Abstract
Purpose
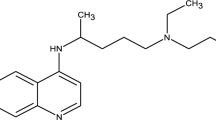
Gamma ray irradiation is considered as an effective way to degrade diclofenac. However, due to the extensive coexisting substances in natural waters, the use of gamma ray irradiation for degradation is often influenced by multiple factors. The various factors that affect degradation efficiency, such as initial diclofenac concentration, initial pH, and the concentration of the additives including H2O2 (·OH radical promoter), CH3OH (·OH radical scavenger), thiourea (·OH, H·, and e −aq scavenger), humic acid, and NO −3 (coexisting substances in natural waters), are investigated. Furthermore, possible intermediate products are identified and corresponding transformation pathways are proposed.
Methods
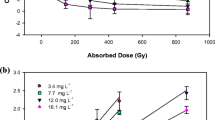
Degradation experiments were performed in a 50-mL airtight Pyrex bottle loaded with 25 mL of diclofenac solutions at various initial concentrations of 20.5, 30.4, and 50.1 mg L−1. The radiation doses were controlled at 0, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, and 1.0 kGy.
Results
Study results indicate that: (1) The degradation efficiency of diclofenac decreases with the increase of its initial concentration. (2) The degradation efficiency is higher under acidic conditions than in neutral and alkaline media. (3) The results obtained when H2O2, CH3OH, and thiourea were added show that the degradation of diclofenac takes place via two pathways: oxidation by ·OH radicals and reduction by e −aq and H·. (4) The extensive coexisting substances in natural waters, such as humic acid and NO −3 , do not affect the degradation efficiency. Based on the identified intermediates, it is proposed that transformation pathways are initiated mainly by H·, e −aq , and ·OH.
Conclusion
Gamma ray irradiation effectively degrades diclofenac.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benotti MJ, Trenholm RA, Vanderford BJ, Standford BD, Snyder SA (2009) Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in US drinking water. Environ Sci Technol 43(3):597–603
Brezonik PL, Fulkerson-Brekken J (1998) Nitrate-induced photolysis in natural waters: controls on concentrations of hydroxyl radical photo-intermediates by natural scavenging agents. Environ Sci Technol 32:3004–3010
Buser HR, Poiger T, Müller M (1999) Occurrence and environmental behavior of the chiral pharmaceutical drug ibuprofen in surface waters and in wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 33:2529–2535
Choi JI, Kim JK, Kim JH, Kweon DK, Lee JW (2010) Degradation of hyaluronic acid powder by electron beam irradiation, gamma ray irradiation, microwave irradiation and thermal treatment: a comparative study. Carbohydr Polym 79(4):1080–1085
Cleuvers M (2004) Mixture toxicity of the anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetylsalicylic acid. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:309–315
Flox C, Ammar S, Arias C, Brillas E, Vargas-Zavala AV, Abdelhedi R (2006) Electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton degradation of indigo carmine in acidic aqueous medium. Appl Catal B Environ 67(1–2):93–104
Güyer GT, Ince NH (2011) Degradation of diclofenac in water by homogeneous and heterogeneous sonolysis. Ultrason Sonochem 18:114–119
Hartmann J, Bartels P, Mau U, Witter M, Tümpling WV, Hofmann J, Nietzschmann E (2008) Degradation of the drug diclofenac in water by sonolysis in presence of catalysts. Chemosphere 70:453–461
Huber M, Canonica S, Park GY, von Gunten U (2003) Oxidation of pharmaceuticals during ozonation and advanced oxidation processes. Environ Sci Technol 37:1016–1024
Irmak S, Yavuz HI, Erbatur O (2006) Degradation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenol in aqueous solution by electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton processes. Appl Catal B Environ 63:243–248
Ito R, Miura N, Ushiro M, Kawaguchi M, Nakamura H, Iguchi H, Ogino JI, Oishi M, Wakui N, Iwasaki Y, Saito K, Nakazawa H (2009) Effect of gamma-ray irradiation on degradation of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in polyvinyl chloride sheet. Int J Pharm 376(1–2):213–218
Joss A, Zabczynski S, Göbel A, Hoffmann B, Löffler D, McArdell CS, Ternes TA, Thomsen A, Siegrist H (2006) Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: proposing a classification scheme. Water Res 40(8):1686–1696
Junko K (1997) Enhancement of wastewater and sludge treatment by ionizing radiation. In: Proceeding of a workshop on the potential for engineering scale processing of waste treatment streams by electron-beam irradiation, University of Miami, Coral Gables, pp. 30–172
Kim SD, Cho J, Kim IS, Vanderford BJ, Snyder SA (2007) Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in South Korean surface, drinking, and waste waters. Water Res 41(5):1013–1021
Kimura A, Taguchi M, Ohtani Y, Takigami M, Shimada Y, Kojima T, Hiratsuka H, Namba H (2006) Decomposition of p-nonylphenols in water and elimination of their estrogen activities by 60Co γ-ray irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 75(1):61–69. doi:10.1016/j.radphyschem.2005.05.016
Kosjek T, Žigon D, Kralj B, Heath E (2008) The use of quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometer for the elucidation of diclofenac biotransformation products in wastewater. J Chromatogr A 1215(1–2):57–63
Leónidas AP, Sixto M, Wolfgang G, Ana A, Thurman EM, Imma F, Amadeo RF (2005) Photo-Fenton degradation of diclofenac: identification of main intermediates and degradation pathway. Environ Sci Technol 39:8300–8306
Lishman L, Smyth SA, Sarafin K, Kleywegt S, Toito J, Peart T, Lee B, Servos M, Beland M, Seto P (2006) Occurrence and reductions of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and estrogens by municipal wastewater treatment plants in Ontario, Canada. Sci Total Environ 367:544–558
Loraine GA, Pettigrove ME (2006) Seasonal variations in concentrations of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in drinking water and reclaimed wastewater in southern California. Environ Sci Technol 40:687–695
Madhavan J, Kumar PSS, Anandan S, Zhou MF, Grieser F, Ashokkumar M (2010) Ultrasound assisted photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac in an aqueous environment. Chemosphere 80:747–752
Mcclellan K, Halden RU (2010) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in archived US biosolids from the 2001 EPA national sewage sludge survey. Water Res 44(2):658–668
Monteiro SC, Boxall ABA (2010) Occurrence and fate of human pharmaceuticals in the environment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 202:53–154
Nickelsen MG, Cooper WJ, Lin KJ, Kurucz CN, Waite TD (1994) High-energy electron-beam generation of oxidants for the treatment of benzene and toluene in the presence of radical scavengers. Water Res 28(5):1227–1237
Pérez-Estrada LA, Maldonado MI, Gernjak W, Agüera A, Fernández-Alba AR, Ballesteros MM, Malato S (2005) Decomposition of diclofenac by solar driven photocatalysis at pilot plant scale. Catal Today 101:219–226. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2005.03.013
Poiger T, Buser HR, Müller MD (2001) Photodegradation of the pharmaceutical drug diclofenac in a lake: pathway, field measurements, and mathematical modeling. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:256–263
Radjenović J, Petrović M, Barceló D (2009) Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (CAS) and advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment. Water Res 43:831–841
Ravina M, Campanella L, Kiwi J (2002) Accelerated mineralization of the drug Diclofenac via Fenton reactions in a concentric photo-reactor. Water Res 36:3553–3560
Rosal R, Rodriguez A, Perdigon-Melon JA, Petre A, Garcia-Calvo E, Gomez MJ, Aguera A, Fernandez-Alba AR (2010) Occurrence of emerging pollutants in urban wastewater and their removal through biological treatment followed by ozonation. Water Res 44:578–588
Sandvik SLH, Bilski P, Pakulski JD, Chignell CF, Coffin RB (2000) Photogeneration of singlet oxygen and free radicals in dissolved organic matter isolated from the Mississippi and Atchafalaya river plumes. Mar Chem 69:139–152
Singh A, Kremers W (2002) Radiolytic dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls using alkaline 2-propanol solutions. Radiat Phys Chem 65:467–472
Strukul G (ed) (1992) Catalytic oxidations with hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. Kluwer Academic, Boston
Stülten D, Zuhlke S, Lamshoft M, Spiteller M (2008) Occurrence of diclofenac and selected metabolites in sewage effluents. Sci Total Environ 405:310–316
Vincenzo N, Vincenzo B, Daniele R, Despo K (2009) Degradation of diclofenac during sonolysis, ozonation and their simultaneous application. Ultrason Sonochem 16:790–794
Vogna D, Marotta R, Napolitano A, Andreozzi R, d'Ischia M (2004) Advanced oxidation of the pharmaceutical drug diclofenac with UV/H2O2 and ozone. Water Res 38:414–422
Weigel S, Kallenborn R, Hühnerfuss H (2004) Simultaneous solid-phase extraction of acidic, neutral and basic pharmaceuticals from aqueous samples at ambient (neutral) pH and their determination by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1023:183–195
Yamazaki M, Sawai T, Sawai T, Yamazaki K, Kawaguchi S (1983) Combined gamma-ray irradiation activated-sludge treatment of humic-acid solution from landfill leachate. Water Res 17(12):1811–1814
Zhan MJ, Yang X, Xian QM, Kong LG (2006) Photosensitized degradation of bisphenol A involving reactive oxygen species in the presence of humic substances. Chemosphere 63:378–386
Zhang JB, Zheng Z, Zhao T, Zhao YF, Wang LH, Zhong Y, Xu Y (2008a) Radiation-induced reduction of diuron by gamma-ray irradiation. J Hazard Mater 151(2–3):465–472
Zhang YJ, Geissen SU, Gal C (2008b) Carbamazepine and diclofenac: removal in wastewater treatment plants and occurrence in water bodies. Chemosphere 73:1151–1161
Acknowledgments
Zheng Zheng gratefully acknowledges support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Foundation item No. 10475040). We would like to thank Zhao YongFu for his help in the experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Luo, X., Zheng, Z. et al. Factors that have an effect on degradation of diclofenac in aqueous solution by gamma ray irradiation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18, 1243–1252 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0457-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0457-9