Abstract
Purpose
Raw “Pinelliae Rhizoma” (RPR) is widely used in Chinese clinics to treat insomnia. This study investigated its underlying sedative and hypnotic mechanisms and main active components.
Methods
A locomotor activity test was used to evaluate the sedative effects of RPR at three dosages (0.2 g/mL, 0.4 g/mL, and 0.8 g/mL) in mice. Polysomnography was used to assess its ability to improve sleep. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/time of flight/mass spectrometry (UPLC-TOF–MS) analysis was used to identify the potential active components of RPR.
Results
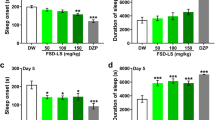
Mice in the RPR groups were less active than mice in the vehicle group; this difference was greatest in the 0.8 g/mL RPR group. Compared with the vehicle, 0.8 g/mL RPR increased the duration of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in the dark phase. In addition, the duration of wakefulness in the 0.8 g/mL RPR group decreased with increasing durations of nonrapid eye movement (NREM) and REM sleep. Compared with diazepam, 0.8 g/mL RPR increased REM sleep duration in both the light and dark phases and increased the number of transitions both from NREM sleep to REM sleep and from REM sleep to wakefulness. A total of 33 RPR constituents, including 15 alkaloids, were identified.
Conclusion
The results preliminarily indicated that RPR exerts sedative and hypnotic effects in mice, mainly leading to improvements in REM sleep. These effects are possibly due to the alkaloid constituents of RPR.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kay-Stacey M, Attarian H (2016) Advances in the management of chronic insomnia. BMJ 354:i2123. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i2123
Yang Y (2018) Experience of treating insomnia with pinellia ternata. Cardiovasc Dis J Integr Tradit Chin West Med (Electronici) 6(25):166. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-6681.2018.25.123
Wu XY, Zhao JL, Zhang M et al (2011) Sedative, hypnotic and anticonvulsant activities of the ethanol fraction from Rhizoma Pinelliae Praeparatum. J Ethnopharmaco 135:325–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.03.016
Lin SS, Nie B, Yao GH et al (2019) Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Makino preparation promotes sleep by increasing REM sleep. Nat Prod Res 33:3326–3329. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1474466
Lin SS, Nie B, Song K et al (2019) Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum Cum alumine extract: sedative and hypnotic effects in mice and component compounds. Biomed Res Int 2019:6198067. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6198067
Sun LM, Zhang B, Wang Y et al (2019) Metabolomic analysis of raw Pinelliae Rhizoma and its alum-processed products via UPLC-MS and their cytotoxicity. Biomed Chromatogr 33(2):e4411. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.4411
Fang MM, Lin SS, Yuan ZZ (2016) The comparison among different prepared Pinellia ternata on the sedation effect in mice. Med Res 45:71–75. https://doi.org/10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2016.02.019
Ryuichi N, Satoko H, Teppei F (2020) Decreased nesting behavior, selective increases in locomotor activity in a novel environment, and paradoxically increased open arm exploration in Neurogranin knockout mice. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep preprint. https://doi.org/10.1002/npr2.12150
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (2019) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 5th edn. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, USA
Sun HX, Wang DR, Ye CB et al (2017) Activation of the ventral tegmental area increased wakefulness in mice. Sleep Biol Rhythms 15:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41105-017-0094-x
Wang YQ, Takata Y, Li R et al (2015) Doxepin and diphenhydramine increased non-rapid eye movement sleep through blockade of histamine H1 receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 129:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.12.002
Liu T, Hong Z (2010) Effects of irrigation and intraperito-nealinjection on locomotor activity in mice. Editorial Board of Acta Academiae Medicinea Wannan 29(04):241–243. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-0217.2010.04.001
Mai W, Liu H, Liu X et al (2011) Influence of irrigation stimulability and IP on independent activity of mice. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med 13(09):201–202. https://doi.org/10.13194/j.jlunivtcm.2011.09.203.maiwl.084c
Wei F, Mo Z, Wang Y (2004) The influence of irrigation stimulability on the independent activity of the mice. Chin Pharmacol Bull 03:356–357
Joshi N, Leslie R, Perrot TJP, et al (2017) Analyzing the experiences of adolescent control rats: effects of the absence of physical or social stimulation on anxiety-like behaviour are dependent on the test 179:30-41 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.05.019c
Padua-Reis M, Noga DA, Tort ABL et al (2021) Diazepam causes sedative rather than anxiolytic effects in C57BL/6J mice. Sci Rep 11(1):9335. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88599-5c
Chen Q, Xiao S, Li Z et al (2015) Chemical and metabolic profiling of Si-Ni decoction analogous formulae by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci Rep 5:11638. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11638
Wu W, Jiao CX, Li H et al (2018) LC-MS based metabolic and metabonomic studies of Panax ginseng. Phytochem Anal 29(4):331–340. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2752
Lee JY, Park NH, Lee W et al (2016) Comprehensive chemical profiling of Pinellia species tuber and processed Pinellia tuber by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1471:164–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.10.033
Ding T, Yan RY, Sun Y et al (2020) Material basis, effect, and mechanism of ethanol extract of Pinellia ternata tubers on oxidative stress-induced cell senescence. Phytomedicine 77:153275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153275
Mao RJ, He ZG (2020) Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Breit: a review of its germplasm resources, genetic diversity and active components. J Ethnopharmacol 263:113252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.113252
Hess S, Baker G, Gyenes G et al (2017) Decreased serum L-arginine and L-citrulline levels in major depression. Psychopharmacology 234(21):3241–3247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4712-8
Tran PV, Nguyen LTN, Yang H et al (2020) Intracerebroventricular injection of L-arginine and D-arginine induces different effects under an acute stressful condition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 533(4):965–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.111
Lazarus M, Chen JF, Huang ZL et al (2019) Adenosine and sleep. Handb Exp Pharmacol 253:359–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2017_36
Deng CX, Wu ZB, Chen Y et al (2019) Pinellia total alkaloids modulate the GABAergic system in hippocampal formation on pilocarpine-induced epileptic rats. Chin J Integr Med 26(2):138–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-2944-7
Yao JH, Li J, Lin YD et al (2013) Research on toxicity of Rhizoma Pinelliae. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med 47:90–93. https://doi.org/10.16305/j.1007-1334.2013.09.030
Xu JY, Xie HH, San JJ et al (2013) Different effects of Rhizoma Pinelliae processed by ginger or decocting on gestation and embryonic development of mice. J Nangjing Univ Tradit Chin Med 29:255–258. https://doi.org/10.14148/j.issn.1672-0482.2013.03.018
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support from the Department of Pharmacology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
Funding
This work was supported by the Outstanding Youth Fund Project for Chinese Medicine of Zhejiang Province, China (Grant No. 2011zq014), and the 2019 incubation project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (Grant No. FHY2019041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Zhengzhong Yuan; methodology: Zhengzhong Yuan; formal analysis and investigation: Sisi Lin, Haipeng Chen, and Chengrou Jiang; data curation: Sisi Lin, Haipeng Chen, and Hui Yang; writing—original draft preparation: Sisi Lin, Haipeng Chen, and Bo Nie; writing—review and editing: Bo Nie and Qinglai Wang; Funding acquisition: Zhengzhong Yuan and Sisi Lin; Resources: Zhengzhong Yuan and Qinglai Wang; and supervision: Zhengzhong Yuan and Qinglai Wang. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The present study was approved by the experimental laboratory animal Ethics Committee of the Laboratory Animal Center at Whenzhou Medical University (wydw 2016–026) and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards provided in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Chen, H., Nie, B. et al. Raw Pinelliae Rhizoma: examination of sedative and hypnotic effects in mice and chemical analysis. Sleep Breath 27, 1143–1153 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-022-02714-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-022-02714-y