals through organo-clay complexes. This research confirmed that the OC-Test, originally developed for mine tailings, could be a useful tool in the dredged sediment field which can allow for intrinsic characterization of reactivity of a material suspected to readily reacting with oxygen and for better understanding of geochemical processes that affect pollutants behavior, conversion, and transfer in the environment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benzaazoua M, Bussière B, Dagenais AM, Archambault M (2004) Kinetic tests comparison and interpretation for prediction of the Joutel tailings acid generation potential. Environ Geol 46:1086–1101. doi:10.1007/s00254-004-1113-1
Blowes DW, Reardon EJ, Jambor JL, Cherry JA (1991) The formation and potential importance of cemented layers in inactive sulfide mine tailings. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:965–978. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(91)90155-X
Bouzahzah H, Califice A, Benzaazoua M, Mermillod-Blondin R, Pirard E (2008) Modal analysis of mineral blends using optical image analysis versus x ray diffraction. In: Proceedings of International Congress for Applied Mineralogy ICAM08, Brisbane, Australia. AusIMM,
Bouzahzah H, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B (2012) Modification and automation of the humidity cell test protocol to favor tailings reactivity Proceedings of the 9th ICARD, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Capilla X, Schwartz C, Bedell J-P, Sterckeman T, Perrodin Y, Morel J-L (2006) Physicochemical and biological characterisation of different dredged sediment deposit sites in France. Environ Pollut 143:106–116. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.11.007
Caplat C, Texier H, Barillier D, Lelievre C (2005) Heavy metals mobility in harbour contaminated sediments: the case of port-en-Bessin. Mar Pollut Bull 50:504–511. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.08.004
Cappuyns V, Swennen R (2008) The use of leaching tests to study the potential mobilization of heavy metals from soils and sediments: a comparison. Water Air Soil Pollut 191:95–111. doi:10.1007/s11270-007-9609-4
Casado-Martínez MC, Forja JM, DelValls TA (2009) A multivariate assessment of sediment contamination in dredged materials from Spanish ports. J Hazard Mater 163:1353–1359. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.106
Chatain V et al (2013a) Mineralogical study and leaching behavior of a stabilized harbor sediment with hydraulic binder. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(1):51–59. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1141-4
Chatain V, Blanc D, Borschneck D, Delolme C (2013b) Determining the experimental leachability of copper, lead, and zinc in a harbor sediment and modeling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(1):66–74. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-1233-1
Demers I, Bussiére B, Mbonimpa M, Benzaazoua M (2009) Oxygen diffusion and consumption in low-sulphide tailings covers. Can Geotech J 46:454–469. doi:10.1139/T08-132
Díez S, Ábalos M, Bayona JM (2002) Organotin contamination in sediments from the Western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Water Res 36:905–918. doi:10.1016/s0043-1354(01)00305-0
Dold B, Fontboté L (2002) A mineralogical and geochemical study of element mobility in sulfide mine tailings of Fe oxide Cu–Au deposits from the Punta del Cobre belt, northern Chile. Chem Geol 189:135–163. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00044-X
Eek E, Cornelissen G, Kibsgaard A, Breedveld GD (2008) Diffusion of PAH and PCB from contaminated sediments with and without mineral capping; measurement and modelling. Chemosphere 71:1629–1638. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.01.051
Elberling B, Nicholson RV (1996) Field determination of sulphide oxidation rates in mine tailings. Water Resour Res 32:1773–1784. doi:10.1029/96wr00487
Elberling B, Nicholson RV, Reardon EJ, Tibble R (1994) Evaluation of sulphide oxidation rates: a laboratory study comparing oxygen fluxes and rates of oxidation product release. Can Geotech J 31:375–383. doi:10.1139/t94-045
Elberling B, Balić-Žunić T, Edsberg A (2003) Spatial variations and controls of acid mine drainage generation. Environ Geol 43:806–813. doi:10.1007/s00254-002-0695-8
European Council (2000) 2000/532/EC: Commission Decision of 3 May 2000 replacing Decision 94/3/EC establishing a list of wastes pursuant to Article 1(a) of Council Directive 75/442/EEC on waste and Council Decision 94/904/EC establishing a list of hazardous waste pursuant to Article 1(4) of Council Directive 91/689/EEC on hazardous waste (notified under document number C(2000) 1147) (Text with EEA relevance). http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32000D0532
Förstner U, Calmano W, Conradt K, Jaksch H, Schimkus C, Schoer J (1981) Chemical speciation of heavy metals in solid waste materials (sewage sludge, mining wastes, dredged materials, polluted sediments) by sequential extraction. Proc. Intern. Conf. Heavy Metals in the Environment, Amsterdam, pp. 698–704. CEP Consultants, Edinburgh
French Official Journal (2006) Arrêté du 09/08/06 relatif aux niveaux à prendre en compte lors d’une analyse de rejets dans les eaux de surface ou de sédiments marins, estuariens ou extraits de cours d’eau ou canaux publié au JORF n°222 du 24 septembre 2006 page 14082 texte n°15. (in French)
Graupner T et al (2007) Formation of sequences of cemented layers and hardpans within sulfide-bearing mine tailings (mine district Freiberg, Germany). Appl Geochem 22:2486–2508. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.07.002
Grosdemange D, Lévêque F, Drousie D, Aqua JL, Méhu J, Bazin C (2008) The SEDIMARD project: presentation and results. In: International Symposium on Sediment Management (I2SM), Lille, France.
Guevara-Riba A, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Rauret G (2004) Assessment of metal mobility in dredged harbour sediments from Barcelona, Spain. Sci Total Environ 321:241–255. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.08.021
Huerta-Diaz MA, Tessier A, Carignan R (1998) Geochemistry of trace metals associated with reduced sulfur in freshwater sediments. Appl Geochem 13:213–233. doi:10.1016/s0883-2927(97)00060-7
Hwang T, Neculita CM (2013) In situ immobilization of heavy metals in severely weathered tailings amended with food waste-based compost and zeolite. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1–9
Hwang T, Neculita CM, Han J-I (2012) Biosulfides precipitation in weathered tailings amended with food waste-based compost and zeolite. J Environ Qual 41:1857–1864
Isaure M-P, Laboudigue A, Manceau A, Sarret G, Tiffreau C, Trocellier P, Lamble G, Hazemann JL, Chateigner D (2002) Quantitative Zn speciation in a contaminated dredged sediment by μ-PIXE, μ-SXRF EXAFS spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:1549–1567
Isaure M-P, Manceau A, Geoffroy N, Laboudigue A, Tamura N, Marcus MA (2005) Zinc mobility and speciation in soil covered by contaminated dredged sediment using micrometer-scale and bulk-averaging x-ray fluorescence, absorption and diffraction techniques. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:1173–1198
Jones B, Turki A (1997) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in surficial sediments from the Tees Estuary, north-east England. Mar Pollut Bull 34:768–779. doi:10.1016/s0025-326x(97)00047-7
Le Guyader C (2011) Enquête “Dragage 2009” - Synthèse des données. CETMEF, Margny Lès Compiègne (in French)
Le Guyader C (2013) Enquête “Dragage 2010” - Synthèse des données. CETMEF, Margny Lès Compiègne (in French)
Lions J, van der Lee J, Guérin V, Bataillard P, Laboudigue A (2007) Zinc and cadmium mobility in a 5-year-old dredged sediment deposit: experiments and modelling. J Soils Sediments 7:207–215. doi:10.1065/jss2007.05.226
Lions J, Guérin V, Bataillard P, van der Lee J, Laboudigue A (2010) Metal availability in a highly contaminated, dredged-sediment disposal site: field measurements and geochemical modeling. Environ Pollut 158:2857–2864. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.06.011
Lowers HA, Breit GN, Foster AL, Whitney J, Yount J, Uddin MN, Muneem AA (2007) Arsenic incorporation into authigenic pyrite, Bengal Basin sediment, Bangladesh. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:2699–2717. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.022
Lowson RT (1982) Aqueous oxidation of pyrite by molecular oxygen. Chem Rev 82:461–497. doi:10.1021/cr00051a001
Mamindy-Pajany Y, Geret F, Roméo M, Hurel C, Marmier N (2012) Ex situ remediation of contaminated sediments using mineral additives: assessment of pollutant bioavailability with the microtox solid phase test. Chemosphere 86:1112–1116. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.001
Mbonimpa M, Aubertin M, Aachib M, Bussière B (2003) Diffusion and consumption of oxygen in unsaturated cover materials. Can Geotech J 40:916–932. doi:10.1139/t03-040
Mbonimpa M, Akué Awoh S, Aubertin M (2012) A simple interpretation for the modified oxygen consumption test on sulphide tailings. Paper presented at the GeoManitoba. Winnipeg, Canada
Morse JW, Luther Iii GW (1999) Chemical influences on trace metal-sulfide interactions in anoxic sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:3373–3378. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(99)00258-6
Mtambanengwe F, Mapfumo P, Kirchmann H (2004) Decomposition of organic matter in soil as influenced by texture and pore size distribution Managing nutrient cycles to sustain soil fertility in sub-Saharan Africa Ed, Bationo, A Centro Internacional de Agriculture Tropical pp 261–276
Ouangrawa M, Molson J, Aubertin M, Bussière B, Zagury GJ (2009) Reactive transport modelling of mine tailings columns with capillarity-induced high water saturation for preventing sulfide oxidation. Appl Geochem 24:1312–1323. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.04.005
Ouellet S, Bussière B, Mbonimpa M, Benzaazoua M, Aubertin M (2006) Reactivity and mineralogical evolution of an underground mine sulphidic cemented paste backfill. Miner Eng 19:407–419. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2005.10.006
Pierret M-C, Blanc G, Clauer N (2000) Sur l’origine de la pyrite framboïdale dans les sédiments de la fosse Suakin (mer Rouge). C R Acad Sci IIA = Earth Planet Sci 330:31–38. doi:10.1016/s1251-8050(00)00103-8
Pourbaix M, de Zoubov N, Van Muylder J (1963) Atlas d’équilibres électrochimiques, vol 1. Gauthier-Villars, Paris
Prokop Z, Vangheluwe ML, Van Sprang PA, Janssen CR, Holoubek I (2003) Mobility and toxicity of metals in sandy sediments deposited on land. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:65–73. doi:10.1016/s0147-6513(02)00022-2
Puget P, Chenu C, Balesdent J (2000) Dynamics of soil organic matter associated with particle-size fractions of water-stable aggregates. Eur J Soil Sci 51:595–605. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2000.00353.x
Raudsepp M, Pani E (2003) Application of Rietveld analysis to environmental mineralogy environmental aspects of mine wastes. Mineral Assoc Can Short Course 3:165–180
Ribecco C, Baker ME, Šášik R, Zuo Y, Hardiman G, Carnevali O (2011) Biological effects of marine contaminated sediments on Sparus aurata juveniles. Aquat Toxicol 104:308–316. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.05.005
Salomons W, Rooij NM, Kerdijk H, Bril J (1987) Sediments as a source for contaminants? Hydrobiologia 149:13–30. doi:10.1007/bf00048643
Sauvé S, Hendershot W, Allen HE (2000) Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 34:1125–1131. doi:10.1021/es9907764
Schenau SJ, Passier HF, Reichart GJ, de Lange GJ (2002) Sedimentary pyrite formation in the Arabian Sea. Mar Geol 185:393–402. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00183-4
Schippers A, Jørgensen BB (2002) Biogeochemistry of pyrite and iron sulfide oxidation in marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:85–92. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(01)00745-1
Sobek AA, Schuller WA, Freeman JR, Smith RM (1978) Field and laboratory methods applicable to overburden and minesoils: EPA-600/2-78-054, U.S. National Technical Information Service Report PB-280 495.
Staniszewska M, Burska D, Sapota G, Bogdaniuk M, Borowiec K, Nosarzewska I, Bolałek J (2011) The relationship between the concentrations and distribution of organic pollutants and black carbon content in benthic sediments in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Baltic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1464–1475. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.04.013
Sundaray SK, Nayak BB, Lin S, Bhatta D (2011) Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments—a case study: Mahanadi basin. India J Hazard Mater 186:1837–1846. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.081
Tanji KK (1969) Solubility of gypsum in aqueous electrolytes as affected by ion association and ionic strengths up to 0.15M and at 25.deg. Environ Sci Technol 3:656–661. doi:10.1021/es60030a003
Tessier E, Garnier C, Mullot J-U, Lenoble V, Arnaud M, Raynaud M, Mounier S (2011) Study of the spatial and historical distribution of sediment inorganic contamination in the Toulon bay (France). Mar Pollut Bull 62:2075–2086. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.07.022
Trefry JH, Metz S (1984) Selective leaching of trace metals from sediments as a function of pH. Anal Chem 56:745–749. doi:10.1021/ac00268a034
Visconti F, De Paz JM, Rubio JL (2010) Calcite and gypsum solubility products in water-saturated salt-affected soil samples at 25°C and at least up to 14 dS m−1. Eur J Soil Sci 61:255–270. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.2009.01214.x
Warwick P, Hall A, Pashley V, Van der Lee J, Maes A (1998) Zinc and cadmium mobility in sand: effects of pH, speciation, cation exchange capacity (CEC), humic acid and metal ions. Chemosphere 36:2283–2290. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)10197-7
Ye S, Laws EA, Zhong S, Ding X, Pang S (2011) Sequestration of metals through association with pyrite in subtidal sediments of the Nanpaishui Estuary on the Western Bank of the Bohai Sea, China. Mar Pollut Bull 62:934–941. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.02.052
Young RA (1993) The Rietveld method. Oxford University Press, New York City
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to EEDEMS (French research network on waste and polluted materials management) for experimental support. Author’s acknowledgments also go to University of Quebec (UQAT) for their support in the mineralogical and physicochemical analyses.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Couvidat, J., Benzaazoua, M., Chatain, V. et al. An innovative coupling between column leaching and oxygen consumption tests to assess behavior of contaminated marine dredged sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 10943–10955 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4323-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4323-z