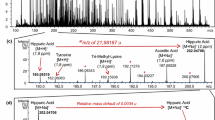
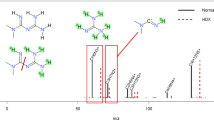
Abstract
Identification of metabolites is a major challenge in biological studies and relies in principle on mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) methods. The increased sensitivity and stability of both NMR and MS systems have made dereplication of complex biological samples feasible. Metabolic databases can be of help in the identification process. Nonetheless, there is still a lack of adequate spectral databases that contain high quality spectra, but new developments in this area will assist in the (semi-)automated identification process in the near future. Here, we discuss new developments for the structural elucidation of low abundant metabolites present in complex sample matrices. We describe how a recently developed combination of high resolution MS multistage fragmentation (MSn) and high resolution one dimensional (1D)-proton (1H)-NMR of liquid chromatography coupled to solid phase extraction (LC–SPE) purified metabolites can circumvent the need for isolating extensive amounts of the compounds of interest to elucidate their structures. The LC–MS–SPE–NMR hardware configuration in conjunction with high quality databases facilitates complete structural elucidation of metabolites even at sub-microgram levels of compound in crude extracts. However, progress is still required to optimally exploit the power of an integrated MS and NMR approach. Especially, there is a need to improve and expand both MSn and NMR spectral databases. Adequate and user-friendly software is required to assist in candidate selection based on the comparison of acquired MS and NMR spectral information with reference data. It is foreseen that these focal points will contribute to a better transfer and exploitation of structural information gained from diverse analytical platforms.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1D-1H-NMR:
-
One dimensional proton nuclear magnetic resonance (spectroscopy)
- 2D:
-
Two dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three dimensional
- DAD:
-
Diode array detector
- Da:
-
Dalton
- HPLC:
-
High pressure/performance liquid chromatography
- LC:
-
Liquid chromatography
- MeOD:
-
Deuterated methanol
- m/z :
-
Mass to charge
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- MSn :
-
Multistage fragmentation mass spectrometry
- MI:
-
Metabolite identification
- MSI:
-
Metabolomics standard initiative
- SPE:
-
Solid phase extraction
- TOF:
-
Time of flight
- Ref:
-
Reference
- RT:
-
Retention time
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
References
Allwood, J. W., De Vos, R. C. H., Moing, A., Deborde, C., Erban, A., Kopka, J., et al. (2011). Plant metabolomics and its potential for systems biology research: Background concepts, technology, and methodology. Methods in Enzymology, 500, 299–336.
Álvarez-Sánchez, B., Priego-Capote, F., & Castro, M. D. L. D. (2010). Metabolomics analysis II. Preparation of biological samples prior to detection. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 29(2), 120–127.
Brand, W., Shao, J., Hoek-Van Den Hil, E. F., Van Elk, K. N., Spenkelink, B., De Haan, L. H. J., et al. (2010). Stereoselective conjugation, transport and bioactivity of S- and R-hesperetin enantiomers in vitro. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 58(10), 6119–6125.
Brand, W., Oosterhuis, B., Krajcsi, P., Barron, D., Dionisi, F., Van Bladeren, P. J., et al. (2011). Interaction of hesperetin glucuronide conjugates with human BCRP, MRP2 and MRP3 as detected in membrane vesicles of overexpressing baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells. Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition, 32(9), 530–535.
Brown, M., Dunn, W. B., Dobson, P., Patel, Y., Winder, C. L., Francis-Mcintyre, S., et al. (2009). Mass spectrometry tools and metabolite-specific databases for molecular identification in metabolomics. Analyst, 134(7), 1322–1332.
Chen, J., Zhao, X., Fritsche, J., Yin, P., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., Wang, W., et al. (2008). Practical approach for the identification and isomer elucidation of biomarkers detected in a metabonomic study for the discovery of individuals at risk for diabetes by integrating the chromatographic and mass spectrometric information. Analytical Chemistry, 80(4), 1280–1289.
Clarkson, C., Staerk, D., Honoré Hansen, S., & Jaroszewski, J. W. (2005). Hyphenation of solid-phase extraction with liquid chromatography and nuclear magnetic resonance: Application of HPLC-DAD-SPE-NMR to identification of constituents of Kanahia laniflora. Analytical Chemistry, 77(11), 3547–3553.
de Rijke, E., Out, P., Niessen, W. M. A., Ariese, F., Gooijer, C., & Brinkman, U. A. T. (2006). Analytical separation and detection methods for flavonoids. Journal of Chromatography A, 1112(1), 31–63.
Elyashberg, M. E., Williams, A. J., & Martin, G. E. (2008). Computer-assisted structure verification and elucidation tools in NMR-based structure elucidation. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, 53(1–2), 1–104.
Exarchou, V., Godejohann, M., Beek, T. A. V., Gerothanassis, I. P., & Vervoort, J. (2003). LC-UV-solid-phase extraction-NMR-MS combined with a cryogenic flow probe and its application to the identification of compounds present in Greek Oregano. Analytical Chemistry, 75, 6288–6294.
Exarchou, V., Krucker, M., Beek, T. A. V., Vervoort, J., Gerothanassis, I. P., & Albert, K. (2005). LC–NMR coupling technology: Recent advancements and applications in natural products analysis. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 43, 681–687.
Harborne, J. B. (1967). Comparative biochemistry of the flavonoids. London: Academic Press.
Heinonen, M., Rantanen, A., Mielikäinen, T., Kokkonen, J., Kiuru, J., Ketola, R. A., et al. (2008). FiD: A software for ab initio structural identification of product ions from tandem mass spectrometric data. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 22(19), 3043–3052.
Hill, A. W., & Mortishire-Smith, R. J. (2005). Automated assignment of high-resolution collisionally activated dissociation mass spectra using a systematic bond disconnection approach. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 19(21), 3111–3118.
Jaroszewski, J. W. (2005). Hyphenated NMR methods in natural products research, part 2: HPLC-SPE-NMR and other new trends in NMR hyphenation. Planta Medica, 71(9), 795–802.
Jewison, T., Knox, C., Neveu, V., Djoumbou, Y., Guo, A. C., Lee, J., et al. (2012). YMDB: The yeast metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(D1), D815–D820.
Kesting, J. R., Olsen, L., Staerk, D., Tejesvi, M. V., Kini, K. R., Prakash, H. S., et al. (2011). Production of unusual dispiro metabolites in Pestalotiopsis virgatula endophyte cultures: HPLC-SPE-NMR, electronic circular dichroism, and time-dependent density-functional computation study. Journal of Natural Products, 74(10), 2206–2215.
Kind, T., & Fiehn, O. (2007). Seven golden rules for heuristic filtering of molecular formulas obtained by accurate mass spectrometry. Bmc Bioinformatics, 8, 105.
Kind, T., & Fiehn, O. (2010). Advances in structure elucidation of small molecules using mass spectrometry. Bioanalytical Reviews, 2(1), 23–60.
Kueger, S., Steinhauser, D., Willmitzer, L., & Giavalisco, P. (2012). High-resolution plant metabolomics: From mass spectral features to metabolites and from whole-cell analysis to subcellular metabolite distributions. Plant Journal, 70(1), 39–50.
Laatikainen, R., Niemitz, M., Weber, U., Sundeun, J., Hassinen, T., & Vepsäläinen, J. (1996). General strategies for total-lineshape-type spectral analysis of NMR spectra using integral-transform iterator. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, Series A, 120(1), 1–10.
Lin, L.-Z., Chen, P., & Harnly, J. M. (2008). New phenolic components and chromatographic profiles of green and fermented teas. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(17), 8130–8140.
Ludwig, C., Easton, J. M., Lodi, A., Tiziani, S., Manzoor, S. E., Southam, A. D., et al. (2012). Birmingham metabolite library: A publicly accessible database of 1-D 1H and 2-D 1H J-resolved NMR spectra of authentic metabolite standards (BML-NMR). Metabolomics, 8(1), 8–18.
Moco, S., & Vervoort, J. (2012). Chemical identification strategies using liquid chromatography-photodiode array-solid-phase extraction-nuclear magnetic resonance/mass spectrometry. In N. W. Hardy, & R. D. Hall (Eds.). Methods in Molecular Biology, 860, 287–316.
Moco, S., Bino, R. J., Vorst, O., Verhoeven, H. A., de Groot, J., van Beek, T. A., et al. (2006). A liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolome database for tomato. Plant Physiology, 141(4), 1205–1218.
Moco, S., Bino, R. J., De Vos, R. C. H., & Vervoort, J. (2007). Metabolomics technologies and metabolite identification. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 26(9), 855–866.
Molinski, T. F. (2010). NMR of natural products at the ‘nanomole-scale’. Natural Products Reports, 27(3), 321–329.
Muñoz, M. A., Perez-Hernandez, N., Pertino, M. W., Schmeda-Hirschmann, G., & Joseph-Nathan, P. (2012). Absolute Configuration and 1H NMR characterization of rosmaridiphenol diacetate. Journal of Natural Products, 75(4), 779–783.
Nicoli, R., Martel, S., Rudaz, S., Wolfender, J. L., Veuthey, J. L., Carrupt, P. A., et al. (2010). Advances in LC platforms for drug discovery. Expert Opinion Drug Discovery, 5(5), 475–489.
Olsen, H., Aaby, K., & Borge, G. I. A. (2009). Characterization and quantification of flavonoids and hydroxycinnamic acids in curly kale (Brassica oleracea L. convar. acephala var. sabellica) by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 57(7), 2816–2825.
Ottaviani, J. I., Momma, T. Y., Heiss, C., Kwik-Uribe, C., Schroeter, H., & Keen, C. L. (2011). The stereochemical configuration of flavanols influences the level and metabolism of flavanols in humans and their biological activity in vivo. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 50(2), 237–244.
Peironcely, J. E., Reijmers, T., Coulier, L., Bender, A., & Hankemeier, T. (2011). Understanding and classifying metabolite space and metabolite-likeness. PLoS One, 6(12), e28966.
Psychogios, N., Hau, D. D., Peng, J., Guo, A. C., Mandal, R., Bouatra, S., et al. (2012). The human serum metabolome. PLoS One, 6(2), e16957.
Puiggròs, F., Solà, R., Bladé, C., Salvadó, M. J., & Arola, L. (2011). Nutritional biomarkers and foodomic methodologies for qualitative and quantitative analysis of bioactive ingredients in dietary intervention studies. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218(42), 7399–7414.
Qiu, F., Imai, A., McAlpine, J. B., Lankin, D. C., Burton, I., Karakach, T., et al. (2012). Dereplication, residual complexity, and rational naming: The case of the actaea triterpenes. Journal of Natural Products, 75(3), 432–443.
Rasche, F., Scheubert, K., Hufsky, F., Zichner, T., Kai, M., Svatoš, A., et al. (2012). Identifying the unknowns by aligning fragmentation trees. Analytical Chemistry, 84(12), 3417–3426.
Ridder, L., van der Hooft, J. J. J., Verhoeven, S., De Vos, R. C. H., Van Schaik, R., & Vervoort, J. (2012). Substructure-based annotation of high-resolution multistage MSn spectral trees. Rapid Communication in Mass Spectrometry, 26(20), 2461–2471.
Rojas-Cherto, M., Peironcely, J. E., Kasper, P. T., van der Hooft, J. J. J., De Vos, R. C. H., Vreeken, R. J., et al. (2012). Metabolite identification using automated comparison of high resolution MSn spectral trees. Analytical Chemistry, 84(13), 5524–5534.
Rojas-Chertó, M., van Vliet, M., Peironcely, J. E., van Doorn, R., Kooyman, M., Beek, T. T., et al. (2012). MetiTree: A web application to organize and process high resolution multi-stage mass spectrometry metabolomics data. Bioinformatics, 28(20), 2707–2709.
Scalbert, A., Andres-Lacueva, C., Arita, M., Kroon, P., Manach, C., Urpi-Sarda, M., et al. (2011). Databases on food phytochemicals and their health-promoting effects. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(9), 4331–4348.
Sprogøe, K., Staerk, D., Ziegler, H. L., Jensen, T. H., Holm-Møller, S. B., & Jaroszewski, J. W. (2008). Combining HPLC-PDA-MS-SPE-NMR with circular dichroism for complete natural product characterization in crude extracts: Levorotatory gossypol in Thespesia danis. Journal of Natural Products, 71(4), 516–519.
Sturm, S., & Seger, C. (2012). Liquid chromatography-nuclear magnetic resonance coupling as alternative to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry hyphenations: Curious option or powerful and complementary routine tool? Journal of Chromatography A, 1259, 50–61.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics, 3(3), 211–221.
Tang, H., Xia, C., & Wang, Y. (2009). Important roles of the hyphenated HPLC-DAD-MS-SPE-NMR technique in metabonomics. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 47, S157–S162.
Tohge, T., & Fernie, A. R. (2009). Web-based resources for mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics: A user’s guide. Phytochemistry, 70(4), 450–456.
van der Hooft, J. J. J., Mihaleva, V., Bino, R. J., de Vos, R. C. H., & Vervoort, J. (2011a). A strategy for fast structural elucidation of metabolites in small volume plant extracts using automated MS-guided LC-MS-SPE-NMR. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 49(S1), S55–S60.
van der Hooft, J. J. J., Vervoort, J., Bino, R. J., Beekwilder, J., & De Vos, R. C. H. (2011b). Polyphenol identification based on systematic and robust high-resolution accurate mass spectrometry fragmentation. Analytical Chemistry, 83(1), 409–416.
van der Hooft, J. J. J., Akermi, M., Ünlü, F. Y., Mihaleva, V., Roldan, V. G., Bino, R. J., et al. (2012a). Structural annotation and elucidation of conjugated phenolic compounds in black, green, and white tea extracts. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60, 8841–8850.
van der Hooft, J. J. J., De Vos, R. C. H., Mihaleva, V., Bino, R. J., Ridder, L., de Roo, N., et al. (2012b). Structural elucidation and quantification of phenolic conjugates present in human urine after tea intake. Analytical Chemistry, 84(16), 7263–7271.
van der Hooft, J. J. J., Vervoort, J., Bino, R. J., & de Vos, R. C. H. (2012c). Spectral trees as a robust annotation tool in LC-MS based metabolomics. Metabolomics, 8(4), 691–703.
Watson, J. T., & Sparkman, O. D. (2007). Introduction to mass spectrometry (4th ed.). West Sussex: Wiley.
Wishart, D. S. (2011). Advances in metabolite identification. Bioanalysis, 3(15), 1769–1782.
Wishart, D. S., Knox, C., Guo, A. C., Eisner, R., Young, N., Gautam, B., et al. (2009). HMDB: A knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Research, 37(Suppl 1), D603–D610.
Wolf, S., Schmidt, S., Möller-Hannemann, M., & Neumann, S. (2010). In silico fragmentation for computer assisted identification of metabolite mass spectra. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 148.
Wolfender, J. L., Marti, G., & Queiroz, E. F. (2010). Advances in techniques for profiling crude extracts and for the rapid identification of natural products: Dereplication, quality control and metabolomics. Current Organic Chemistry, 14(16), 1808–1832.
Wubshet, S. G., Johansen, K. T., Nyberg, N. T., & Jaroszewski, J. W. (2012). Direct 13C NMR detection in HPLC hyphenation mode: Analysis of Ganoderma lucidum terpenoids. Journal of Natural Products, 75(5), 876–882.
Xiao, J. F., Zhou, B., & Ressom, H. W. (2012). Metabolite identification and quantitation in LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 32, 1–14.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Dr. Alan Crozier for his time to read and comment on the manuscript. This research was funded by the Netherlands Metabolomics Centre (JJJvdH, JV, RCHdV) and the Centre for BioSystems Genomics (RJB, RCHdV), both of which are part of the Netherlands Genomics Initiative/Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Hooft, J.J.J., de Vos, R.C.H., Ridder, L. et al. Structural elucidation of low abundant metabolites in complex sample matrices. Metabolomics 9, 1009–1018 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0519-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0519-8