Abstract
Objective
The objectives of this paper are to examine the effect of chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) on the morphological changes in the kidney of growing rats and to explore the mechanisms underlying the CIH-induced renal damage.
Methods
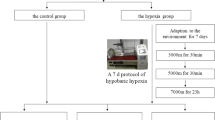
Forty Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into two groups: 2 and 4 weeks CIH groups (2IH, 4IH), and in the control group 2 and 4 weeks air-stimulated groups (2C, 4C), with 10 rats in each group. Pathological changes of renal tissue were observed by HE staining, PAS staining, and Masson staining. Real-time PCR method was used to detect the mRNA expression of HIF-1α, CuZnSOD/ZnSOD, and MnSOD in renal tissue.
Results
(1) Intermittent hypoxia (IH) caused morphological damage in the kidney. Hypertrophy of epithelial cells in the kidney tubules and dilation in the glomeruli were observed under light microscope in HE and PAS stain, especially in 4IH group. Masson staining showed no significant fibrotic response in the IH groups. (2) Compared with the corresponding control groups, the levels of serum SOD were significantly lower in CIH groups, and especially in 4IH group. The mRNA expression of Cu/ZnSOD and MnSOD in CIH groups decreased significantly as compared to control groups. The mRNA levels of HIF-1α in the kidney were significantly higher in CIH groups than those in the corresponding control groups.
Conclusion
Oxidative stress played a critical role in renal damage by up-regulating HIF-1α transcription and down-regulating Cu/ZnSOD and MnSOD transcription after chronic intermittent hypoxia exposure in growing rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CIH:
-
chronic intermittent hypoxia
- OSAHS:
-
obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome
- HIF-1α:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- Cu/ZnSOD:
-
copper-zinc superoxide dismutase
- MnSOD:
-
manganese superoxide dismutase
- PAS:
-
periodic acid–Schiff stain
- HE:
-
hematoxylin and eosin stain
- qRT-PCR:
-
real-time polymerase chain reaction
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- IRI:
-
ischemia reperfusion injury
References
Guilleminault C, Abad VC (2004) Obstructive sleep apnea syndromes. Med Clin N Am 88(3):611–630, viii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2004.01.002
Wildhaber JH, Moeller A (2007) Sleep and respiration in children: time to wake up! Swiss Med Wkly 137(49–50):689–694
Li AM, So HK, Au CT, Ho C, Lau J, Ng SK, Abdullah VJ, Fok TF, Wing YK (2010) Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome in Chinese children: a two-phase community study. Thorax 65(11):991–997. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2010.134858
Levy P, Tamisier R, Arnaud C, Monneret D, Baguet JP, Stanke-Labesque F, Dematteis M, Godin-Ribuot D, Ribuot C, Pepin JL (2012) Sleep deprivation, sleep apnea and cardiovascular diseases. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 4:2007–2021
Schober AK, Neurath MF, Harsch IA (2011) Prevalence of sleep apnoea in diabetic patients. Clin Respir J 5(3):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-699X.2010.00216.x
Badran M, Golbidi S, Devlin A, Ayas N, Laher I (2014) Chronic intermittent hypoxia causes endothelial dysfunction in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Sleep Med 15(5):596–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2014.01.013
Bhattacharjee R, Kheirandish-Gozal L, Pillar G, Gozal D (2009) Cardiovascular complications of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: evidence from children. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 51(5):416–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.03.002
Serebrovskaya TV, Xi L (2015) Intermittent hypoxia in childhood: the harmful consequences versus potential benefits of therapeutic uses. Front Pediatr 3:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2015.00044
Martin RJ, Wang K, Koroglu O, Di Fiore J, Kc P (2011) Intermittent hypoxic episodes in preterm infants: do they matter? Neonatology 100(3):303–310. https://doi.org/10.1159/000329922
Martin RJ, Di Fiore JM, Macfarlane PM, Wilson CG (2012) Physiologic basis for intermittent hypoxic episodes in preterm infants. Adv Exp Med Biol 758:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4584-1_47
Bass JL, Corwin M, Gozal D, Moore C, Nishida H, Parker S, Schonwald A, Wilker RE, Stehle S, Kinane TB (2004) The effect of chronic or intermittent hypoxia on cognition in childhood: a review of the evidence. Pediatrics 114(3):805–816. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2004-0227
Cai XH, Li XC, Jin SW, Liang DS, Wen ZW, Cao HC, Mei HF, Wu Y, Lin ZD, Wang LX (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage after chronic intermittent hypoxia in growing rats. Exp Neurol 257:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.04.029
Cai XH, Li XC, QQ H, CY Y, Zhou YH, MS S, Zhao YP, YL H, Wang LX (2013) Multiple system morbidities associated with children with snore symptom. Pediatr Pulmonol 48(4):381–389. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppul.22653
Verhulst SL, Van Hoeck K, Schrauwen N, Haentjens D, Rooman R, Van Gaal L, De Backer W, Desager KN (2008) Sleep-disordered breathing and proteinuria in overweight and obese children and adolescents. Horm Res 70(4):224–229. https://doi.org/10.1159/000151594
Krishna J, Shah ZA, Merchant M, Klein JB, Gozal D (2006) Urinary protein expression patterns in children with sleep-disordered breathing: preliminary findings. Sleep Med 7(3):221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2005.09.010
Eckardt KU, Rosenberger C, Jurgensen JS, Wiesener MS (2003) Role of hypoxia in the pathogenesis of renal disease. Blood Purif 21(3):253–257
Wang Y, Guo SZ, Bonen A, Li RC, Kheirandish-Gozal L, Zhang SX, Brittian KR, Gozal D (2011) Monocarboxylate transporter 2 and stroke severity in a rodent model of sleep apnea. J Neurosci 31(28):10241–10248. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1462-11.2011
Cai XH, Zhou YH, Zhang CX, LG H, Fan XF, Li CC, Zheng GQ, Gong YS (2010) Chronic intermittent hypoxia exposure induces memory impairment in growing rats. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 70(3):279–287
Lee EJ, Woodske ME, Zou B, O'Donnell CP (2009) Dynamic arterial blood gas analysis in conscious, unrestrained C57BL/6J mice during exposure to intermittent hypoxia. J Appl Physiol (1985) 107(1):290–294. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.91255.2008
Morgan BJ (2009) Intermittent hypoxia: keeping it real. J Appl Physiol (1985) 107(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00304.2009
Jurado-Gamez B, Fernandez-Marin MC, Gomez-Chaparro JL, Munoz-Cabrera L, Lopez-Barea J, Perez-Jimenez F, Lopez-Miranda J (2011) Relationship of oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 37(4):873–879. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00027910
Nair D, Dayyat EA, Zhang SX, Wang Y, Gozal D (2011) Intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits are mediated by NADPH oxidase activity in a murine model of sleep apnea. PLoS One 6(5):e19847. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019847
Khayat R, Patt B, Hayes D Jr (2009) Obstructive sleep apnea: the new cardiovascular disease. Part I: obstructive sleep apnea and the pathogenesis of vascular disease. Heart Fail Rev 14(3):143–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-008-9112-z
Chou YT, Lee PH, Yang CT, Lin CL, Veasey S, Chuang LP, Lin SW, Lin YS, Chen NH (2011) Obstructive sleep apnea: a stand-alone risk factor for chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(7):2244–2250. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq821
Nicholl DD, Ahmed SB, Loewen AH, Hemmelgarn BR, Sola DY, Beecroft JM, Turin TC, Hanly PJ (2012) Declining kidney function increases the prevalence of sleep apnea and nocturnal hypoxia. Chest 141(6):1422–1430. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-1809
Ding W, Cai Y, Wang W, Ji L, Dong Y, Zhang X, Su M, Liu J, Lu G, Zhang X (2016) Adiponectin protects the kidney against chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced injury through inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sleep Breath. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-016-1321-4
Abuyassin B, Sharma K, Ayas NT, Laher I (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea and kidney disease: a potential bidirectional relationship? J Clin Sleep Med 11(8):915–924. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.4946
Buchner NJ, Wissing KR, Stegbauer J, Quack I, Weiner SM, Kramer BK, Rump LC (2011) The renal resistance index is increased in mild-to-moderate obstructive sleep apnoea and is reduced under continuous positive airway pressure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(3):914–920. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq472
Wissing KR, Buchner NJ, Stegbauer J, Rump LC (2007) Renal resistance index in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 132(36):1815–1819. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-984970
Bonventre JV, Yang L (2011) Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest 121(11):4210–4221. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI45161
Tirapelli LF, Barione DF, Trazzi BF, Tirapelli DP, Novas PC, Silva CS, Martinez M, Costa RS, Tucci S Jr, Suaid HJ, Cologna AJ, Martins AC (2009) Comparison of two models for evaluation histopathology of experimental renal ischemia. Transplant Proc 41(10):4083–4087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.09.061
Sun W, Yin X, Wang Y, Tan Y, Cai L, Wang B, Cai J, Fu Y (2012) Intermittent hypoxia-induced renal antioxidants and oxidative damage in male mice: hormetic dose response. Dose Response 11(3):385–400. https://doi.org/10.2203/dose-response.12-027.Cai
Gozal E, Sachleben LR Jr, Rane MJ, Vega C, Gozal D (2005) Mild sustained and intermittent hypoxia induce apoptosis in PC-12 cells via different mechanisms. Am J Phys Cell Physiol 288(3):C535–C542. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00270.2004
Yuan G, Nanduri J, Khan S, Semenza GL, Prabhakar NR (2008) Induction of HIF-1alpha expression by intermittent hypoxia: involvement of NADPH oxidase, Ca2+ signaling, prolyl hydroxylases, and mTOR. J Cell Physiol 217(3):674–685. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21537
da Rosa DP, Forgiarini LF, Baronio D, Feijo CA, Martinez D, Marroni NP (2012) Simulating sleep apnea by exposure to intermittent hypoxia induces inflammation in the lung and liver. Mediat Inflamm 2012:879419. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/879419
Westhoff M, Litterst P (2012) Obstructive sleep apnoea and oxidative stress. Pneumologie 66(10):610–615. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1325691
Ntalapascha M, Makris D, Kyparos A, Tsilioni I, Kostikas K, Gourgoulianis K, Kouretas D, Zakynthinos E (2013) Oxidative stress in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 17(2):549–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-012-0718-y
Katsoulis K, Kontakiotis T, Spanogiannis D, Vlachogiannis E, Kougioulis M, Gerou S, Daskalopoulou E (2011) Total antioxidant status in patients with obstructive sleep apnea without comorbidities: the role of the severity of the disease. Sleep Breath 15(4):861–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-010-0456-y
Nanduri J, Wang N, Yuan G, Khan SA, Souvannakitti D, Peng YJ, Kumar GK, Garcia JA, Prabhakar NR (2009) Intermittent hypoxia degrades HIF-2alpha via calpains resulting in oxidative stress: implications for recurrent apnea-induced morbidities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(4):1199–1204. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0811018106
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation Grant (LY17H010004), Scientific Research Foundation of Health Bureau of Zhejiang Province (2018ZD010), Wenzhou City Science and Technology Bureau Grant (Y20170133), National Science-technology Support Program (2015BAI12B09), and Project of Key Innovative Disciplines of Children Sleep Medicine of Zhejiang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poonit, ND., Zhang, YC., Ye, CY. et al. Chronic intermittent hypoxia exposure induces kidney injury in growing rats. Sleep Breath 22, 453–461 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-017-1587-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-017-1587-1