Abstract
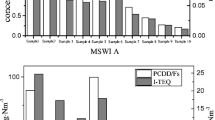
Nine typical waste incinerating plants were investigated for polychlorinated naphthalene (PCN) contents in their stack gas. The incinerators investigated include those used to incinerate municipal solid, aviation, medical, and hazardous wastes including those encountered in cement kilns. PCNs were qualified and quantified by isotope dilution high resolution gas chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry techniques. An unexpectedly high concentration of PCNs (13,000 ng Nm−3) was found in the stack gas emitted from one waste incinerator. The PCN concentrations ranged from 97.6 to 874 ng Nm−3 in the other waste incinerators. The PCN profiles were dominated by lower chlorinated homologues, with mono- to tetra-CNs being the main homologues present. Furthermore, the relationships between PCNs and other unintentional persistent organic pollutants involving polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans, polychlorinated biphenyls, hexachlorobenzene, and pentachlorobenzene were examined to ascertain the closeness or otherwise of their formation mechanisms. A good correlation was observed between ΣPCN (tetra- to octa-CN) and ΣPCDF (tetra- to octa-CDF) concentrations suggesting that a close relationship may exist between their formation mechanisms. The results would provide an improved understanding of PCN emissions from waste incinerators.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad E, Caixach J, Rivera J (1999) Dioxin like compounds from municipal waste incinerator emissions: assessment of the presence of polychlorinated naphthalenes. Chemosphere 38:109–120
Ba T, Zheng M, Zhang B, Liu W, Su G, Liu G, Xiao K (2010) Estimation and congener-specific characterization of polychlorinated naphthalene emissions from secondary nonferrous metallurgical facilities in China. Environ Sci Technol 44:2441–2446
Behnisch PA, Hosoe K, Shiozaki K, Kiryu T, Komatsu K, Schramm KW, Sakai S (2002) Melting and incineration plants of municipal waste—chemical and biochemical diagnosis of thermal processing samples (emission, residues). Environ Sci Pollut Res 9:337–344
Bidleman TF, Helm PA, Braune BM, Gabrielsen GW (2010) Polychlorinated naphthalenes in polar environments—a review. Sci Total Environ 408:2919–2935
Blankenship AL, Kannan K, Villalobos SA, Villeneuve DL, Falandysz J, Imagawa T, Jakobsson E, Giesy JP (2000) Relative potencies of individual polychlorinated naphthalenes and halowax mixtures to induce Ah receptor-mediated responses. Environ Sci Technol 34:3153–3158
Domingo JL (2004) Polychlorinated naphthalenes in animal aquatic species and human exposure through the diet: a review. J Chromatogr A 1054:327–334
Falandysz J (1998) Polychlorinated naphthalenes: an environmental update. Environ Pollut 101:77–90
Falandysz J, Kawano M, Ueda M, Matsuda M, Kannan K, Giesy JP, Wakimoto T (2000) Composition of chloronaphthalene congeners in technical chloronaphthalene formulations of the Halowax series. J Environ Sci Health, Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 35:281–298
Falandysz J, Nose K, Ishikawa Y, Lukaszewicz E, Yamashita N, Noma Y (2006a) HRGC/HRMS analysis of chloronaphthalenes in several batches of Halowax 1000, 1001, 1013, 1014 and 1099. J Environ Sci Health, Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 41:2237–2255
Falandysz J, Nose K, Ishikawa Y, Lukaszewicz E, Yamashita N, Noma Y (2006b) Chloronaphthalenes composition of several batches of Halowax 1051. J Environ Sci Health, Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 41:291–301
Guo L, Zhang B, Xiao K, Zhang Q, Zheng M (2008) Levels and distributions of polychlorinated naphthalenes in sewage sludge of urban wastewater treatment plants. Chin Sci Bull 53:508–513
Hanberg A, Waern F, Asplund L, Haglund E, Safe S (1990) Swedish dioxin survey: determination of 2,3,7,8-TCDD toxic equivalent factors for some polychlorinated-biphenyls and naphthalenes using biological tests. Chemosphere 20:1161–1164
Helm PA, Bidleman TF (2003) Current combustion-related sources contribute to polychlorinated naphthalene and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl levels and profiles in air in Toronto, Canada. Environ Sci Technol 37:1075–1082
Helm PA, Bidleman TF, Li HH, Fellin P (2004) Seasonal and spatial variation of polychlorinated naphthalenes and Non-/Mono-Ortho-substituted polychlorinated biphenyls in arctic Air. Environ Sci Technol 38:5514–5521
Iino F, Tsuchiya K, Imagawa T, Gullett BK (2001) An isomer prediction model for PCNs, PCDD/Fs, and PCBs from municipal waste incinerators. Environ Sci Technol 35:3175–3181
Imagawa T, Lee CW (2001) Correlation of polychlorinated naphthalenes with polychlorinated dibenzofurans formed from waste incineration. Chemosphere 44:1511–1520
Jansson S, Fick J, Marklund S (2008) Formation and chlorination of polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) in the post-combustion zone during MSW combustion. Chemosphere 72:1138–1144
Jansson S, Antti H, Marklund S, Tysklind M (2009) Multivariate relationships between molecular descriptors and isomer distribution patterns of PCDD/Fs formed during MSW combustion. Environ Sci Technol 43:7032–7038
Liu G, Zheng M, Liu W, Wang C, Zhang B, Gao L, Su G, Xiao K, Lv P (2009) Atmospheric emission of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, hexachlorobenzene, and pentachlorobenzene from the coking industry. Environ Sci Technol 43:9196–9201
Liu G, Zheng M, Lv P, Liu W, Wang C, Zhang B, Xiao K (2010) Estimation and characterization of polychlorinated naphthalene emission from coking industries. Environ Sci Technol 44:8156–8161
Liu G, Zheng M, Du B, Nie Z, Zhang B, Liu W, Li C, Hu J (2012) Atmospheric emission of polychlorinated naphthalenes from iron ore sintering processes. Chemosphere 89:467–472
Marti-Cid R, Llobet JM, Castell V, Domingo JL (2008) Human exposure to polychlorinated naphthalenes and polychlorinated diphenyl ethers from foods in Catalonia, Spain: temporal trend. Environ Sci Technol 42:4195–4201
Ni Y, Zhang H, Fan S, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Chen J (2009) Emissions of PCDD/Fs from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere 75:1153–1158
Noma Y, Yamamoto T, Sakai SI (2004) Congener-specific composition of polychlorinated naphthalenes, coplanar PCBs, dibenzo-p-dioxins, and dibenzofurans in the halowax series. Environ Sci Technol 38:1675–1680
Oh J-E, Gullett B, Ryan S, Touati A (2007) Mechanistic relationships among PCDDs/Fs, PCNs, PAHs, CIPhs, and CIBzs in municipal waste incineration. Environ Sci Technol 41:4705–4710
Olivero-Verbel J, Vivas-Reyes R, Pacheco-Londoño L, Johnson-Restrepo B, Kannan K (2004) Discriminant analysis for activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by polychlorinated naphthalenes. J Mol Struct (THEOCHEM) 678:157–161
Pan X, Tang J, Chen Y, Li J, Zhang G (2011) Polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) in riverine and marine sediments of the Laizhou Bay area, North China. Environ Pollut 159:3515–3521
Park H, Kang J-H, Baek S-Y, Chang Y-S (2010) Relative importance of polychlorinated naphthalenes compared to dioxins, and polychlorinated biphenyls in human serum from Korea: contribution to TEQs and potential sources. Environ Pollut 158:1420–1427
Schneider M, Stieglitz L, Will R, Zwick G (1998) Formation of polychlorinated naphthalenes on fly ash. Chemosphere 37:2055–2070
Shin SK, Kim KS, You JC, Song BJ, Kim JG (2006) Concentration and congener patterns of polychlorinated biphenyls in industrial and municipal waste incinerator flue gas, Korea. J Hazard Mater 133:53–59
Takasuga T, Inoue T, Ohi E, Kumar KS (2004) Formation of polychlorinated naphthalenes, dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, biphenyls, and organochlorine pesticides in thermal processes and their occurrence in ambient air. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:419–431
Villeneuve DL, Kannan K, Khim JS, Falandysz J, Nikiforov VA, Blankenship AL, Giesy JP (2000) Relative potencies of individual polychlorinated naphthalenes to induce dioxin-like responses in fish and mammalian in vitro bioassays. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:273–281
Weber R, Iino F, Imagawa T, Takeuchi M, Sakurai T, Sadakata M (2001) Formation of PCDF, PCDD, PCB, and PCN in de novo synthesis from PAH: mechanistic aspects and correlation to fluidized bed incinerators. Chemosphere 44:1429–1438
Węgiel M, Chrząszcz R, Maślanka A, Grochowalski A (2011) Study on the determination of PCDDs/Fs and HCB in exhaust gas. Chemosphere 85:481–486
Yamashita N, Kannan K, Imagawa T, Miyazaki A, Giesy JP (2000) Concentrations and profiles of polychlorinated naphthalene congeners in eighteen technical polychlorinated biphenyl preparations. Environ Sci Technol 34:4236–4241
Yan M, Li XD, Lu SY, Chen T, Chi Y, Yan JH (2011) Persistent organic pollutant emissions from medical waste incinerators in China. J Mater Cy Waste Manag 13:213–218
Acknowledgments
Financial support for the present work was obtained from the National 973 Program (nos. 2011CB201500 and 2009CB421606), Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-JS406) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21037003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerhard Lammel
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Sample preparation and analysis for PCDD/Fs, PCBs, HxCBz and PeCBz; relative potency factors (RPFs) of the PCN congeners (Table S1); recoveries of sampling and extraction standards in the samples (Table S2); concentrations of PCDD/F, PCB, HxCBz, and PeCBz in the stack gas samples (Table S3) and correlation among the concentrations of ΣPCNs and other U-POPs (Fig. S1); ratios of some characteristic PCN congeners in technical formulations of PCNs and PCBs (Fig. S2). DOCX 210 kb
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Zheng, M., Liu, W. et al. Characterization of polychlorinated naphthalenes in stack gas emissions from waste incinerators. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 2905–2911 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1218-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1218-0