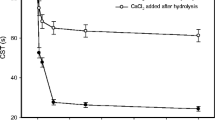
Abstract
The effect of short-time aerobic digestion on bioflocculation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) from waste activated sludge (WAS) was investigated. Bioflocculation of the EPS was found to be enhanced by 2∼6 h of WAS aerobic digestion under the conditions of natural sludge pH (about 7), high sludge concentration by gravity thickening, and dissolved oxygen of about 2 mg/L. With the same EPS extraction method, the total suspended solid content reduction of 0.20 and 0.36 g/L and the volatile suspended solid content reduction of 0.19 and 0.26 g/L were found for the WAS samples before and after aerobic digestion of 4 h. It indicates that more EPS is produced by short-time aerobic digestion of WAS. The scanning electron microscopy images of the WAS samples before and after aerobic digestion of 4 h showed that more EPS appeared on the surface of zoogloea by aerobic digestion, which reconfirmed that WAS aerobic digestion induced abundant formation of EPS. By WAS aerobic digestion, the flocculating rate of the EPS showed about 31 % growth, almost consistent with the growth of its yield (about 34 %). The EPSs obtained before and after the aerobic digestion presented nearly the same components, structures, and Fourier transform infrared spectra. These results revealed that short-time aerobic digestion of WAS enhanced the flocculation of the EPS by promoting its production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA, WEF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, D.C., USA
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chaplin MF, Kennedy JF (1994) Carbohydrate analysis, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Chen F (2007) Bacterial auto-aggregation and co-aggregation in activated sludge. Clemson University, Clemson
Decho AW (2011) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). In: Reitner J, Thiel V (eds) Encyclopedia of geobiology, encyclopedia of earth sciences. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 359–361
Ghosh M, Ganguli A, Pathak S (2009) Application of a novel biopolymer for removal of Salmonella from poultry wastewater. Environ Technol 30:337–344
Gong WX, Wang SG, Sun XF, Liu XW, Yue QY, Gao BY (2008) Bioflocculant production by culture of Serratia ficaria and its application in wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 99:4668–4674
Grönroos A, Kyllonen H, Korpijarvi K, Pirkonen P, Paavola T, Jokela J, Rintala J (2005) Ultrasound assisted method to increase soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) of sewage sludge for digestion. Ultrason Sonochem 12:115–120
He PJ, Yu GH, Shao LM, Zhu YS (2008) Extracellular proteins, polysaccharides and enzymes impact on sludge aerobic digestion after ultrasonic pretreatment. Water Res 42:1925–1934
Khanal SK, Grewell D, Sung S, Van Leeuwen J (2007) Ultrasound applications in wastewater sludge pretreatment: a review. Crit Rev Env Sci Technol 37:277–313
Kurane R, Toeda K, Takeda K, Suzuki T (1986) Culture conditions for production of microbial flocculant by Rhodococcus erythropolis. Agr Biol Chem 50:2309–2313
Liao BQ, Allen DG, Droppo IG, Leppard GG, Liss SN (2001) Surface properties of sludge and their role in bioflocculation and settleability. Water Res Water Res 35:339–350
Liu WJ, Wang K, Li BZ, Yuan HL, Yang JS (2010a) Production and characterization of an intracellular bioflocculant by Chryseobacterium daeguense W6 cultured in low nutrition medium. Bioresour Technol 101:1044–1048
Liu WJ, Yuan HL, Yang JS, Li BZ (2009) Characterization of bioflocculants from biologically aerated filter backwashed sludge and its application in dying wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 100:2629–2632
Liu XM et al (2010b) Contribution of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the sludge aggregation. Environ Sci Technol Environ Sci Technol 44:4355–4360
Liu XM, Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2007) DLVO approach to the flocculability of a photosynthetic H-2-producing bacterium, Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Environ Sci Technol 41:4620–4625
Nakata K, Kurane R (1999) Production of an extracellular polysaccharide bioflocculant by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63:2064–2068
Nomura T, Araki S, Nagao T, Konishi Y (2007) Resource recovery treatment of waste sludge using a solubilizing reagent. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 9:34–39
Rittmann BE, McCarty PL (2001) Environmental biotechnology: principles and applications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Salehizadeh H, Shojaosadati SA (2001) Extracellular biopolymeric flocculants—recent trends and biotechnological importance. Biotechnol Adv 19:371–385
Sponza DT (2003) Investigation of extracellular polymer substances (EPS) and physicochemical properties of different activated sludge flocs under steady-state conditions. Enzyme Microb Tech Enzyme Microb Tech 32:375–385
Subramanian SB, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) producing bacterial strains of municipal wastewater sludge: isolation, molecular identification, EPS characterization and performance for sludge settling and dewatering. Water Res 44:2253–2266
Subramanian SB, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY, Lohani BN (2008) Isolation and molecular identification of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) producing bacterial strains for sludge settling and dewatering. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 43:1495–1503
Sun YD, Clinkenbeard KD, Clarke C, Cudd L, Highlander SK, Dabo SM (1999) Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin induced apoptosis of bovine lymphocytes involves DNA fragmentation. Vet Microbiol 65:153–166
Tenney MW, Stumm W (1965) Chemical flocculation of microorganisms in biological waste treatment. J Water Pollut Control Fed 37:1370–1388
Ugwuanyi JO, Harvey LM, McNeil B (2005a) Effect of aeration rate and waste load on evolution of volatile fatty acids and waste stabilization during thermophilic aerobic digestion of a model high strength agricultural waste. Bioresour Technol 96:721–730
Ugwuanyi JO, Harvey LM, McNeil B (2005b) Effect of digestion temperature and pH on treatment efficiency and evolution of volatile fatty acids during thermophilic aerobic digestion of model high strength agricultural waste. Bioresour Technol 96:707–719
Weemaes MPJ, Verstraete WH (1998) Evaluation of current wet sludge disintegration techniques. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 73:83–92
Xia SQ, Zhang ZQ, Wang XJ, Yang A, Chen L, Zhao JF, Leonard D, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2008) Production and characterization of a bioflocculant by Proteus mirabilis TJ-1. Bioresour Technol 99:6520–6527
Yang SF, Li XY (2009) Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the characteristics of activated sludge under non-steady-state conditions. Process Biochem Process Biochem 44:91–96
Yu GH, He PJ, Shao LM (2009) Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) fractions from excess sludges and their effects on bioflocculability. Bioresour Technol 100:3193–3198
Zhang ZQ, Zhang J (2013) Preparation of microbial flocculant from excess sludge of municipal wastewater treatment plant. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 22:142–145
Zhang ZQ, Xia SQ, Zhang J (2010a) Enhanced dewatering of waste sludge with microbial flocculant TJ-F1 as a novel conditioner. Water Res 44:3087–3092
Zhang ZQ, Xia SQ, Zhao JF, Zhang J (2010b) Characterization and flocculation mechanism of high efficiency microbial flocculant TJ-F1 from Proteus mirabilis. Colloids Surf, B 75:247–251
Zhang ZQ, Zhang J (2012) Waste activated sludge treated by the cation exchange resin method for microbial flocculant preparation. Adv Mater Res 518–523:3585–3589
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely acknowledge the supports provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51008218), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (0400219210), SRF for ROCS SEM, Shanghai Shuguang Tracking Program (10GG12), and 863 Program 2009AA062902.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Zhao, J. et al. Effect of short-time aerobic digestion on bioflocculation of extracellular polymeric substances from waste activated sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 1812–1818 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1887-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1887-3