Abstract
Introduction
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is the main etiologic risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Early studies indicated that the increase of omega-6-derived oxylipins may be involved in the pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC, yet their changes during the distinct clinical phases of chronic HBV infection remain unclear. To fill this gap, in this study we investigated the omega-6-derived oxylipin profiles in patients with three major clinical stages of chronic HBV infection (chronic hepatitis B, liver cirrhosis, and HCC).
Methods
Eighteen omega-6-derived oxylipins were quantified in serum samples of 34 patients with chronic hepatitis B, 46 patients with HBV-related liver cirrhosis, 38 patients with HBV-related HCC, and 50 healthy controls using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.
Results
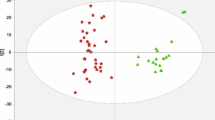
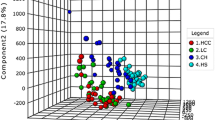
Seven oxylipins were found to be altered in patients with HBV-related liver diseases, including 9,10-dihydroxyoctadecenoic acid (9,10-DiHOME), 12,13-DiHOME, 14,15-dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid (14,15-DiHETrE), 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE), 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE), 11-HETE, and thromboxane B2 (TXB2). Of these, three oxylipins derived from the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) pathways including 9,10-DiHOME, 12,13-DiHOME, and 14,15-DiHETrE were found to be associated with the levels of α-fetoprotein (AFP), a tumor marker. In combination with AFP, age, and gender, a combination of these seven differential oxylipins could significantly enhance the prediction of HBV-related liver diseases, particularly for liver cirrhosis (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
This study for the first time shows the correlations between CYP450-derived oxylipins and the progression of chronic HBV infection, and sheds a new light on the surveillance of HBV-related live diseases using oxylipins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, S. H., Jung, E. S., Park, Y. M., Kim, B. S., Kim, B. K., Kim, D. G., et al. (2001). Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in hepatocellular carcinoma and growth inhibition of hepatoma cell lines by a COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398. Clinical Cancer Research, 7(5), 1410–1418.
Bertomeu, M., Gallo, S., Lauri, D., Haas, T., Orr, F. W., Bastida, E., et al. (1993). Interleukin 1-induced cancer cell/endothelial cell adhesion in vitro and its relationship to metastasis in vivo: Role of vessel wall 13-HODE synthesis and integrin expression. Clinical & Experimental Metastasis, 11(3), 243–250.
Fang, J., Cui, L., Sun, Y., Feng, L., & Ong, C. N. (2017). Targeted metabolomics reveals altered oxylipin profiles in plasma of mild cognitive impairment patients. Metabolomics, 13(10), 112.
Fitian, A. I., Nelson, D. R., Liu, C., Xu, Y., Ararat, M., & Cabrera, R. (2014). Integrated metabolomic profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C cirrhosis through GC/MS and UPLC/MS-MS. Liver International, 34(9), 1428–1444.
Georgakilas, A. G., Mosley, W. G., Georgakila, S., Ziech, D., & Panayiotidis, M. I. (2010). Viral-induced human carcinogenesis: An oxidative stress perspective. Molecular Biosystems, 6(7), 1162–1172.
Hanai, T., Hashimoto, T., Nishiwaki, K., Ono, M., Akamo, Y., Tanaka, M., et al. (1993). Comparison of prostanoids and their precursor fatty acids in human hepatocellular carcinoma and noncancerous reference tissues. Journal of Surgical Research, 54(1), 57–60.
Honn, K. V., Tang, D. G., Gao, X., Butovich, I. A., Liu, B., Timar, J., et al. (1994). 12-lipoxygenases and 12(S)-HETE: Role in cancer metastasis. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 13(3–4), 365–396.
Huerta-Yépez, S., Tirado-Rodriguez, A. B., & Hankinson, O. (2016). Role of diets rich in omega-3 and omega-6 in the development of cancer. Boletín Médico del Hospital Infantil de México, 73(6), 446–456.
Koh, W. P., Dan, Y. Y., Goh, G. B., Jin, A., Wang, R., & Yuan, J. M. (2016). Dietary fatty acids and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Singapore Chinese health study. Liver International, 36(6), 893–901.
Lawrence, G. D. (2013). Dietary fats and health: Dietary recommendations in the context of scientific evidence. Advances in Nutrition, 4(3), 294–302.
Lee, Y. H., Cui, L., Fang, J., Chern, B. S., Tan, H. H., & Chan, J. K. (2016). Limited value of pro-inflammatory oxylipins and cytokines as circulating biomarkers in endometriosis: A targeted ‘omics study. Scientific Reports, 6, 26117.
Leng, J., Han, C., Demetris, A. J., Michalopoulos, G. K., & Wu, T. (2003). Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through AKT activation: Evidence for AKT inhibition in celecoxib-induced apoptosis. Hepatology, 38(3), 756–768.
Lu, Y., Fang, J., Ong, C. N., Chen, S., Li, N., Cui, L., et al. (2017). Targeted analysis of omega-6-derived oxylipins and parent polyunsaturated fatty acids in serum of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Metabolomics, 13(1), 6.
Lu, Y. H., Huang, C., Gao, L., Xu, Y. J., Chia, S. E., Chen, S. S., et al. (2015). Identification of serum biomarkers associated with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis using mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics. Metabolomics, 11(6), 1526–1538.
Morisseau, C., & Hammock, B. D. (2013). Impact of soluble epoxide hydrolase and epoxyeicosanoids on human health. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 53, 37–58.
Pasqualini, M., Heyd, V., Manzo, P., & Eynard, A. (2003). Association between E-cadherin expression by human colon, bladder and breast cancer cells and the 13-HODE: 15-HETE ratio. A possible role of their metastatic potential. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, 68(1), 9–16.
Poli, G. (2000). Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: Role of oxidative stress. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 21(3), 49–98.
Shan, C., Xu, F., Zhang, S., You, J., You, X., Qiu, L., et al. (2010). Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes liver cell proliferation via a positive cascade loop involving arachidonic acid metabolism and p-ERK1/2. Cell Research, 20(5), 563–575.
Strassburg, K., Huijbrechts, A. M., Kortekaas, K. A., Lindeman, J. H., Pedersen, T. L., Dane, A., et al. (2012). Quantitative profiling of oxylipins through comprehensive LC–MS/MS analysis: Application in cardiac surgery. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 404(5), 1413–1426.
Sun, Y., Koh, H. W., Choi, H., Koh, W. P., Yuan, J. M., Newman, J. W., et al. (2016). Plasma fatty acids, oxylipins, and risk of myocardial infarction: The Singapore Chinese Health Study. Journal of Lipid Research, 57(7), 1300–1307.
Villeneuve, J. P., & Pichette, V. (2004). Cytochrome P450 and liver diseases. Current Drug Metabolism, 5(3), 273–282.
Yu, Y., Gong, R., Mu, Y., Chen, Y., Zhu, C., Sun, Z., et al. (2011). Hepatitis B virus induces a novel inflammation network involving three inflammatory factors, IL-29, IL-8, and cyclooxygenase-2. Journal of Immunology, 187(9), 4844–4860.
Zhang, X., You, X., Wang, Q., Zhang, T., Du, Y., Lv, N., et al. (2012). Hepatitis B virus X protein drives multiple cross-talk cascade loops involving NF-kappaB, 5-LOX, OPN and Capn4 to promote cell migration. PLoS One, 7(2), e31458.
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants for their invaluable contribution to the study. This study was partially supported by NUS secondment Funds to CNO (706-000-005-133) and NUS Environmental Research Institute (NERI) (608-000-007-731). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Yonghai Lu and Jinling Fang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Fang, J., Zou, L. et al. Omega-6-derived oxylipin changes in serum of patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases. Metabolomics 14, 26 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1326-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1326-z