Abstract
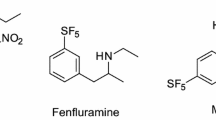
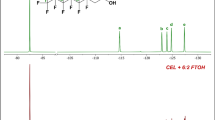
We report, for the first time, the biotransformation of potential pollutants bearing the pentafluorosulfanyl (SF5-) functional group in a fungus and bacteria. Cunninghamella elegans transformed p-methoxy phenyl SF5 via demethylation; Pseudomonas knackmussii and P. pseudoalcaligenes KF707 transformed amino-, hydroxyamino- and diamino- substituted phenyl SF5, forming the N-acetylated derivatives as the main product. Cell-free extract of Streptomyces griseus transformed 4-amino-3-hydroxy-phenyl SF5 to the N-acetylated derivative in the presence of acetyl CoA, confirming that an N-acetyltransferase is responsible for the bacterial biotransformations. Approximately 25 % of drugs and 30 % of agrochemicals contain fluorine, and the trifluoromethyl group is a prominent feature of many of these since it improves lipophilicity and stability. The pentafluorosulfanyl substituent is seen as an improvement on the trifluoromethyl group and research efforts are underway to develop synthetic methods to incorporate this moiety into biologically active compounds. It is important to determine the potential environmental impact of these compounds, including the potential biotransformation reactions that may occur when they are exposed to microorganisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alotomonte S, Zanda M (2012) Synthetic chemistry and biological activity of pentafluorosulphanyl (SF5) organic molecules. J Fluorine Chem 143:57–93
Amadio J, Murphy CD (2010) Biotransformation of fluorobiphenyl by Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:345–351
Beier P, Pastyrikova T, Vida N, Iakobson G (2011) SNAr reactions of nitro-(pentafluorosulfanyl)benzenes to generate SF5 aryl ethers and sulfides. Org Lett 13:1466–1469
Beier P, Pastyrikova T (2011) Hydroxylation of nitro-(pentafluorosulfanyl)benzenes via vicarious nucleophilic substitution of hydrogen. Tetrahedron Lett 52:4392–4394
Boersma FGH, McRoberts WC, Cobb SL, Murphy CD (2004) A F-19 NMR study of fluorobenzoate biodegradation by Sphingomonas sp. HB-1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 237:355–361
Bright TV, Dalton F, Elder VL, Murphy CD, O’Connor NK, Sandford G (2013) A convenient chemical-microbiological method for developing fluorinated pharmaceuticals. Org Biomol Chem 11:1135–1142
Cerniglia CE, Miller DW, Yang SK, Freeman JP (1984) Effects of a fluoro substituent on the fungal metabolism of 1-fluoronaphthalene. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:294–300
Dolbier WR (2005) Fluorine chemistry at the millennium. J Fluorine Chem 126:157–163
Donnelly C, Murphy CD (2009) Purification and properties of fluoroacetate dehalogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens DSM 8341. Biotechnol Lett 31:245–250
Engesser KH, Cain RB, Knackmuss HJ (1988a) Bacterial metabolism of side-chain fluorinated aromatics—co-metabolism of 3-trifluoromethyl(tfm)-benzoate by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2 and Rhodococcus rubropertinctus N657. Arch Microbiol 149:188–197
Engesser KH, Rubio MA, Knackmuss HJ (1990) Bacterial metabolism of side-chain-fluorinated aromatics—unproductive meta-cleavage of 3-trifluoromethylcatechol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32:600–608
Engesser KH, Rubio MA, Ribbons DW (1988b) Bacterial metabolism of side-chain fluorinated aromatics—co-metabolism of 4-trifluoromethyl(tfm)-benzoate by 4-isopropylbenzoate grown Pseudomonas putida Jt strains. Arch Microbiol 149:198–206
Ferreira MIM, Marchesi JR, Janssen DB (2008) Degradation of 4-fluorophenol by Arthrobacter sp. strain IF1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:709–717
Harper DB, O’Hagan D (1994) The fluorinated natural products. Nat Prod Rep 11:123–133
Hughes D, Clark BR, Murphy CD (2011) Biodegradation of polyfluorinated biphenyl in bacteria. Biodegradation 22:741–749
Jackson DA, Mabury SA (2009) Environmental properties of pentafluorosulfanyl compounds: physical properties and photodegradation. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1866–1873
Key BD, Howell RD, Criddle CS (1997) Fluorinated organics in the biosphere. Environ Sci Technol 31:2445–2454
Kubiak X, Dervins-Ravault D, Pluvinage B, Chaffotte AF, Gomez-Valero L, Dairou J, Busi F, Dupret JM, Buchrieser C, Rodrigues-Lima F (2012) Characterization of an acetyltransferase that detoxifies aromatic chemicals in Legionella pneumophila. Biochem J 445:219–228
Lim DS, Choi JS, Pak CS, Welch JT (2007) Synthesis and herbicidal activity of a pentafluorosulfanyl analog of trifluralin. J Pestic Sci 32:255–259
Misiak K, Casey E, Murphy CD (2011) Factors influencing 4-fluorobenzoate degradation in biofilm cultures of Pseudomonas knackmussii B13. Water Res 45:3512–3520
Murphy CD (2010) Biodegradation and biotransformation of organofluorine compounds. Biotechnol Lett 32:351–359
Murphy CD, Quirke S, Balogun O (2008) Degradation of fluorobiphenyl by Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707. FEMS Microbiol Lett 286:45–49
Pastyrikova T, Iakobson G, Vida N, Pohl R, Beier P (2012) Direct amination of nitro(pentafluorosulfanyl)benzenes through vicarious nucleophilic substitution of hydrogen. Eur J Org Chem 2012(11):2123–2126
Stolz A, Busse HJ, Kampfer P (2007) Pseudomonas knackmussii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:572–576
Suzuki H, Ohnishi Y, Horinouchi S (2007) Arylamine N-acetyltransferase responsible for acetylation of 2-aminophenols in Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol 189:2155–2159
Takenaka S, Cheng MY, Mulyono Koshiya A, Murakami S, Aoki K (2009) Gene cloning and characterization of arylamine N-acetyltransferase from Bacillus cereus strain 10-L-2. J Biosci Bioeng 107:27–32
Tweedy BG, Loeppky C, Ross JA (1970) Metobromuron—acetylation of aniline moiety as a detoxification mechanism. Science 168:482
Welch JT, Lim DS (2007) The synthesis and biological activity of pentafluorosulfanyl analogs of fluoxetine, fenfluramine, and norfenfluramine. Bioorg Med Chem 15:6659–6666
Wipf P, Mo TT, Geib SJ, Caridha D, Dow GS, Gerena L, Roncal N, Milner EE (2009) Synthesis and biological evaluation of the first pentafluorosulfanyl analogs of mefloquine. Org Biomol Chem 7:4163–4165
Wright GD (1999) Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:499–503
Zhang DL, Yang YF, Leakey JEA, Cerniglia CE (1996) Phase I and phase II enzymes produced by Cunninghamella elegans for the metabolism of xenobiotics. FEMS Microbiol Lett 138:221–226
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted with financial assistance from the Society for General Microbiology (UK), Science Foundation Ireland, Irish Research Council, Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (P207/12/0072) and the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic (RVO: 61388963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 458 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavanagh, E., Winn, M., Gabhann, C.N. et al. Microbial biotransformation of aryl sulfanylpentafluorides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 753–758 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1985-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1985-2