Abstract
Introduction
Endurance races have been associated with a substantial amount of adverse effects which could lead to chronic disease and long-term performance impairment. However, little is known about the holistic metabolic changes occurring within the serum metabolome of athletes after the completion of a marathon.
Objectives
Considering this, the aim of this study was to better characterize the acute metabolic changes induced by a marathon.
Methods
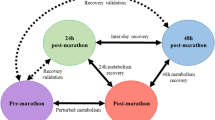
Using an untargeted two dimensional gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry metabolomics approach, pre- and post-marathon serum samples of 31 athletes were analyzed and compared to identify those metabolites varying the most after the marathon perturbation.
Results
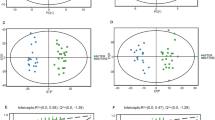
Principle component analysis of the comparative groups indicated natural differentiation due to variation in the total metabolite profiles. Elevated concentrations of carbohydrates, fatty acids, tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates, ketones and reduced concentrations of amino acids indicated a metabolic shift between various fuel substrate systems. Additionally, elevated odd-chain fatty acids and α-hydroxy acids indicated the utilization of α-oxidation and autophagy as alternative energy-producing mechanisms. Adaptations in gut microbe-associated markers were also observed and correlated with the metabolic flexibility of the athlete.
Conclusion
From these results it is evident that a marathon places immense strain on the energy-producing pathways of the athlete, leading to extensive protein degradation, oxidative stress, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 inhibition and autophagy. A better understanding of this metabolic shift could provide new insights for optimizing athletic performance, developing more efficient nutrition regimens and identify strategies to improve recovery.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The current analysis is part of a larger study consisting of multiple aims which are being drafted into various manuscripts. Considering this, the datasets generated from this investigation are not publically available, but can be acquired from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The authors declare that all the results included within this study have been presented clearly, honestly and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation.
References
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 57, 289–300.
Bonasia, D. E., Rosso, F., Cottino, U., & Rossi, R. (2015). Exercise-induced leg pain. Asia-Pacific Journal of Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation and Technology, 2, 73–84.
Brioche, T., Pagano, A. F., Py, G., & Chopard, A. (2016). Muscle wasting and aging: Experimental models, fatty infiltrations, and prevention. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 50, 56–87.
Bujak, R., Mateo, J., Blanco, I., Izquierdo-Garcia, J. L., Dudzik, D., Markuszewski, M. J., et al. (2016). New biochemical insights into the mechanisms of pulmonary arterial hypertension in humans. PLoS ONE, 11, 1–14.
Cahill, G. F., & Vech, R. L. (2003). Ketoacids? Good medicine? American Clinical and Climatological Association, 114, 149–163.
Charlton-Menys, V., & Durrington, P. N. (2007). Human cholesterol metabolism and therapeutic molecules. Experimental Physiology, 93, 27–42.
Ebner, M. J., Corol, D. I., Havlikova, H., Honour, J. W., & Fry, J. P. (2006). Identification of neuroactive steroids and their precursors and metabolites in adult male rat brain. Endocrinology, 147, 179–190.
Eigenvector Reserch. (2016). PLS_Toolbox 8.2.1 (Version 8.2.1). Manson: Eigenvector Reserch Inc.
Eisenberg, F., & Parthasarathy, R. (1987) Measurement of biosynthesis of myo-inositol from glucose 6-phosphate. Methods in Enzymology, 141, 127–143.
Esterhuizen, K., van der Westhuizen, F. H., & Louw, R. (2017). Metabolomics of mitochondrial disease. Mitochondrion, 35, 97–110.
Fernandez, J. A. M., Vida, C. B., & Glahn, V. P. (2000). Zero replacement in compositional data sets. In H. A. L. Kiers, J.-P. Rasson, P. J. F. Groenen & M. Schader (Eds.), Data analysis, classification, and related methods (pp. 155–160). Berlin: Springer.
Gall, W. E., Beebe, K., Lawton, K. A., Adam, K. P., Mitchell, M. W., Nakhle, P. J., et al. (2010). Alpha-hydroxybutyrate is an early biomarker of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in a nondiabetic population. PLoS ONE, 5, e10883.
Ghoraba, D. A., Mohamed, M. M., & Zaki, O. K. (2014). Screening of diseases associated with abnormal metabolites for evaluation of HPLC in organic aciduria profiling. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, 15, 69–78.
Guzik, G. P., & Stachowicz, W. (2016). Study on radiation-induced radicals giving rise to stable EPR signal suitable for the detection of irradiation in L-sorbose-containing fruits. Nukleonika, 61, 461–465.
Heaney, L. M., Deighton, K., & Suzuki, T. (2017) Non-targeted metabolomics in sport and exercise science. Journal of Sports Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2017.1305122
Holloszy, J. O., & Coyle, E. F. (1984). Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. Journal of Applied Physiology, 56, 831–838.
Holm, P. l. I., Ueland, P. M., Kvalheim, G., & Lien, E. A. (2003). Determination of choline, betaine, and dimethylglycine in plasma by a high-throughput method based on normal-phase chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Clinical Chemistry, 49, 286–294.
Hootman, K. C., Trezzi, J. P., Kraemer, L., Burwell, L. S., Dong, X., Guertin, K. A., et al. (2017) Erythritol is a pentose-phosphate pathway metabolite and associated with adiposity gain in young adults. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114, 4233–4240.
Howatson, G., McHugh, M. P., Hill, J. A., Brouner, J., Jewell, A. P., van Someren, K. A., et al. (2010). Influence of tart cherry juice on indices of recovery following marathon running. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, 20, 843–852.
Hu, X., Shi, Y., Zhang, P., Miao, M., Zhang, T., & Jiang, B. (2016). D-Mannose: Properties, production, and applications: An overview. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 15, 773–785.
Hu, X., Wu, L., Wang, Y., Song, Y., Mourant, D., Gunawan, R., et al. (2013). Acid-catalyzed conversion of mono- and poly-sugars into platform chemicals: Effects of molecular structure of sugar substrate. Bioresource Technology, 133, 469–474.
Jastrzebski, Z., Zychowska, M., Radziminski, L., Konieczna, A., & Kortas, J. (2015). Damage to liver and skeletal muscles in marathon runners during a 100 km run with regard to age and running speed. Journal of Human Kinetics, 45, 93–102.
Jenkins, B. J., Seyssel, K., Chiu, S., Pan, P. H., Lin, S. Y., Stanley, E., et al. (2017). Odd chain fatty acids; new insights of the relationship between the gut microbiota, dietary intake, biosynthesis and glucose intolerance. Scientific Reports, 7, 1–8.
Jeukendrup, A. E. (2011). Nutrition for endurance sports: Marathon, triathlon, and road cycling. Journal of Sport Science, 29, 91–99.
Kishimoto, Y., Williams, M., Moser, H. W., Hignite, C., & Biemann, K. (1973). Branched-chain and odd-numbered fatty acids and aldehydes in the nervous system of a patient with deranged vitamin B12 metabolism. Journal of Lipid Research, 14, 69–77.
Kitamura, T., Seki, N., & Kihara, A. (2017). Phytosphingosine degradation pathway includes fatty acid α-oxidation reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 114, 1–8.
Kondo, N., Ohno, Y., Yamagata, M., Obara, T., Seki, N., Kitamura, T., et al. (2014). Identification of the phytosphingosine metabolic pathway leading to odd-numbered fatty acids. Nature Communications, 5338, 1–11.
Korman, S. H., Andresen, B. S., Zeharia, A., Gutman, A., Boneh, A., & Pitt, J. J. (2005). 2-Ethylhydracrylic aciduria in short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Application to diagnosis and implications for the R-pathway of isoleucine oxidation. Clinical Chemistry, 51, 610–617.
Kroger, M., Meister, K., & Kava, R. (2006). Low-calorie sweeteners and other sugar substitutes: A review of the safety issues. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 5, 35–47.
Kujala, U. M., Mäkinen, V.-P., Heinonen, I., Soininen, P., Kangas, A. J., Leskinen, T. H., et al. (2013). Long-term leisure-time physical activity and serum metabolome. Circulation, 127, 340–348.
Kumar, A., & Bachhawat, A. K. (2012). Pyroglutamic acid: Throwing light on a lightly studied metabolite. Current Science, 102, 288–297.
Kumdam, H., Murthy, S. N., & Gummadi, S. N. (2014). Arabitol production by microbial fermentation—biosynthesis and future applications. International Journal of Sciences and Applied Research, 1, 1–12.
Laplante, M., & Sabatini, D. M. (2009). mTOR signaling at a glance. Journal of Cell Science, 122, 3589–3594.
Lewis, G. D., Farrell, L., Wood, M. J., Martinovic, M., Arany, Z., Rowe, G. C., et al. (2010). Metabolic signatures of exercise in human plasma. Science Translational Medicine, 2, 33–37.
Liebich, H. M., & Pickert, A. (1985). Gas chromatographic profiling of phenolic acids in urine of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Chromatography, 338, 25–32.
Lippi, G., Schena, F., Montagnana, M., Salvagno, G. L., Banfi, G., & Guidi, G. C. (2011). Significant variation of traditional markers of liver injury after a half-marathon run. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 22, E36–E38.
Luies, L., & Loots, D. T. (2016). Tuberculosis metabolomics reveals adaptations of man and microbe in order to outcompete and survive. Metabolomics, 12, 1–9.
Mach, N., & Fuster-Botella, D. (2017). Endurance exercise and gut microbiota: A review. Journal of Sport and Health Science, 6, 179–197.
MacLaren, D., & Morton, J. (2012). Biochemistry for sport and exercise metabolism (1 ed.). West Sussex: Wiley
Maes, M., Smith, R., Christophe, A., Cosyns, P., Desnyder, R., & Meltzer, H. (1996). Fatty acid composition in major depression: Decreased w3 fractions in cholesteryl esters and increased C20:4w6/C20:5w3 ratio in cholesteryl esters and phospholipids. Journal of Affective Disorders, 38, 35–46.
MATLAB. (2012). MATLAB and Statistics toolbox (Version 2012b). Natick: The MathWorks Inc.
Mcanulty, S. R., Owens, J. T., Mcanulty, L. S., Nieman, D. C., Morrow, J. D., Dumke, C. L., & Milne, G. L. (2007). Ibuprofen use during extreme exercise: Effects on oxidative stress and PGE2. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 39, 1075–1079.
McNutt, K. (2000). What clients need to know about sugar replacers. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 100, 466–469.
Mistou, M. Y., Sutcliffe, I. C., & van Sorge, N. M. (2016). Bacterial glycobiology: Rhamnose-containing cell wall polysaccharides in Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Review, 40, 464–479.
Mock, D. M., Stratton, S. L., Horvath, T. D., Bogusiewicz, A., Matthews, N. I., Henrich, C. L., et al. (2011). Brain, behavior, and immunity urinary excretion of 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid and 3-hydroxyisovaleryl carnitine increases in response to a leucine challenge in marginally biotin-deficient humans. Journal of Nutrition, 141, 1925–1930.
Nieman, D. C., Henson, D. A., Dumke, C. L., Oley, K., McAnulty, S. R., Davis, J. M., et al. (2006). Ibuprofen use, endotoxemia, inflammation, and plasma cytokines during ultramarathon competition. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 20, 578–584.
Ojiambo, R. M. (2013). Physical activity and well-being: A review of the health benefits of physical activity on health outcomes. Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, 2, 69–78.
Peake, J. M., Tan, S. J., Markworth, J. F., Broadbent, J. A., Skinner, T. L., & Cameron-Smith, D. (2014). Metabolic and hormonal responses to isoenergetic high-intensity interval exercise and continuous moderate-intensity exercise. American Journal of Pathology, 307, 539–552.
Peake, R. W. A. (2016). Seizures, dystonia, and spasms in a 14-year-old child. Clinical Chemistry, 62, 1159–1168.
Pechlivanis, A., Kostidis, S., Saraslanidis, P., Petridou, A., Tsalis, G., Mougios, V., et al. (2010). H NMR-based metabonomic investigation of the effect of two different exercise sessions on the metabolic fingerprint of human urine. Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 6405–6416.
Pfeiffer, B., Stellingwerff, T., Hodgson, A. B., Randell, R., Pottgen, K., Res, P., et al. (2012). Nutritional intake and gastrointestinal problems during competitive endurance events. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 44, 344–351.
Pfeuffer, M., & Jaudszus, A. (2016). Pentadecanoic and heptadecanoic acids: Multifaceted odd-chain fatty acids. Advances in Nutrition, 7, 730–734.
Qiang, F. (2015). Effect of malate-oligosaccharide solution on antioxidant capacity of endurance athletes. The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 9, 326–329.
Richter, E. A., Turcotte, L., Hespel, P., & Kiens, B. (1992). Metabolic responses to exercise: Effects of endurance training and implications for diabetes. Diabetes Care, 15, 1767–1776.
Robson-Ansley, P., Howatson, G., Tallent, J., Mitcheson, K., Walshe, I., Toms, C., et al. (2012). Prevalence of allergy and upper respiratory tract symptoms in runners of the London marathon. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 44, 999–1004.
Roe, C. R., & Ding, J. (2001). Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation disorders. In The online metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Rosner, B., Glynn, R. J., & Lee, M.-L. T. (2006). The Wilcoxon signed rank test for paired comparisons of clustered data. Biometrics, 62, 185–192.
Ryan, R. O. (2015). Metabolic annotation of 2-ethylhydracrylic acid. Clinical Chimica Acta, 448, 91–97.
Salway, J. G. (2012). Medical biochemistry at a glance (3rd ed.). Oxford: Wiley.
Simpson, G. L. W., & Ortwerth, B. J. (2000). The non-oxidative degradation of ascorbic acid at physiological conditions. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1501, 12–24.
Singh, R., & Cuervo, A. M. (2011). Autophagy in the cellular energetic balance. Cellular Metababolism, 13, 495–504.
Staron, R. S., Hikida, R. S., Murray, T. F., Hagerman, F. C., & Hagerman, M. T. (1989). Lipid depletion and repletion in skeletal muscle following a marathon. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 94, 29–40.
Stellingwerff, T. (2012). Case study: Nutrition and training periodization in three elite marathon runners. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metablism, 22, 392–400.
Tomczak, M., & Tomczak, E. (2014). The need to report effect size estimates revisited: An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends in Sport Science, 1, 19–25.
Turer, A. T., Lewis, G. D., O’Sullivan, J. F., Elmariah, S., Mega, J. L., Addo, T. A., et al. (2014). Increases in myocardial workload induced by rapid atrial pacing trigger alterations in global metabolism. PLoS ONE, 9, 1–9.
Van den Berg, R. A., Hoefsloot, H. C., Westerhuis, J. A., Smilde, A. K., & van der Werf, M. J. (2006). Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics, 7, 142.
Wadman, S. K., Duran, M., Ketting, D., Bruinvis, L., De Bree, P. K., Kamerling, J. P., et al. (1976). D-Glyceric acidemia in a patient with chronic metabolic acidosis. Clinica Chimica Acta, 71, 477–484.
Waśkiewicz, Z., Klapcinska, B., Sadowska-Krepa, E., Czuba, M., Kempa, K., Kimsa, E., et al. (2012). Acute metabolic responses to a 24-h ultra-marathon race in male amateur runners. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 112, 1679–1688.
Webner, D., DuPrey, K. M., Drezner, J. A., Cronholm, P., & Roberts, W. O. (2012). Sudden cardiac arrest and death in United States marathons. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 44, 1843–1845.
Wendel, U., Langenbeck, U., & Seakins, J. W. T. (1989). Interrelation between the metabolism of LIsoleucine and L-allo-isoleucine in patients with maple syrup urine disease. Pediatric Research, 25, 11–15.
Wikoff, W. R., Anfora, A., Liu, T. J., Schultz, P. G., Lesley, S. A., Peters, E. C., & Siuzdak, G. (2009). Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 3698–3703.
Żółtaszek, R., Hanausek, M., Kiliańska, Z. M., & Walaszek, Z. (2008). The biological role of D-glucaric acid and its derivatives: Potential use in medicine. Postepy Gigieny i Medycyny Doswiadczalnej, 62, 451–462.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Mari van Reenen for assistance with statistical analysis, Mrs. Derylize Beukes-Maasdorp for sample analysis and Prof. Nico L. Smit for initiating the collaboration.
Funding
The authors have no specific funding to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The concept and study were designed by DTL, ZS, GH, TC, KMK and EJS; samples were acquired from the Northumbria University in collaboration with GH, TC, KMK and EMS. ZS was responsible for manuscript drafting, data analysis and interpretation, the latter of which was assisted by DTL, LL and LJM. LL, LJM and DTL were involved in repeated manuscript reviewing, of which LL was greatly involved with structural (format) editing. All of the authors revised and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest, and that this manuscript, and the work described therein, is unpublished and has not been submitted for publication elsewhere.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval for this investigation, conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and International Conference on Harmonization Guidelines, was obtained from the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Health and Life Sciences at the Northumbria University in Newcastle upon Tyne, UK (Reference Number: HLSTC120716).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stander, Z., Luies, L., Mienie, L.J. et al. The altered human serum metabolome induced by a marathon. Metabolomics 14, 150 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1447-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1447-4