Abstract
Objectives
In this review we compare the advantages and disadvantages of different model biological systems for determining the metabolic functions of cells in complex environments, how they may change in different disease states, and respond to therapeutic interventions.
Introduction
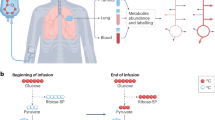
All preclinical drug-testing models have advantages and drawbacks. We compare and contrast established cell, organoid and animal models with ex vivo organ or tissue culture and in vivo human experiments in the context of metabolic readout of drug efficacy. As metabolism reports directly on the biochemical state of cells and tissues, it can be very sensitive to drugs and/or other environmental changes. This is especially so when metabolic activities are probed by stable isotope tracing methods, which can also provide detailed mechanistic information on drug action. We have developed and been applying Stable Isotope-Resolved Metabolomics to examine metabolic reprogramming of human lung cancer cells in monoculture, in mouse xenograft/explant models, and in lung cancer patients in situ (Lane et al. in Omics 15:173–182, 2011; Fan et al. in Metabolomics 7(2):257–269, 2011a, in Pharmacol Ther 133:366–391, 2012a, in Metabolomics 8(3):517–527, b; Xie et al. in Cell Metab 19:795–809, 2014; Ren et al. in Sci Rep 4:5414, 2014; Sellers et al. in J Clin Investig 125(2):687–698, 2015). We are able to determine the influence of the tumor microenvironment using these models. We have now extended the range of models to fresh human tissue slices, similar to those originally described by Warburg (Biochem Z 142:317–333, 1923), which retain the native tissue architecture and heterogeneity with a paired benign versus cancer design under defined cell culture conditions. This platform offers an unprecedented human tissue model for preclinical studies on metabolic reprogramming of human cancer cells in their tissue context, and response to drug treatment (Xie et al. 2014). As the microenvironment of the target human tissue is retained and individual patient’s response to drugs is obtained, this platform promises to transcend current limitations of drug selection for clinical trials or treatments
Conclusions
Development of ex vivo human tissue and animal models with humanized organs including bone marrow and liver show considerable promise for analyzing drug responses that are more relevant to humans. Similarly using stable isotope tracer methods with these improved models in advanced stages of the drug development pipeline, in conjunction with tissue biopsy is expected significantly to reduce the high failure rate of experimental drugs in Phase II and III clinical trials.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IRB:
-
Institutional Review Board
- PDX:
-
Patient derived xenograft
- (m)SIRM:
-
(multiplexed) Stable Isotope-Resolved Metabolomics
References
Adams, C. P., & Brantner, V. V. (2010). Spending on new drug development. Health Economics, 19(2), 130–141.
Ahuja, D., Sáenz-Robles, M. T., & Pipas, J. M. (2005). SV40 large T antigen targets multiple cellular pathways to elicit cellular transformation. Oncogene, 24, 7729–7745.
Amiri-Kordestani, L., & Fojo, T. (2012). Why do phase III clinical trials in oncology fail so often? JNCI, 104, 568–569.
Aparicio, S., Hidalgo, M., & Kung, A. L. (2015). Examining the utility of patient-derived xenograft mouse models. Nature Reviews Cancer, 15, 311–316.
Arinze, I. J., & Hanson, R. W. (1980). Compartmentation and its role in metabolic regulation. In R. M. Cohn, R. H. Herman, & P. D. McNamara (Eds.), Principles of metabolic control in mammalian systems (pp. 495–534). US: Springer.
Arita, M. (2004). The metabolic world of Escherichia coli is not small. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(6), 1543–1547.
Arrowsmith, J. (2011). Biobusiness briefs: Trial watch: Phase II failures: 2008–2010. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 10, 328–329.
Azuma, H., Paulk, N., Ranade, A., Dorrell, C., Al-Dhalimy, M., Ellis, E., et al. (2007). Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah(−/−)/Rag2(−/−)/Il2rg(−/−) mice. Nature Biotechnology, 25(8), 903–910.
Beloribi-Djefaflia, S., Siret, C., & Lombardo, D. (2015). Exosomal lipids induce human pancreatic tumoral MiaPaCa-2 cells resistance through the CXCR4-SDF-1alpha signaling axis. Oncoscience, 2(1), 15–30.
Belteki, G., Haigh, J., Kabacs, N., Haigh, K., Sison, K., Costantini, F., et al. (2005). Conditional and inducible transgene expression in mice through the combinatorial use of Cre-mediated recombination and tetracycline induction. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, e51.
Berndt, W. O. (1976). Use of tissue slice technique for evaluation of renal transport processes. Environmental Health Perspectives, 15, 73–88.
Bility, M. T., Zhang, L., Washburn, M. L., Curtis, T. A., Kovalev, G. I., & Su, L. (2012). Generation of a humanized mouse model with both human immune system and liver cells to model hepatitis C virus infection and liver immunopathogenesis. Nature Protocols, 7(9), 1608–1617. doi:10.1038/nprot.2012.083.
Bissell, M. J., Rizki, A., & Mian, I. S. (2003). Tissue architecture: The ultimate regulator of breast epithelial function. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 15(6), 753–762.
Blacker, T. S., Mann, Z. F., Gale, J. E., Ziegler, M., Bain, A. J., Szabadkai, G., et al. (2014). Separating NADH and NADPH fluorescence in live cells and tissues using FLIM. Nature Communications, 5, 3936.
Bonuccelli, G., Whitaker-Menezes, D., Castello-Cros, R., Pavlides, S., Pestell, R. G., Fatatis, A., et al. (2010). The reverse Warburg effect: Glycolysis inhibitors prevent the tumor promoting effects of caveolin-1 deficient cancer associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle, 9(10), 1960–1971.
Boumezbeur, F., Petersen, K. F., Cline, G. W., Mason, G. F., Behar, K. L., Shulman, G. I., et al. (2010). The contribution of blood lactate to brain energy metabolism in humans measured by dynamic C-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(42), 13983–13991.
Bousamra, M., Day, J., Fan, T. W.-M., Higashi, R. M., Kloecker, G., Lane, A. N., et al. (2012). Clinical aspects of metabolomics. In The handbook of metabolomics. (Vol. 17, Vol. Methods in Pharmacology and Toxicology). Totoya: Humana.
Brehm, M. A., Shultz, L. D., & Greiner, D. L. (2010). Humanized mouse models to study human diseases. Current opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity, 17(2), 120–125.
Brehm, M. A., Shultz, L. D., Luban, J., & Greiner, D. L. (2013). Overcoming current limitations in humanized mouse research. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 208, S125–S130.
Buescher, J. M., Antoniewicz, M. R., Boros, L. G., Burgess, S. C., Brunengraber, H., Clish, C. B., et al. (2015). A roadmap for interpreting (13)C metabolite labeling patterns from cells. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 34, 189–201.
Caneba, C. A., Yang, L., Baddour, J., Curtis, R., Win, J., Hartig, S., et al. (2014). Nitric oxide is a positive regulator of the Warburg effect in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death and Disease, 5, e1302.
Cascante, M., Franco, R., & Canela, E. I. (1989). Use of implicit methods from general sensitivity theory to develop a systematic-approach to metabolic control. 2. Complex-systems. Mathematical Biosciences, 94(2), 289–309.
Cascante, M., Selivanov, V., & Ramos-Montoya, A. (2012). Application of traceer-based metabolomics and flux analysis in targteted cancer drug design. In T. W.-M. Fan, A. N. Lane, & R. M. Higashi (Eds.), The handbook of metabolomics (pp. 299–320, Methods in Pahrmacology and Toxicology). New York: Springer.
Cassidy, J. W., Caldas, C., & Bruna, A. (2015). Maintaining tumor heterogeneity in patient-derived tumor xenografts. Cancer Research, 75, 2963–2968.
Chatham, J. C., & Seymour, A.-M. L. (2002). Cardiac carbohydrate metabolism in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Cardiovascular Research, 55(1), 104–112.
Cheung, V. G., Conlin, L. K., Weber, T. M., Arcaro, M., Jen, K.-Y., Morley, M., et al. (2003). Natural variation in human gene expression assessed in lymphoblastoid cells. Nature Genetics, 33, 422–425.
Choudhary, C., Kumar, C., Gnad, F., Nielsen, M. L., Rehman, M., Walther, T. C., et al. (2009). Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science, 325, 834–840.
Christofk, H. R., Vander Heiden, M. G., Wu, N., Asara, J. M., & Cantley, L. C. (2008). Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Nature, 452, 181–186.
Covassin, L., Jangalwe, S., Jouvet, N., Laning, J., Burzenski, L., Shultz, L. D., et al. (2013). Human immune system development and survival of non-obese diabetic (NOD)-scid IL2r gamma(null) (NSG) mice engrafted with human thymus and autologous haematopoietic stem cells. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 174, 372–388.
Damhofer, H., Ebbing, E. A., Steins, A., Welling, L., Tol, J. A., Krishnadath, K. K., et al. (2015). Establishment of patient-derived xenograft models and cell lines for malignancies of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Journal of Translational Medicine, 13, 115.
Davidson, S. M., Papagiannakopoulos, T., Olenchock, B. A., Heyman, J. E., Keibler, M. A., Luengo, A., et al. (2016). Environment impacts the metabolic dependencies of Ras-driven non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Metabolism, 23, 517–528.
de Graaf, R. A., Rothman, D. L., & Behar, K. L. (2011). State of the art direct C-13 and indirect H-1- C-13 NMR spectroscopy in vivo. A practical guide. NMR in Biomedicine, 24(8), 958–972.
deGraaf, I. A. M., Olinga, P., deJager, M. H., Merema, M. T., deKanter, R., van de Kerkhof, E. G., et al. (2010). Preparation and incubation of precision-cut liver and intestinal slices for application in drug metabolism and toxicity studies. Nature Protocols, 5, 1540–1551.
Delitto, D., Perez, C., Han, S., Gonzalo, D. H., Pham, K., Knowlton, A. E., et al. (2015). Downstream mediators of the intratumoral interferon response suppress antitumor immunity, induce gemcitabine resistance and associate with poor survival in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 64(12), 1553–1563.
Dixit, P., Jain, D. K., & Dumbwani, J. (2012). Standardization of an ex vivo method for determination of intestinal permeability of drugs using everted rat intestine apparatus. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods, 65, 13–17.
Fan, T. W.-M., Kucia, M., Jankowski, K., Higashi, R. M., Rataczjak, M. Z., Rataczjak, J., et al. (2008). Proliferating Rhabdomyosarcoma cells shows an energy producing anabolic metabolic phenotype compared with Primary Myocytes. Molecular Cancer, 7, 79.
Fan, T. W.-M., & Lane, A. N. (2016). Applications of NMR spectroscopy to systems biochemistry. Progress NMR Spectroscopy, 92, 18–53.
Fan, T. W.-M., Lane, A. N., & Higashi, R. M. (2016a). Stable isotope resolved metabolomics studies in ex vivo tissue slices. Bio-protocol, 6, e1730.
Fan, T. W., Lane, A. N., Higashi, R. M., Farag, M. A., Gao, H., Bousamra, M., et al. (2009). Altered regulation of metabolic pathways in human lung cancer discerned by 13C stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM). Molecular Cancer, 8, 41.
Fan, T. W., Lane, A. N., Higashi, R. M., & Yan, J. (2011a). Stable isotope resolved metabolomics of lung cancer in a SCID mouse model. Metabolomics, 7(2), 257–269.
Fan, T. W.-M., Lane, A. N., Higashi, R. M., & Yan, J. (2011b). Stable isotope resolved metabolomics of lung cancer in a SCID mouse model. Metabolomics, 7, 257–269.
Fan, T. W.-M., Lorkiewicz, P., Sellers, K., Moseley, H. N. B., Higashi, R. M., & Lane, A. N. (2012a). Stable isotope-resolved metabolomics and applications to drug development. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 133, 366–391.
Fan, T. W.-M., Tan, J. L., McKinney, M. M., & Lane, A. N. (2012b). Stable isotope resolved metabolomics analysis of ribonucleotide and RNA metabolism in human lung cancer cells. Metabolomics, 8(3), 517–527.
Fan, T. W.-M., Warmoes, M. O., Sun, Q., Song, H., T, Turchan-Cholewo, J., Martin, J. T., et al. (2016b). Distinctly perturbed metabolic networks underlie differential tumor tissue damages induced by immune modulator β-glucan in a two-case ex vivo non-small cell lung cancer study. CSH Molecular Case Studies Journal. doi:10.1101/mcs.a000893.
Feenstra, J., Grobbee, D. E., Remme, W. J., & Stricker, B. H. C. (1999). Drug-induced heart failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 33, 1152–1162.
Fell, D. (1997). Understanding the control of metabolism (Frontiers in metabolism). London: Portland Press.
Fogh, J. (Ed.). (1982). The nude mouse in experimental and clinical research. Cambridge: Academic Press.
Freeman, B. A., & Oneil, J. J. (1984). Tissue-slices in the study of lung metabolism and toxicology. Environmental Health Perspectives, 56, 51–60.
Gadian, D. G. (1986). In vivo NMR. In Supramolecular structure and function. Proceedings in life sciences (pp. 93–103).
Gadian, D. G. (1995). NMR and its applications to living systems (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Gould, S. E., Junttila, M. R., & de Sauvage, F. J. (2015). Translational value of mouse models in oncology drug development. Nature Medicine, 21, 431–439.
Guillaumond, F., Leca, J., Olivares, O., Lavaut, M.-N., Vidal, N., Berthezene, P., et al. (2013). Strengthened glycolysis under hypoxia supports tumor symbiosis and hexosamine biosynthesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(10), 3919–3924.
Hahne, H., Gholami, A. M., & Kuster, B. (2012). Discovery of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins in published large-scale proteome data. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 11(10), 843–850.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell, 144(5), 646–674.
Hasegawa, M., Kawai, K., Mitsui, T., Taniguchi, K., Monnai, M., Wakui, M., et al. (2011). The reconstituted ‘humanized liver’ in TK-NOG mice is mature and functional. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 405(3), 405–410.
Hensley, C. T., Faubert, B., Yuan, Q., Lev-Cohain, N., Jin, E., Kim, J., et al. (2016). Metabolic heterogeneity in human lung tumors. Cell, 164, 681–694.
Herzenberg, J. R. (2009). Renal toxicity of therapeutic drugs. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 62, 505–515.
Hidalgo, M., Bruckheimer, E., Rajeshkumar, N. V., Garrido-Laguna, I., De Oliveira, E., Rubio-Viqueira, B., et al. (2011). A pilot clinical study of treatment guided by personalized tumorgrafts in patients with advanced cancer. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 10(8), 1311–1316.
Ho, P.-C., Bihuniak, J. D., Macintyre, A. N., Staron, M., Liu, X., Amezquita, R., et al. (2016). Phosphoenolpyruvate is a metabolic checkpoint of anti-tumor T cell responses. Cell, 162(6), 1217–1228.
Hornbeck, P. V. (2015). PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(D1), D512–D520.
Hougardy, B. M. T., Reesink-Peters, N., van den Heuvel, F. A. J., ten Hoor, K. A., Hollema, H., de Vries, E. G. E., et al. (2008). A robust ex vivo model for evaluation of induction of apoptosis by rhTRAIL in combination with proteasome inhibitor MG132 in human premalignant cervical explants. International Journal of Cancer, 123(6), 1457–1465.
Hu, S., Yoshihara, H. A. I., Bok, R., Zhou, J., Zhu, M. H., Kurhanewicz, J., et al. (2012). Use of hyperpolarized 1-C-13 pyruvate and 2-C-13 pyruvate to probe the effects of the anticancer agent dichloroacetate on mitochondrial metabolism in vivo in the normal rat. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 30(10), 1367–1372.
Huang, K. Y., Su, M. G., Kao, H. J., Hsieh, Y. C., Jhong, J. H., Cheng, K. H., et al. (2016). dbPTM 2016: 10-year anniversary of a resource for post-translational modification of proteins. Nucleic Acids Research, 44(D1), D435–D446.
Hyder, F., Fulbright, R. K., Shulman, R. G., & Rothman, D. L. (2013). Glutamatergic function in the resting awake human brain is supported by uniformly high oxidative energy. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 33(3), 339–347.
Ishida, Y., Yamasaki, C., Yanagi, A., Yoshizane, Y., Fujikawa, K., Watashi, K., et al. (2015). Novel robust in vitro hepatitis B virus infection model using fresh human hepatocytes isolated from humanized mice. American Journal of Pathology, 185(5), 1275–1285.
Jack, J., Rotroff, D., & Motsinger-Reif, A. (2014). Lymphoblastoid cell lines models of drug response: Successes and lessons from this pharmacogenomic model. Current Molecular Medicine, 14(7), 833–840.
Jitrapakdee, S., St Maurice, M., Rayment, I., Cleland, W. W., Wallace, J. C., & Attwood, P. V. (2008). Structure, mechanism and regulation of pyruvate carboxylase. Biochemical Journal, 413, 369–387.
Keshari, K. R., Kurhanewicz, J., Bok, R., Larson, P. E. Z., Vigneron, D. B., & Wilson, D. M. (2011). Hyperpolarized C-13 dehydroascorbate as an endogenous redox sensor for in vivo metabolic imaging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(46), 18606–18611.
Keshari, K. R., Sriram, R., Van Criekinge, M., Wilson, D. M., Wang, Z. J., Vigneron, D. B., et al. (2013). Metabolic reprogramming and validation of hyperpolarized C-13 lactate as a prostate cancer biomarker using a human prostate tissue slice culture bioreactor. Prostate, 73(11), 1171–1181.
Kim, J. W., & Dang, C. V. (2005). Multifaceted roles of glycolytic enzymes. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 30(3), 142–150.
Kirby, T. O., Rivera, A., Rein, D., Wang, M., Ulasov, I., Breidenbach, M., et al. (2004). A novel ex vivo model system for evaluation of conditionally replicative adenoviruses therapeutic efficacy and toxicity. Clinical Cancer Research, 10(24), 8697–8703.
Kopetz, S., Lemos, R., & Powis, G. (2012). The promise of patient-derived xenografts: The best laid plans of mice and men. Clinical Cancer Research, 18, 5160–5162.
Lane, A. N., Fan, T. W.-M., Bousamra, M, I. I., Higashi, R. M., Yan, J., & Miller, D. M. (2011). Clinical applications of stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM) in non-small cell lung cancer. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 15, 173–182.
Lane, A. N., Fan, T. W., & Higashi, R. M. (2008a). Isotopomer-based metabolomic analysis by NMR and mass spectrometry. Biophysical Tools for Biologists., 84, 541–588.
Lane, A. N., Fan, T. W.-M., Higashi, R. M., Deleeuw, L., & Yang, T. H. (2008). Stable isotope tracing in metabolic pathways. Paper presented at the modelling complex biological systems in the context of the genome, Lille.
Lane, A. N., Fan, T. W.-M., Xie, X., Moseley, H. N., & Higashi, R. M. (2009). Stable isotope analysis of lipid biosynthesis by high resolution mass spectrometry and NMR. Analytica Chimica Acta, 651, 201–208.
Lane, A. N., Yan, J., & Fan, T. W.-M. (2015). 13C tracer studies of metabolism in mouse tumor xenografts. Bio-protocol, 5, e1650.
Ledford, H. (2015). CRISPR, the disruptor. Nature, 522, 20–24.
Lee, K. M., Choi, K. H., & Ouellette, M. M. (2004). Use of exogenous hTERT to immortalize primary human cells. Cytotechnology, 45, 33–38.
Lee, J., Cuddihy, M. J., & Kotov, N. A. (2008). Three-dimensional cell culture matrices: State of the art. Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews, 14(1), 61–86.
Lee, G. Y., Kenny, P. A., Lee, E. H., & Bissell, M. J. (2007). Three-dimensional culture models of normal and malignant breast epithelial cells. Nature Methods, 4, 359–365.
Leithner, K., Wohlkoenig, C., Stacher, E., Lindenmann, J., Hofmann, N. A., Galle, B., et al. (2014). Hypoxia increases membrane metallo-endopeptidase expression in a novel lung cancer ex vivo model-role of tumor stroma cells. BMC Cancer, 14, 40.
Lincet, J., & Icard, P. (2015). How do glycolytic enzymes favour cancer cell proliferation by nonmetabolic functions? Oncogene, 34, 3751–3759.
Maher, E. A., Marin-Valencia, I., Bachoo, R. M., Mashimo, T., Raisanen, J., Hatanpaa, K. J., et al. (2012). Metabolism of U-13C glucose in human brain tumors in vivo. NMR in Biomedicine, 25(11), 1234–1244.
Marin, R., Perez, J. C. G., Ralph, S. J., Rodriguez-Enriquez, S., & Moreno-Sanchez, R. (2009). HIF-1α modulates energy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing over-expression of specific glycolytic isoforms. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 9, 1084–1101.
Martinez-Garcia, R., Juan, D., Rausell, A., Munoz, M., Banos, N., Menendez, C., et al. (2014). Transcriptional dissection of pancreatic tumors engrafted in mice. Genome Medicine, 6, 27.
Mason, G. F., Petersen, K. F., de Graaf, R. A., Kanamatsu, T., Otsuki, T., & Rothman, D. L. (2002). A comparison of C-13 NMR measurements of the rates of glutamine synthesis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle during oral and intravenous administration of 1-C-13 glucose. Brain Research Protocols, 10(3), 181–190.
Mathupala, S. P., Ko, Y. H., & Pedersen, P. L. (2010). The pivotal roles of mitochondria in cancer: Warburg and beyond and encouraging prospects for effective therapies. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1797, 1225–1230.
Maykel, J., Liu, J. H., Li, H., Shultz, L. D., Greiner, D. L., & Houghton, J. (2014). NOD-scidIl2rg (tm1Wjl) and NOD-Rag1 (null) Il2rg (tm1Wjl): a model for stromal cell-tumor cell interaction for human colon cancer. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 59, 1169–1179.
McCracken, K. W., Cata, E. M., Crawford, C. M., Sinagoga, K. L., Schumacher, M., Rockich, B. E., et al. (2014). Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids. Nature, 516(7531), 400–404.
Mestas, J., & Hughes, C. C. W. (2004). Of mice and not men: Differences between mouse and human immunology. Journal of Immunology, 172, 2731–2738.
Minárik, P., Tomásková, N., Kollárová, M., & Antalik, M. (2002). Malate dehydrogenases–structure and function. General Physiology and Biophysics, 21, 257–265.
Mitchell, J. M., Fan, T. W.-M., Lane, A. N., & Moseley, H. N. B. (2014). Development and in silico evaluation of large-scale metabolite identification methods using functional group detection for metabolomics. Frontiers in Genetics, 5, 273.
Moore, C. B., Guthrie, E. H., Huang, M. T.-H., & Taxman, D. J. (2010). Short hairpin RNA (shRNA): Design, delivery, and assessment of gene knockdown. Methods in Molecular Biology, 629, 141–158.
Muruganandan, S., & Sinal, C. J. (2008). Mice as clinically relevant models for the study of cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 83, 818–828.
Natoli, M., Leoni, B. D., D’Agnano, I., Zucco, F., & Felsani, A. (2012). Good Caco-2 cell culture practices. Toxicology in Vitro, 26, 1243–1246.
Neitzel, H. (1986). A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Human Genetics, 73, 320–326.
Nelson, S. J., Kurhanewicz, J., Vigneron, D. B., Larson, P. E. Z., Harzstark, A. L., Ferrone, M., et al. (2013). Metabolic imaging of patients with prostate cancer using hyperpolarized 1-C-13 pyruvate. Science Translational Medicine, 5, 198.
Niu, N. F., & Wang, L. W. (2015). In vitro human cell line models to predict clinical response to anticancer drugs. Pharmacogenomics, 16(3), 273–285.
Ostapowicz, G., Fontana, R. J., Schiødt, F. V., Larson, A., Davern, T. J., Han, S. H., et al. (2002). Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Annals of Internal Medicine, 137, 947–954.
Pajic, A., Spitkovsky, D., Christoph, B., Kempkes, B., Schuhmacher, M., Staege, M. S., et al. (2000). Cell cycle activation by c-myc in a Burkitt lymphoma model cell line. International Journal of Cancer, 87, 787–793.
Patel, A. B., de Graaf, R. A., Mason, G. F., Rothman, D. L., Shulman, R. G., & Behar, K. L. (2005). The contribution of GABA to glutamate/glutamine cycling and energy metabolism in the rat cortex in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(15), 5588–5593.
Pawlik, T. M., Souba, W. W., Sweeney, T. J., & Bode, B. P. (2000). Amino acid uptake and regulation in multicellular hepatoma spheroids. Journal of Surgical Research, 91(1), 15–25.
Pfeiffer, T., Soyer, O. S., & Bonhoeffer, S. (2005). The evolution of connectivity in metabolic networks. PLoS Biology, 3, e228.
Poulo, J. M., Elston, T., Lane, A. N., Macdonald, J. M., & Cascante, M. (2012). Introduction to metabolic control analysis (MCA). In T. W.-M. Fan, R. M. Higashi, & A. N. Lane (Eds.), Handbook of metabolomics. New York: Humana Press.
Ravi, M., Paramesh, V., Kaviya, S. R., Anuradha, E., & Paul Solomon, F. D. P. (2014). 3D cell culture systems: advantages and applications. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 230, 16–26.
Ren, J. G., Seth, P., Clish, C. B., Lorkiewicz, P. K., Higashi, R. M., Lane, A. N., et al. (2014). Knockdown of malic enzyme 2 suppresses lung tumor growth, induces differentiation and impacts PI3K/AKT signaling. Scientific Reports, 4, 5414.
Richmond, A., & Su, Y. (2008). Mouse xenograft models vs GEM models for human cancer therapeutics. Disease Models & Mechanisms, 1(2–3), 78–82.
Roberts, J. K. M., Lane, A. N., Clark, R. A., & Nieman, R. H. (1985). Relationships between the rate of synthesis of ATP and the concentrations of reactants and products of ATP hydrolysis in maize root-tips, determined by P-31 nuclear magnetic-resonance. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 240(2), 712–722.
Rose, J., Martin, C., MacDonald, T., & Ellis, C. (2006). High-resolution intravital NADH fluorescence microscopy allows measurements of tissue bioenergetics in rat ileal mucosa. Microcirculation, 13(1), 41–47.
Ruprecht, B., & Lemeer, S. (2014). Proteomic analysis of phosphorylation in cancer. Expert Review of Proteomics, 11(3), 259–267.
Sander, J. D., & Joung, J. K. (2014). CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nature Biotechnology, 32, 347–355.
Saunders, T. (2011). Inducible transgenic mouse models. Methods in Molecular Biology, 693, 103–115.
Savageau, M. A., Voit, E. O., & Irvine, D. H. (1987a). Biochemical systems-theory and metabolic control-theory. 1. Fundamental similarities and differences. Mathematical Biosciences, 86(2), 127–145.
Savageau, M. A., Voit, E. O., & Irvine, D. H. (1987b). Biochemical systems-theory and metabolic control-theory. 2. The role of summation and connectivity relationships. Mathematical Biosciences, 86(2), 147–169.
Scaduto, R. C., & Davis, E. J. (1985). Serine synthesis by an isolated perfused rat kidney preparation. Biochemical Journal, 230, 303–311.
Scott, C. L., Becker, M. A., Haluska, P., & Samimi, G. (2013). Patient-derived xenograft models to improve targeted therapy in epithelial ovarian cancer treatment. Frontiers in Oncology, 3, 295.
Sellers, K., Fox, M. P., Bousamra, M, I. I., Slone, S. P., Higashi, R. M., Miller, D. M., et al. (2015). Pyruvate carboxylase is critical for non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 125(2), 687–698.
Shultz, L. D., Ishikawa, F., & Greiner, D. L. (2007). Humanized mice in translational biomedical research. Nature Reviews Immunology, 7, 118–130.
Siolas, D., & Hannon, G. J. (2013). Patient derived tumor xenografts: Transforming clinical samples into mouse models. Cancer Research, 73, 5315–5319.
Sonveaux, P., Vegran, F., Schroeder, T., Wergin, M. C., Verrax, J., Rabbani, Z. N., et al. (2008). Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 118(12), 3930–3942.
Spence, J. R., Mayhew, C. N., Rankin, S. A., Kuhar, M. F., Vallance, J. E., Tolle, K., et al. (2011). Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature, 470(7332), 105–109.
Sriram, G., Martinez, J. A., McCabe, E. R. B., Liao, J. C., & Dipple, K. M. (2005). Single-gene disorders: What role could moonlighting enzymes play? American Journal of Human Genetics, 76, 911–924.
Stern, R., Shuster, S., Neudecker, B. A., & Formby, B. (2002). Lactate stimulates fibroblast expression of hyaluronan and CD44: the Warburg effect revisited. Experimental Cell Research, 276(1), 24–31.
Stringari, C., Donovan, P., & Gratton, E. (2012). Phasor FLIM metabolic mapping of stem cells and cancer cells in live tissues. In A. Periasamy, K. Konig, & P. T. C. So (Eds.), Multiphoton microscopy in the biomedical sciences Xii (Vol. 8226, Proceedings of SPIE).
Stringari, C., Wang, H., Geyfman, M., Crosignani, V., Kumar, V., Takahashi, J. S., et al. (2015). In vivo single-cell detection of metabolic oscillations in stem cells. Cell Reports, 10(1), 1–7.
Subbaraman, N. (2011). Flawed arithmetic on drug development costs. Nature Biotechnology, 29(5), 381.
Sugimoto, M., Tahara, H., Ide, T., & Furuichi, Y. (2004). Steps involved in immortalization and tumorigenesis in human B-lymphoblastoid cell lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Research, 64, 3361–3364.
Tateno, C., Kawase, Y., Tobita, Y., Hamamura, S., Ohshita, H., Yokomichi, H., et al. (2015a). Generation of novel chimeric mice with humanized livers by using hemizygous cDNA-uPA/SCID Mice. Plos One, 10(11), e0142145.
Tateno, C., Yamamoto, T., Utoh, R., Yamasaki, C., Ishida, Y., Myoken, Y., et al. (2015b). Chimeric mice with hepatocyte-humanized liver as an appropriate model to study human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha. Toxicologic Pathology, 43(2), 233–248.
Tateno, C., Yoshizane, Y., Saito, N., Kataoka, M., Utoh, R., Yamasaki, C., et al. (2004). Near completely humanized liver in mice shows human-type metabolic responses to drugs. American Journal of Pathology, 165(3), 901–912.
Telang, S., Lane, A. N., Nelson, K. K., Arumugam, S., & Chesney, J. A. (2007). The oncoprotein H-RasV12 increases mitochondrial metabolism. Molecular Cancer, 6, 77–91.
Telang, S., Yalcin, A., Clem, A. L., Bucala, R., Lane, A. N., Eaton, J. W., et al. (2006). Ras transformation requires metabolic control by 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase. Oncogene, 25(55), 7225–7234.
Tentler, J. J., Tan, A. C., Weekes, C. D., Jimeno, A., Leong, S., & Pitts, T. M. (2012). Patient-derived tumour xenografts as models for oncology drug development. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 9, 338–350.
Thayanithy, V., Babatunde, V., Dickson, E. L., Wong, P., Oh, S., Ke, X., et al. (2014). Tumor exosomes induce tunneling nanotubes in lipid raft-enriched regions of human mesothelioma cells. Experimental Cell Research, 323(1), 178–188.
Thelwall, P. E., Simpson, N. E., Rabbani, Z. N., Clark, M. D., Pourdeyhimi, R., Macdonald, J. M., et al. (2012). In vivo MR studies of glycine and glutathione metabolism in a rat mammary tumor. NMR in Biomedicine, 25, 271–278.
Thelwall, P. E., Yemin, A. Y., Gillian, T. L., Simpson, N. E., Kasibhatla, M. S., Rabbani, Z. N., et al. (2005). Noninvasive in vivo detection of glutathione metabolism in tumors. Cancer Research, 65(22), 10149–10153.
Uhlen, M., Fagerberg, L., Hallstrom, B. M., Lindskog, C., Oksvold, P., Mardinoglu, A., et al. (2015). Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science, 347(6220), 394.
Unger, F. T., Bentz, S., Krüger, J., Rosenbrock, C., Schaller, J., Pursche, K., et al. (2015). Precision cut cancer tissue slices in anti-cancer drug testing. Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology, 4, 108–121.
Unger, F. T., Krueger, J., Schaller, J., Uhlig, P., Juhl, H., & David, K. A. (2014). Precision cut cancer tissue slices as a preclinical drug testing platform. European Journal of Cancer, 50, S166.
Uppal, A., & Gupta, P. K. (2003). Measurement of NADH concentration in normal and malignant human tissues from breast and oral cavity. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 37, 45–50.
Uriel, J. (1979). Retrodifferentiation and the fetal patterns of gene expression in cancer. Advances in Cancer Research, 29, 127–174.
Vaira, V., Fedele, G., Pyne, S., Fasoli, E., Zadra, G., Bailey, D., et al. (2010). Preclinical model of organotypic culture for pharmacodynamic profiling of human tumors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(18), 8352–8356.
Walenta, S., Schroeder, T., & Mueller-Klieser, W. (2004). Lactate in solid malignant tumors: Potential basis of a metabolic classification in clinical oncology. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 11(16), 2195–2204.
Warburg, O. (1923). Versuche an überlebendem Carcinomgewebe (Methoden). Biochem. Zeitschr., 142, 317–333.
Wehrle, J. P., Ng, C. E., McGovern, K. A., Aiken, N. R., Shungu, D. C., Chance, E. M., et al. (2000). Metabolism of alternative substrates and the bioenergetic status of EMT6 tumor cell spheroids. NMR in Biomedicine, 13(6), 349–360.
Whittle, J. R., Lewis, M. T., Lindeman, G. J., & Visvader, J. E. (2015). Patient-derived xenograft models of breast cancer and their predictive power. Breast Cancer Research, 17, 17.
Wilding, J. L., & Bodmer, W. F. (2014). Cancer cell lines for drug discovery and development. Cancer Research, 74(9), 2377–2384.
Willyard, C. (2015). The boom in mini stomachs, brains, breasts, kidneys and more. Nature, 523, 520–522.
Wilson, D. M., & Kurhanewicz, J. (2014). Hyperpolarized C-13 MR for molecular imaging of prostate cancer. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 55(10), 1567–1572.
Winnike, J. H., Pediaditakis, P., Wolak, J. E., McClelland, R. W., Watkins, P. B., & Macdonald, J. M. (2012). Stable isotope resolved metabolomics of primary human hepatocytes reveals a stressed phenotype. Metabolomics, 8, 34–49.
Wolak, J., Rahimi-Keshari, K., Jeffries, R. E., Joy, M. P., Todd, A., Pediatikakis, P., et al. (2012). Noninvasive fluxomics in mammals by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In T. W.-M. Fan, A. N. Lane, & R. M. Higashi (Eds.), The handbook of metabolomics (pp. 321–392). New York: Springer.
Wong, N. C., Bhadri, V. A., Maksimovic, J., Parkinson-Bates, M., Ng, J., Craig, J. M., et al. (2014). Stability of gene expression and epigenetic profiles highlights the utility of patient-derived paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia xenografts for investigating molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. BMC Genomics, 15, 416.
Wysoczynski, M., & Ratajczak, M. Z. (2009). Lung cancer secreted microvesicles: Underappreciated modulators of microenvironment in expanding tumors. International Journal of Cancer, 125(7), 1595–1603.
Xie, H., Hanai, J., Ren, J.-G., Kats, L., Burgess, K., Bhargava, P., et al. (2014). Targeting lactate dehydrogenase-A (LDH-A) inhibits tumorigenesis and tumor progression in mouse models of lung cancer and impacts tumor initiating cells. Cell Metabolism, 19, 795–809.
Xu, D., & Peltz, G. (2016). Can humanized mice predict drug “behavior” in humans? Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 56, 323–338.
Yoshizato, K., & Tateno, C. (2009). In vivo modeling of human liver for pharmacological study using humanized mouse. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology, 5(11), 1435–1446.
Yue, F., Cheng, Y., Breschi, A., Vierstra, J., Wu, W., Ryba, T., et al. (2014). A comparative encyclopedia of DNA elements in the mouse genome. Nature, 515, 355–364.
Zachara, N. E., & Hart, G. W. (2004). O-GlcNAc a sensor of cellular state: the role of nucleocytoplasmic glycosylation in modulating cellular function in response to nutrition and stress. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-General Subjects, 1673(1–2), 13–28.
Zamanakou, M., Germenis, A. E., & Karanikas, V. (2007). Tumor immune escape mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Immunology Letters, 111(2), 69–75.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NIH P01CA163223-01A1, 1U24DK097215-01A1, 1R01ES022191-01 and 1R21ES025669-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Andrew Lane, Richard Higashi and Teresa Fan declare no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
Human tissues reported in Fig. 3 were obtained with informed consent under an IRB-approved protocol at the University of Kentucky.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lane, A.N., Higashi, R.M. & Fan, T.WM. Preclinical models for interrogating drug action in human cancers using Stable Isotope Resolved Metabolomics (SIRM). Metabolomics 12, 118 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1065-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1065-y