Abstract
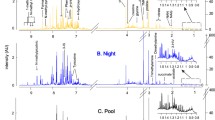
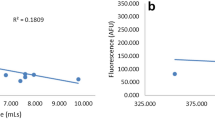
Urine is often sampled from patients participating in clinical and metabolomic studies. Biological homeostasis occurs in humans, but little is known about the variability of metabolites found in urine. It is important to define the inter- and intra-individual metabolite variance within a normal population before scientific or clinical conclusions are made regarding different pathophysiologies. This study investigates the variability of selected urine metabolites in a group of 60 healthy men and women over a period of 30 days. To monitor individual variation, 6 women from the normal population were randomly selected and followed for 30 days. To determine the influence of extraneous environmental factors urine was collected from 25 guinea pigs with similar genetics, diet, and living environment. For both studies, 24 metabolites were identified and quantified using high-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). The data demonstrated large inter and intra-individual variation in metabolite concentrations in both normal human and control animal populations. A defined normal baseline is essential before any conclusions may be drawn regarding changes in urine metabolite concentrations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aspevall, O., Hallander, H., Gant, V., & Kouri, T. (2001). European guidelines for urinalysis: a collaborative document produced by European clinical microbiologists and clinical chemists under ECLM in collaboration with ESCMID. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 7, 173–178.
Assadi, F. K. (2002). Quantitation of microalbuminuria using random urine samples. Pediatric Nephrology, 17, 107–110.
Bollard, M. E., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., Mitchell, S. C., Branstetter, D., Zhang, W., & Nicholson, J. K. (2001). Investigations into biochemical changes due to diurnal variation and estrus cycle in female rats using high-resolution (1)H NMR spectroscopy of urine and pattern recognition. Analytical Biochemistry, 295, 194–202.
Bollard, M. E., Stanley, E. G., Lindon, J. C., Nicholson, J. K., & Holmes, E. (2005). NMR-based metabonomic approaches for evaluating physiological influences on biofluid composition. NMR in Biomedicine, 18, 143–162.
Brindle, J. T., Antti, H., Holmes, E., Tranter, G., Nicholson, J. K., Bethell, H. W., Clarke, S., Schofield, P. M., Mckilligin, E., Mosedale, D. E., & Grainger, D. J. (2002). Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1H-NMR-based metabonomics. Nature Medicine, 8, 1439–1244.
Cavaluzzi, M. J., Kerwood, D. J., & Borer, P. N. (2002). Accurate nucleic acid concentrations by nuclear magnetic resonance. Analytical Biochemistry, 308, 373–380.
Chadha, V., Garg, U., & Alon, U. S. (2001). Measurement of urinary concentration: A critical appraisal of methodologies. Pediatric Nephrology, 16, 374–382.
Chung, Y. L., Rider, L. G., Bell, J. D., Summers, R. M., Zemel, L. S., Rennebohm, R. M., Passo, M. H., Hicks, J., Miller, F. W., & Scott, D. L. (2005). Muscle metabolites, detected in urine by proton spectroscopy, correlate with disease damage in juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 53, 565–570.
Coen, M., O’Sullivan, M., Bubb, W. A., Kuchel, P. W., & Sorrell, T. (2005). Proton nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomics for rapid diagnosis of meningitis and ventriculitis. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 41, 1582–1590.
Crockford, D. J., Keun, H. C., Smith, L. M., Holmes, E., & Nicholson, J. K. (2005). Curve-fitting method for direct quantitation of compounds in complex biological mixtures using 1H NMR: Application in metabonomic toxicology studies. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 4556–4562.
De Jongste, J. C. (2000). Surrogate markers of airway inflammation: Inflammometry in paediatric respiratory medicine. Paediatric Respiratory Reviews, 1, 354–360.
Duarte, I. F., Stanley, E. G., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., Gil, A. M., Tang, H., Ferdinand, R., Mckee, C. G., Nicholson, J. K., Vilca-Melendez, H., Heaton, N., & Murphy, G. M. (2005). Metabolic assessment of human liver transplants from biopsy samples at the donor and recipient stages using high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 5570–5578.
Dunn, W. B., Bailey, N. J., & Johnson, H. E. (2005). Measuring the metabolome: Current analytical technologies. The Analyst, 130, 606–625.
Dyer, A., Elliott, P., Chee, D., & Stamler, J. (1997). Urinary biochemical markers of dietary intake in the INTERSALT study. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 65, 1246S–1253S.
Ebbels, T. M., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2004). Evaluation of metabolic variation in normal rat strains from a statistical analysis of 1H NMR spectra of urine. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 36, 823–833.
Ekins, S., Nikolsky, Y., & Nikolskaya, T. (2005). Techniques: Application of systems biology to absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 26, 202–209.
Gavaghan, C. L., Wilson, I. D., & Nicholson, J. K. (2002). Physiological variation in metabolic phenotyping and functional genomic studies: Use of orthogonal signal correction and PLS-DA. FEBS Letters, 530, 191–196.
Geigy, A. L. (1981–1992). Geigy scientific tables. West Cadwell, NJ: Ciba-Geigy Corp.
Green, R. H., Brightling, C. E., Mckenna, S., Hargadon, B., Parker, D., Bradding, P., Wardlaw, A. J., & Pavord, I. D. (2002). Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet, 360, 1715–1721.
Guneral, F., & Bachmann, C. (1994). Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population. Clinical Chemistry, 40, 862–866.
Holmes, E., Nicholls, A. W., Lindon, J. C., Connor, S. C., Connelly, J. C., Haselden, J. N., Damment, S. J., Spraul, M., Neidig, P., & Nicholson, J. K. (2000). Chemometric models for toxicity classification based on NMR spectra of biofluids. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 13, 471–478.
Keller, N. P., Turner, G., & Bennett, J. W. (2005). Fungal secondary metabolism—from biochemistry to genomics. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 3, 937–947.
Keun, H. C., Ebbels, T. M., Antti, H., Bollard, M. E., Beckonert, O., Schlotterbeck, G., Senn, H., Niederhauser, U., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., & Nicholson, J. K. (2002). Analytical reproducibility in (1)H NMR-based metabonomic urinalysis. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 15, 1380–1386.
Kraut, J. A., & Kurtz, I. (2005). Metabolic acidosis of CKD: Diagnosis, clinical characteristics, and treatment. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 45, 978–993.
Kubitz, R., Keitel, V., & Haussinger, D. (2005). Inborn errors of biliary canalicular transport systems. Methods in Enzymology, 400, 558–569.
Kumar, A., Ernst, R. R., & Wuthrich, K. (1980). A two-dimensional nuclear overhauser enhancement (2D NOE) experiment for the elucidation of complete proton–proton cross-relaxation networks in biological macromolecules. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 95, 1–6.
Lenz, E. M., Bright, J., Wilson, I. D., Morgan, S. R., & Nash, A. F. (2003). A 1H NMR-based metabonomic study of urine and plasma samples obtained from healthy human subjects. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 33, 1103–1115.
Lenz, E. M., Bright, J., Wilson, I. D., Hughes, A., Morrisson, J., Lindberg, H., & Lockton, A. (2004). Metabonomics, dietary influences and cultural differences: A 1H NMR-based study of urine samples obtained from healthy British and Swedish subjects. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 36, 841–849.
Lindon, J. C., Holmes, E., Bollard, M. E., Stanley, E. G., & Nicholson, J. K. (2004). Metabonomics technologies and their applications in physiological monitoring, drug safety assessment and disease diagnosis. Biomarkers, 9, 1–31.
Moolenaar, S. H., Engelke, U. F., & Wevers, R. A. (2003). Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of body fluids in the field of inborn errors of metabolism. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, 40, 16–24.
Phipps, A. N., Stewart, J., Wright, B., & Wilson, I. D. (1998). Effect of diet on the urinary excretion of hippuric acid and other dietary-derived aromatics in rat. A complex interaction between diet, gut microflora and substrate specificity. Xenobiotica, 28, 527–537.
Rastall, R. A., Gibson, G. R., Gill, H. S., Guarner, F., Klaenhammer, T. R., Pot, B., Reid, G., Rowland, I. R., & Sanders, M. E. (2005). Modulation of the microbial ecology of the human colon by probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics to enhance human health: An overview of enabling science and potential applications. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 52, 145–152.
Sabatine, M. S., Liu, E., Morrow, D. A., Heller, E., Mccarroll, R., Wiegand, R., Berriz, G. F., Roth, F. P., & Gerszten, R. E. (2005). Metabolomic identification of novel biomarkers of myocardial ischemia. Circulation, 112, 3868–3875.
Sardari, S., & Sardari, D. (2002). Applications of artificial neural network in AIDS research and therapy. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 8, 659–670.
Saude, E. J., Slupsky, C. M., & Sykes, B. D. (2006). Optimization of NMR analysis of biological fluids for quantitative accuracy. Metabolomics, 2, 113–123.
Saude, E. J., Sykes, B. D. (2007). Urine stability for metabolomic studies: Effects of preparation and storage. Metabolomics, 3, 19–27.
Shockcor, J. P., & Holmes, E. (2002). Metabonomic applications in toxicity screening and disease diagnosis. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 2, 35–51.
Singer, M. (2005). Metabolic failure. Critical Care Medicine, 33, S539–s542.
Slupsky, C. M., Rankin, K., Wagner, J., Fu, H., Chang, D., Weljie, A. M., Saude, E. J., Lix, B., Adamko, D. J., Shah, S., Greiner, R., Sykes, B. D., Marrie, T. J. (2007). Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Analytical Chemistry, 79, in press.
Somorjai, R. L., Dolenko, B., Demko, A., Mandelzweig, M., Nikulin, A. E., Baumgartner, R., & Pizzi, N. J. (2004). Mapping high-dimensional data onto a relative distance plane—an exact method for visualizing and characterizing high-dimensional patterns. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 37, 366–379.
Stanley, E. G., Bailey, N. J., Bollard, M. E., Haselden, J. N., Waterfield, C. J., Holmes, E., & Nicholson, J. K. (2005). Sexual dimorphism in urinary metabolite profiles of Han Wistar rats revealed by nuclear-magnetic-resonance-based metabonomics. Analytical Biochemistry, 343, 195–202.
Stoyanova, R., & Brown, T. R. (2001). NMR spectral quantitation by principal component analysis. NMR in Biomedicine, 14, 271–277.
Symanski, E., & Greeson, N. M. (2002). Assessment of variability in biomonitoring data using a large database of biological measures of exposure. AIHA Journal (Fairfax, Va), 63, 390–401.
Tate, A. R., Damment, S. J., & Lindon, J. C. (2001). Investigation of the metabolite variation in control rat urine using (1)H NMR spectroscopy. Analytical Biochemistry, 291, 17–26.
Trachtenbarg, D. E. (2005). Diabetic ketoacidosis. American Family Physician, 71, 1705–1714.
Van Rhijn, B. W., Van Der Poel, H. G., & Van Der Kwast, T. H. (2005). Urine markers for bladder cancer surveillance: A systematic review. European Urology, 47, 736–748.
Weckwerth, W. (2003). Metabolomics in systems biology. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 54, 669–689.
Wennergren, G. (2000). Inflammatory mediators in blood and urine. Paediatric Respiratory Review, 1, 259–265.
Zuppi, C., Messana, I., Forni, F., Rossi, C., Pennacchietti, L., Ferrari, F., & Giardina, B. (1997). 1H NMR spectra of normal urines: Reference ranges of the major metabolites. Clinica Chimica Acta, 265, 85–97.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the volunteers for their participation in the study, Bruce Lix for his assistance with organization, Shana Regush for her assistance with sample preparation and data acquisition, Carol Mangan for her logistical management of the study, Dr. Edward Akhmetshin for his expertise in statistical analysis, and Ryan McKay for his thorough reviews of the manuscript. This research was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), Genome Prairie, and Genome Canada, and by an establishment grant from the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research (AHFMR) to T. Marrie. We would like to thank the Canadian National High Field NMR Centre (NANUC) for their assistance and use of the facilities. CIHR, the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the University of Alberta fund the operation of NANUC. Drs. Rowe and Sykes are supported by Canada Research Chairs. Dr. Adamko is supported by AHFMR as a Clinical Investigator. Magnetic Resonance Diagnostic Centre (MRDC) is supported by establishment grants from the Alberta Science and Research Authority (ASRA), and Western Economic Development (WED). All of the authors are members of the Medical Resonance Diagnostics Centre (MRDC) at the University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.
Support: Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), Genome Prairie, Genome Canada, an establishment grant from the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research (AHFMR), the Canadian National High Field NMR Centre (NANUC), the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the University of Alberta fund, the Magnetic Resonance Diagnostic Centre (MRDC), the Alberta Science and Research Authority (ASRA), and Western Economic Development (WED).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saude, E.J., Adamko, D., Rowe, B.H. et al. Variation of metabolites in normal human urine. Metabolomics 3, 439–451 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0091-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-007-0091-1