Abstract
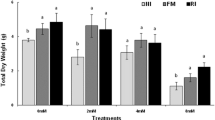
Endophytic bacteria from roots and crude seed extracts of a Cu-tolerant population of Agrostis capillaris were inoculated to a sunflower metal-tolerant mutant line, and their influence on Cu tolerance and phytoextraction was assessed using a Cu-contaminated soil series. Ten endophytic bacterial strains isolated from surface-sterilized A. capillaris roots were mixed to prepare the root endophyte inoculant (RE). In parallel, surface-sterilized seeds of A. capillaris were crushed in MgSO4 to prepare a crude seed extract containing seed endophytes (SE). An aliquot of this seed extract was filtered at 0.2 μm to obtain a bacterial cell-free seed extract (SEF). After surface sterilization, germinated sunflower seeds were separately treated with one of five modalities: no treatment (C), immersion in MgSO4 (CMg) or SEF solutions and inoculation with RE or SE. All plants were cultivated on a Cu-contaminated soil series (13–1020 mg Cu kg−1). Cultivable RE strains were mostly members of the Pseudomonas genera, and one strain was closely related to Labrys sp. The cultivable SE strains belonged mainly to the Bacillus genera and some members of the Rhodococcus genera. The treatment effects depended on the soil Cu concentration. Both SE and SEF plants had a higher Cu tolerance in the 13–517 mg Cu kg−1 soil range as reflected by increased shoot and root DW yields compared to control plants. This was accompanied by a slight decrease in shoot Cu concentration and increase in root Cu concentration. Shoot and root DW yields were more promoted by SE than SEF in the 13–114 mg Cu kg−1 soil range, which could reflect the influence of seed-located bacterial endophytes. At intermediate soil Cu (416–818 mg Cu kg−1 soil), the RE and CMg plants had lower shoot Cu concentrations than the control, SE and SEF plants. At high total soil Cu (617–1020 mg Cu kg−1), root DW yield of RE plants slightly increased and their root Cu concentration rose by up to 1.9-fold. In terms of phytoextraction efficiency, shoot Cu removal was increased for sunflower plants inoculated with crude and bacterial cell-free seed extracts by 1.3- to 2.2-fold in the 13–416 mg Cu kg−1 soil range. Such increase was mainly driven by an enhanced shoot DW yield. The number and distribution of endophytic bacteria in the harvested sunflower tissues must be further examined.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate
- C:
-
Untreated plants
- Chl TOT:
-
Total chlorophyll content
- CMg:
-
Control plants supplemented with a solution of MgSO4
- CuTOT:
-
Total soil Cu
- DMF:
-
N,N-Dimethylformamide
- DW SH:
-
Shoot dry weight yield
- DW RT:
-
Root dry weight yield
- IAA:
-
Indoleacetic acid
- PGPB:
-
Plant growth-promoting bacteria
- RE:
-
Inoculant with endophytic bacteria from the surface-sterilized A. capillaris roots
- SE:
-
Inoculant with endophytic bacteria from the A. capillaris seeds
- SEF:
-
Bacterial cell-free seed extract obtained by filtering a SE aliquot at 0.2 μm
- SL:
-
Maximum stem length
- TE:
-
Trace element
References
Adesodun JK, Atayese MO, Agbaje TA, Osadiaye BA, Mafe OF, Soretire AA (2010) Phytoremediation potentials of sunflowers (Tithonia diversifolia and Helianthus annuus) for metals in soils contaminated with zinc and lead nitrates. Water Air Soil Pollut 207(1–4):195–201. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0128-3
Alaoui-Sosse B, Genet P, Vinit-Dunand F, Toussaint ML, Epron D, Badot PM (2004) Effect of copper on growth in cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus) and its relationships with carbohydrate accumulation and changes in ion contents. Plant Sci 166(5):1213–1218. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2003.12.032
Babu AG, Kim J-D, Oh B-T (2013) Enhancement of heavy metal phytoremediation by Alnus firma with endophytic Bacillus thuringiensis GDB-1. J Hazard Mater 250:477–483. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.02.014
Barac T, Taghavi S, Borremans B, Provoost A, Oeyen L, Colpaert JV, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D (2004) Engineered endophytic bacteria improve phytoremediation of water-soluble, volatile, organic pollutants. Nat Biotechnol 22(5):583–588. doi:10.1038/nbt960
Bazely DR, Ball JP, Vicari M, Tanentzap AJ, Berenger M, Rakocevic T, Koh S (2007) Broad-scale geographic patterns in the distribution of vertically-transmitted, asexual endophytes in four naturally-occurring grasses in Sweden. Ecography 30(3):367–374. doi:10.1111/j.2007.0906-7590.04985.x
Becerra-Castro C, Kidd PS, Prieto-Fernandez A, Weyens N, Acea M-J, Vangronsveld J (2011) Endophytic and rhizoplane bacteria associated with Cytisus striatus growing on hexachlorocyclohexane-contaminated soil: isolation and characterisation. Plant Soil 340(1–2):413–433. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0613-x
Becerra-Castro C, Monterroso C, Prieto-Fernández A, Rodríguez-Lamas L, Loureiro-Viñas M, Acea MJ, Kidd PS (2012) Pseudometallophytes colonising Pb/Zn mine tailings: a description of the plant–microorganism–rhizosphere soil system and isolation of metal-tolerant bacteria. J Hazard Mater 217–218:350–359. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.03.039
Belimov AA, Hontzeas N, Safronova VI, Demchinskaya SV, Piluzza G, Bullitta S, Glick BR (2005) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol Biochem 37(2):241–250. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.033
Bes C, Mench M, Aulen M, Gasté H, Taberly J (2010) Spatial variation of plant communities and shoot Cu concentrations of plant species at a timber treatment site. Plant Soil 330:267–280. doi:10.1007/s11104-009-0198-4
Bressan W, Borges MT (2004) Delivery methods for introducing endophytic bacteria into maize. Biocontrol 49(3):315–322. doi:10.1023/b:bico.0000025372.51658.93
Burd GI, Dixon DG, Glick BR (2000) Plant growth-promoting bacteria that decrease heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can J Microbiol 46(3):237–245. doi:10.1139/cjm-46-3-237
CETIOM (1995) Les stades repères du tournesol (détails). Available at http://www.cetiom.fr/tournesol/cultiver-du-tournesol/atouts-points-cles/stades-reperes/stades-reperes-detailles/?print=1. Access on 21 May 2014
Chen H, Cutright TJ (2003) Preliminary evaluation of microbially mediated precipitation of cadmium, chromium, and nickel by rhizosphere consortium. J Environ Eng 129(1):4–9. doi:10.1061/(asce)0733-9372(2003)129:1(4)
Chen YX, Wang YP, Lin Q, Luo YM (2005) Effect of copper-tolerant rhizosphere bacteria on mobility of copper in soil and copper accumulation by Elsholtzia splendens. Environ Int 31(6):861–866. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.044
Cherian S, Weyens N, Lindberg S, Vangronsveld J (2012) Phytoremediation of trace element-contaminated environments and the potential of endophytic bacteria for improving this process. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42(21):2215–2260. doi:10.1080/10643389.2011.574106
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37(Database issue):D141–D145. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn879PMCID, PMC2686447
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clement C, Barka EA (2005a) Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: Principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(9):4951–4959. doi:10.1128/aem. 71.9.4951-4959.2005
Compant S, Reiter B, Sessitsch A, Nowak J, Clement C, Barka EA (2005b) Endophytic colonization of Vitis vinifera L. by plant growth promoting bacterium Burkholderia sp strain PsJN. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(4):1685–1693. doi:10.1128/aem. 71.4.1685-1693.2005
Compant S, Clement C, Sessitsch A (2010) Plant growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizo- and endosphere of plants: their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization. Soil Biol Biochem 42(5):669–678. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.024
De la Iglesia R, Castro D, Ginocchio R, van der Lelie D, Gonzalez B (2006) Factors influencing the composition of bacterial communities found at abandoned copper-tailings dumps. J Appl Microbiol 100(3):537–544. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02793.x
Dickinson NM, Baker AJM, Doronila A, Laidlaw S, Reeves RD (2009) Phytoremediation of inorganics: realism and synergies. Int J Phytoremediation 11(2):97–114. doi:10.1080/15226510802378368
Evon P, Vandenbossche V, Rigal L (2012) Manufacturing of renewable and biodegradable fiberboards from cake generated during biorefinery of sunflower whole plant in twin-screw extruder: Influence of thermopressing conditions. Polymer Degradation and Stability 97(10):1940–1947. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.01.025
Faessler E, Robinson BH, Stauffer W, Gupta SK, Papritz A, Schulin R (2010) Phytomanagement of metal-contaminated agricultural land using sunflower, maize and tobacco. Agric Ecosyst Environ 136(1–2):49–58. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2009.11.007
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28(3):367–374. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.02.001
Glick BR, Stearns JC (2011) Making phytoremediation work better: maximizing a plant’s growth potential in the midst of adversity. Int J Phytoremediation 13(Suppl 1):4–16
Hardoim PR, van Overbeek LS, van Elsas JD (2008) Properties of bacterial endophytes and their proposed role in plant growth. Trends Microbiol 16(10):463–471. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2008.07.008
Herzig R, Nehnevajova E, Pfistner C, Schwitzguébel JP, Ricci A, Keller C (2014) Feasibility of labile Zn phytoextraction using enhanced tobacco and sunflower: results of five- and one-year field-scale experiments in Switzerland. Int J Phytoremediation 16(7–8):735–754. doi:10.1080/15226514.2013.856846
Hewitt E (1966) Sand and water culture methods used in the study of plant nutrition. The Eastern press Ltd, London
Idris R, Trifonova R, Puschenreiter M, Wenzel WW, Sessitsch A (2004) Bacterial communities associated with flowering plants of the Ni hyperaccumulator Thlaspi goesingense. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(5):2667–2677. doi:10.1128/a-em.70.5.2667-2677.2004
ISO (2005) Soil quality—determination of the effects of pollutants on soil flora Part 2: effects of chemicals on the emergence and growth of higher plants, vol ISO 11269–2. Geneva
Kabagale AC, Cornu B, van Vliet F, Meyer C-L, Mergeay M, Simbi J-BL, Droogmans L, Vander Wauven C, Verbruggen N (2010) Diversity of endophytic bacteria from the cuprophytes Haumaniastrum katangense and Crepidorhopalon tenuis. Plant Soil 334(1–2):461–474. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0396-0
Kinraide TB, Pedler JF, Parker DR (2004) Relative effectiveness of calcium and magnesium in the alleviation of rhizotoxicity in wheat induced by copper, zinc, aluminum, sodium, and low pH. Plant Soil 259(1–2):201–208. doi:10.1023/b:plso.0000020972.18777.99
Kiran B, Lalitha V, Raveesha KA (2011) Antifungal and growth promoting potentiality of seeds of Psoralea corylifolia L. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 2(3):564–573, Available at http://www.rjpbcs.com/pdf/2011_2(3)/68.pdf. Access on November 21, 2014
Kolbas A, Mench M, Herzig R, Nehnevajova E, Bes CM (2011) Copper phytoextraction in tandem with oilseed production using commercial cultivars and mutant lines of sunflower. Int J Phytoremediation 13(Suppl 1):55–76. doi:10.1080/15226514.2011.568536
Kolbas A, Mench M, Marchand L, Herzig R, Nehnevajova E (2014) Phenotypic seedling responses of a metal-tolerant mutant line of sunflower growing on a Cu-contaminated soil series: potential uses for biomonitoring of Cu exposure and phytoremediation. Plant Soil 376(1–2):377–397. doi:10.1007/s11104-013-1974-8
Kuffner M, Puschenreiter M, Wieshammer G, Gorfer M, Sessitsch A (2008) Rhizosphere bacteria affect growth and metal uptake of heavy metal accumulating willows. Plant Soil 304(1–2):35–44. doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9517-9
Kuffner M, De Maria S, Puschenreiter M, Fallmann K, Wieshammer G, Gorfer M, Strauss J, Rivelli AR, Sessitsch A (2010) Culturable bacteria from Zn- and Cd-accumulating Salix caprea with differential effects on plant growth and heavy metal availability. J Appl Microbiol 108(4):1471–1484. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04670.x
Lagriffoul A, Mocquot B, Mench M, Vangronsveld J (1998) Cadmium toxicity effects on growth, mineral and chlorophyll contents, and activities of stress related enzymes in young maize plants (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 200(2):241–250. doi:10.1023/a:1004346905592
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Lebeau T, Braud A, Jezequel K (2008) Performance of bioaugmentation-assisted phytoextraction applied to metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Pollut 153(3):497–522. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.09.015
Lequeux H, Hermans C, Lutts S, Verbruggen N (2010) Response to copper excess in Arabidopsis thaliana: impact on the root system architecture, hormone distribution, lignin accumulation and mineral profile. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(8):673–682. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.05.005
Li L, Henry GE, Seeram NP (2009) Identification and bioactivities of resveratrol oligomers and flavonoids from Carex folliculata seeds. J Agric Food Chem 57(16):7282–7287. doi:10.1021/jf901716j
Lodewyckx C, Taghavi S, Mergeay M, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H, van der Lelie D (2001) The effect of recombinant heavy metal-resistant endophytic bacteria on heavy metal uptake by their host plant. Int J Phytoremediation 3(2):173–187. doi:10.1080/15226510108500055
Luo S, Xu T, Chen L, Chen J, Rao C, Xiao X, Wan Y, Zeng G, Long F, Liu C, Liu Y (2012) Endophyte-assisted promotion of biomass production and metal-uptake of energy crop sweet sorghum by plant-growth-promoting endophyte Bacillus sp SLS18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(4):1745–1753. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3483-0
Lyubun Y, Chernyshova M (2010) Use of rhizobacteria to inoculate agricultural crops grown on arsenic-polluted soil. J Biotechnol 150:S247–S247. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.09.118
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2009) Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacterium Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain Ax10 for the improvement of copper phytoextraction by Brassica juncea. J Environ Manag 90(2):831–837. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.01.014
Ma Y, Prasad MNV, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2011a) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and endophytes accelerate phytoremediation of metalliferous soils. Biotechnol Adv 29(2):248–258. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.12.001
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Luo Y, Freitas H (2011b) Inoculation of endophytic bacteria on host and non-host plants—effects on plant growth and Ni uptake. J Hazard Mater 195:230–237. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.034
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Sa T (2007) Metal tolerating methylotrophic bacteria reduces nickel and cadmium toxicity and promotes plant growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Chemosphere 69(2):220–228. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.017
Malinowski DP, Zuo H, Belesky DP, Alloush GA (2004) Evidence for copper binding by extracellular root exudates of tall fescue but not perennial ryegrass infected with Neotyphodium spp. endophytes. Plant Soil 267(1–2):1–12. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-2575-y
Mastretta C, Taghavi S, van der Lelie D, Mengoni A, Galardi F, Gonnelli C, Barac T, Boulet J, Weyens N, Vangronsveld J (2009) Endophytic bacteria from seeds of Nicotiana tabacum can reduce cadmium phytotoxicity. Int J Phytoremediation 11(3):251–267. doi:10.1080/15226510802432678
Meers E, Ruttens A, Hopgood M, Lesage E, Tack FMG (2005) Potential of Brassica rapa, Cannabis sativa, Helianthus annuus and Zea mays for phytoextraction of heavy metals from calcareous dredged sediment derived soils. Chemosphere 61(4):561–572. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.026
Mench M, Schwitzguebel J-P, Schroeder P, Bert V, Gawronski S, Gupta S (2009) Assessment of successful experiments and limitations of phytotechnologies: contaminant uptake, detoxification and sequestration, and consequences for food safety. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16(7):876–900. doi:10.1007/s11356-009-0252-z
Mench M, Lepp N, Bert V, Schwitzguebel J-P, Gawronski SW, Schroeder P, Vangronsveld J (2010) Successes and limitations of phytotechnologies at field scale: outcomes, assessment and outlook from COST Action 859. J Soils Sediments 10(6):1039–1070. doi:10.1007/s11368-010-0190-x
Mergeay M, Nies D, Schlegel HG, Gerits J, Charles P, Vangijsegem F (1985) Alcaligenes-eutrophus CH34 is a facultative chemolithotroph with plasmid-bound resistance to heavy-metals. J Bacteriol 162(1):328–334
Navari-Izzo F, Cestone B, Cavallini A, Natali L, Giordani T, Quartacci MF (2006) Copper excess triggers phospholipase D activity in wheat roots. Phytochemistry 67(12):1232–1242. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.04.006
Poschenrieder P, Cabot C, Martos S, Gallego B, Barceló J (2013) Do toxic ions induce hormesis in plants? Plant Sci 212:15–25. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.07.012
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Freitas H (2009) Endophytic bacteria and their potential to enhance heavy metal phytoextraction. Chemosphere 77(2):153–160. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.047
Rajkumar M, Sandhya S, Prasad MNV, Freitas H (2012) Perspectives of plant-associated microbes in heavy metal phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 30(6):1562–1574. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.04.011
Rani A, Shouche YS, Goel R (2008) Declination of copper toxicity in pigeon pea and soil system by growth-promoting Proteus vulgaris KNP3 strain. Curr Microbiol 57(1):78–82. doi:10.1007/s00284-008-9156-2
Reed MLE, Glick BR (2005) Growth of canola (Brassica napus) in the presence of plant growth-promoting bacteria and either copper or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Can J Microbiol 51(12):1061–1069. doi:10.1139/w05-094
Rivelli AR, Sd M, Puschenreiter M, Gherbin P, de Maria S (2012) Accumulation of cadmium, zinc, and copper by Helianthus annuus L.: impact on plant growth and uptake of nutritional elements. Int J Phytoremediation 14(4):320–334. doi:10.1080/15226514.2011.620649
Ronda JC, Lligadas G, Galia M, Cadiz V (2011) Vegetable oils as platform chemicals for polymer synthesis. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 113(1):46–58. doi:10.1002/ejlt.201000103
Ryan RP, Germaine K, Franks A, Ryan DJ, Dowling DN (2008) Bacterial endophytes: recent developments and applications. FEMS Microbiol Lett 278(1):1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00918.x
Rylo Sona Janarthine S, Eganathan P (2012) Plant growth promoting of endophytic Sporosarcina aquimarina SJAM16103 isolated from the pneumatophores of Avicennia marina L. Int J Microbiol 2012(ID 532060):1–10. doi:10.1155/2012/532060
Saikkonen K, Ahlholm J, Helander M, Lehtimaki S, Niemelainen O (2000) Endophytic fungi in wild and cultivated grasses in Finland. Ecography 23(3):360–366. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0587.2000.d01-1645.x
Sarkar D, Bhowmik PC, Kwon Y-I, Shetty K (2009) Clonal response to cold tolerance in creeping bentgrass and role of proline-associated pentose phosphate pathway. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5332–5339. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.086
Sessitsch A, Kuffner M, Kidd P, Vangronsveld J, Wenzel WW, Fallmann K, Puschenreiter M (2013) The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 60:182–194. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.01.012
Shaul O (2002) Magnesium transport and function in plants: the tip of the iceberg. Biometals 15(3):309–323
Sheng X, Xia J, Jiang C, He L, Qian M, Sheng XF, Xia JJ, Jiang CY, He LY, Qian M (2008) Characterization of heavy metal-resistant endophytic bacteria from rape (Brassica napus) roots and their potential in promoting the growth and lead accumulation of rape. Environ Pollut 156(3):1164–1170. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.04.007
Sturz AV, Nowak J (2000) Endophytic communities of rhizobacteria and the strategies required to create yield enhancing associations with crops. Appl Soil Ecol 15(2):183–190. doi:10.1016/s0929-1393(00)00094-9
Sun L-N, Zhang Y-F, He L-Y, Chen Z-J, Wang Q-Y, Qian M, Sheng X-F (2010) Genetic diversity and characterization of heavy metal-resistant-endophytic bacteria from two copper-tolerant plant species on copper mine wasteland. Bioresour Technol 101(2):501–509. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.011
Sziderics AH, Rasche F, Trognitz F, Sessitsch A, Wilhelm E (2007) Bacterial endophytes contribute to abiotic stress adaptation in pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). Can J Microbiol 53(11):1195–1202. doi:10.1139/w07-082
Truyens S, Jambon I, Croes S, Janssen J, Weyens N, Mench M, Carleer R, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J (2014) The effect of long-term Cd and Ni exposure on seed endophytes of Agrostis capillaris and their potential application in phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediation 16(7–8):643–659. doi:10.1080/15226514.2013.837027
Vangronsveld J, Herzig R, Weyens N, Boulet J, Adriaensen K, Ruttens A, Thewys T, Vassilev A, Meers E, Nehnevajova E, van der Lelie D, Mench M (2009) Phytoremediation of contaminated soils and groundwater: lessons from the field. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16(7):765–794. doi:10.1007/s11356-009-0213-6
Wang ZW, Wang SM, Ji YL, Zhao MW, Yu HS (2005) Plant endophyte research-detection and distribution of endophytic fungi in poaceous plants in saline-alkali areas in Dongying, Shandong, China. Pratacultural Sci 22(2):60–64
Wang W, Deng Z, Tan H, Cao L (2013) Effects of Cd, Pb, Zn, Cu-resistant endophytic enterobacter sp CBSB1 and Rhodotorula sp CBSB79 on the growth and phytoextraction of Brassica plants in multimetal contaminated soils. Int J Phytoremediation 15(5):488–497. doi:10.1080/15226514.2012.716101
Weyens N, van der Lelie D, Taghavi S, Vangronsveld J (2009) Phytoremediation: plant-endophyte partnerships take the challenge. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20(2):248–254. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2009.02.012
Wood JE, Senthilmohan ST, Peskin AV (2002) Antioxidant activity of procyanidin-containing plant extracts at different pHs. Food Chem 77(2):155–161
Wu L, Huang Z, Qin P, Yao Y, Meng X, Zou J, Zhu K, Ren G (2011) Chemical characterization of a procyanidin-rich extract from sorghum bran and its effect on oxidative stress and tumor inhibition in vivo. J Agric Food Chem 59(16):8609–8615. doi:10.1021/jf2015528
Xie P, HaoX, Herzberg M, Luo Y, Nies DH, Wei G (2014) Genomic analyses of metal resistance genes in three plant growth promoting bacteria of legume plants in Northwest mine tailings, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences (in press). doi:10.1016/j.jes.2014.07.017
Y-f Z, L-y H, Z-j C, Q-y W, Qian M, X-f S (2011) Characterization of ACC deaminase-producing endophytic bacteria isolated from copper-tolerant plants and their potential in promoting the growth and copper accumulation of Brassica napus. Chemosphere 83(1):57–62. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.041
Zagorchev L, Seal CE, Kranner I, Odjakova M (2013) A central role for thiols in plant tolerance to abiotic stress. Int J Mol Sci 14(4):7405–7432. doi:10.3390/ijms14047405
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by ADEME, Department of Urban Brownfields and Polluted Sites, Angers, France, and the European Commission under the Seventh Framework Programme for Research (FP7-KBBE-266124, GREENLAND). This study has been carried out in the framework of the Cluster of Excellence COTE. The authors thank Dr. Jean-Paul Maalouf for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolbas, A., Kidd, P., Guinberteau, J. et al. Endophytic bacteria take the challenge to improve Cu phytoextraction by sunflower. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 5370–5382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4006-1