Abstract
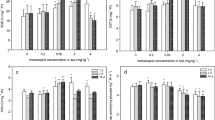
Thiacloprid, a neonicotinoid insecticide, has been used widely in agriculture worldwide. In recent years, the adverse effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on non-target organisms have attracted more and more attention. In the present study, effects of thiacloprid on molecular biomarkers (GST, CarE, CAT, SOD, POD, and DNA damage) of earthworm Eisenia fetida were investigated using the artificial OECD soil for the first time. Earthworms were exposed to thiacloprid (1 and 3 mg/kg) for 7, 14, and 28 days and then transferred to the clean OECD soil for 35, 42, and 56 days. Results showed that activities of GST, CarE, CAT, SOD, and POD are inhibited following the exposure to thiacloprid at one or more sample times and then increased during the recovery course compared with the control. Significant DNA damage to E. fetida was also observed by olive tail moments in comet assay. These results suggested that thiacloprid could have harmful effect on earthworms, and these studied biomarkers might be used in the assessment of the risk of thiacloprid to the soil ecosystem environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly MA, Schröder P (2008) Effect of herbicides on glutathione S-transferases in the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 15:143–149
Beketov MA, Liess M (2008) Acute and delayed effects of the neonicotinoid insecticide thiacloprid on seven freshwater arthropods. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:461–470
Bernard F, Brulle F, Dumez S, Lemiere S, Platel A, Nesslany F, Cuny D, Deram A, Vandenbulcke F (2014) Antioxidant responses of Annelids, Brassicaceae and Fabaceae to pollutants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.024
Booth LH, O’Halloran K (2001) A comparison of biomarker responses in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa to the organophosphorus insecticides diazinon and chlorpyrifos. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2494–2502
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bunyan PJ, Jennings DM, Taylor A (1968) Organophosphorus poisoning. Properties of avian esterase. J Agric Food Chem 16:326–331
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Mazzia C, Belzunces L (2003) Earthworm behavior as a biomarker—a case study using imidacloprid: the 7th International Symposium on Earthworm Ecology Cardiff Wales 2002. Pedobiologia 47:542–547
Capowiez Y, Bastardie F, Costagliola G (2006) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behavior of two earthworm species: modifications of the 3D burrow systems in artificial cores and consequences on gas diffusion in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:285–293
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J (2003) Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J 17:1195–1214
Cotelle S, Férard JF (1999) Comet assay in genetic ecotoxicology: a review. Environ Mol Mutagen 34:246–255
Damalas CA, Eleftherohorinos IG (2011) Pesticide exposure, safety issues, and risk assessment indicators. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:1402–1419
Dittbrenner N, Moser I, Triebskorn R, Capowiez Y (2011) Assessment of short and long-term effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species (Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris) by using 2D and 3D post-exposure techniques. Chemosphere 84:1349–1355
Elbert A, Erdelen C, Kuhnhold J, Nauen R, Schmidt HW, Hattori Y (2000) Thiacloprid, a novel neonicotinoid insecticide for foliar application. The BCPC conference: pests and diseases. Proc Int Conf Held Brighton Hilto 1:21–26
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick LC, Venables BJ, Cooper EL (1991) A non-invasive technique for sequential collection of earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during subchronic immunotoxicity studies. Lab Anim 25:61–67
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Goulson D (2013) An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J Appl Ecol 50:977–987
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione-S-transferase: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 617–783
Jemec A, Drobne D, Tisler T, Sepcić K (2010) Biochemical biomarkers in environmental studies—lessons learnt from enzymes catalase, glutathione S-transferase and cholinesterase in two crustacean species. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 17:571–581
Jeschke P, Moriya K, Lantzsch R, Seifert H, Lindner W, Jelich K, Gohrt A, Beck ME, Etzel W (2001) Thiacloprid (Bay YRC 2894)—a new member of the chloronicotinyl insecticide (CNI) family. Pflanzenschutz Nachr Bayer 54:147–160
Kammenga JE, Dallinger R, Donker MH, Köhler HR, Simonsen V, Triebskorn R, Weeks JM (2000) Biomarkers in terrestrial invertebrates for ecotoxicological soil risk assessment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 164:93–147
Kochba J, Lavee S, Spiegel-Roy P (1977) Differences in peroxidase activity and isoenzymes in embryogenic ane non-embryogenic ‘Shamouti’ orange ovular callus lines. Plant Cell Physiol 18:463–467
Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Góźdź S, Koza Z, Wojcik A (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res 534:15–20
Lal OP, Palta RK, Srivastava YNS (2001) Impact of imidacloprid and carbofuran on earthworm castings in okra field. Ann Plant Prot Sci 9:137–138
Langer-Jaesrich M, Köhler HR, Gerhardt A (2010) Assessing toxicity of the insecticide thiacloprid on Chironomus riparius (Insecta: Diptera) using multiple end points. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:963–972
Lin D, Xie X, Zhou Q, Liu Y (2012a) Biochemical and genotoxic effect of triclosan on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) using contact and soil tests. Environ Toxicol 27:385–392
Lin D, Zhou Q, Xu Y, Chen C, Li Y (2012b) Physiological and molecular responses of the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) to soil contaminated with HHCB. Chemosphere 83:1080–1086
Liu XL, Sun ZJ, Chong W, Sun ZT, He CK (2009) Growth and stress responses of the earthworm Eisenia fetida to Escherichia coli O157: H7 in an artificial soil. Microb Pathog 46:266–272
Luo Y, Zang Y, Zhong Y, Kong ZM (1999) Toxicological study of two novel pesticides on earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere 39:2347–2356
Novais SC, Gomes NC, Soares AM, Amorim MJ (2014) Antioxidant and neurotoxicity markers in the model organism Enchytraeus albidus (Oligochaeta): mechanisms of response to atrazine, dimethoate and carbendazim. Ecotoxicol 23:1220–1233
OECD (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals no. 207: earthworm, acute toxicity tests (filter paper test and artificial soil test). Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), Paris
OECD (2004) Guidelines for testing of chemicals no. 222: earthworm reproduction tests (Eisenia fetida/Esienia Andrei). Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), Paris
Pelosi C, Barot S, Capowiez Y, Hedde M, Vandenbulcke F (2014) Pesticides and earthworms. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:199–228
Pisa LW, Amaral-Rogers V, Belzunces LP, Bonmatin JM, Downs CA, Goulson D, Kreutzweiser DP, Krupke C, Liess M, McField M, Morrissey CA, Noome DA, Settele J, Simon-Delso N, Stark JD, Van der Sluijs JP, Van Dyck H, Wiemers M (2014) Effects of neonicotinoids and fipronil on non-target invertebrates. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3471-x
Rodríguez-Castellano L, Sanchez-Hernández JC (2007) Earthworm biomarkers of pesticide contamination: current status and perspectives. J Pestic Sci 32:360–371
Römbke J, Jänsch S, Didden W (2005) The use of earthworms in ecological soil classification and assessment concepts. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:249–265
Sanchez-Hernández JC (2006) Earthworm biomarkers in ecological risk assessment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 188:85–126
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia fetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41:905–909
Vejares SG, Sabat P, Sanchez-Hernández JC (2010) Tissue-specific inhibition and recovery of esterase activities in Lumbricus terrestris experimentally exposed to chlorpyrifos. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 151:351–359
Velki M, Hackenberger BK (2013) Different sensitivities of biomarker responses in two epigeic earthworm species after exposure to pyrethroid and organophosphate insecticides. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:498–509
Velki M, Hackenberger BK, Lončarić Z, Hackenberger DK (2014) Application of microcosmic system for assessment of insecticide effects on biomarker responses in ecologically different earthworm species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:110–119
Viswanathan R (1997) Physiological basis in the assessment of ecotoxicity of pesticides to soil organisms. Chemosphere 35:323–323
Wheelock CE, Phillips BM, Anderson BS, Miller JL, Miller MJ, Hammock BD (2008) Applications of carboxylesterase activity in environmental monitoring and toxicity identification evaluations (TIES). Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 195:117–178
Xu JB, Yuan XF, Lang PZ (1997) The determination of enzymic activity and its inhibition on catalase by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Environ Chem 18:73–76 (in Chinese)
Zang Y, Zhong Y, Luo Y, Kong ZM (2000) Genotoxicity of two novel pesticides for the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 108:271–278
Zhang QM, Zhang BH, Wang CX (2014) Ecotoxicological effects on the earthworm Eisenia fetida following exposure to soil contaminated with imidacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12345–12353
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31171878 and 31272079).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Henner Hollert
Lei Feng and Lan Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y. et al. Inhibition and recovery of biomarkers of earthworm Eisenia fetida after exposure to thiacloprid. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 9475–9482 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4122-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4122-6