Abstract
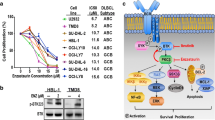
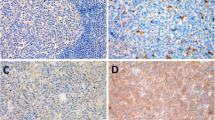
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of invasive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 60–70% of patients are curable with current chemoimmunotherapy, whereas the rest are refractory or relapsed. Understanding of the interaction between DLBCL cells and tumor microenvironment raises the hope of improving overall survival of DLBCL patients. P2X7, a member of purinergic receptors P2X family, is activated by extracellular ATP and subsequently promotes the progression of various malignancies. However, its role in DLBCL has not been elucidated. In this study, the expression level of P2RX7 in DLBCL patients and cell lines was analyzed. MTS assay and EdU incorporation assay were carried out to study the effect of activated/inhibited P2X7 signaling on the proliferation of DLBCL cells. Bulk RNAseq was performed to explore potential mechanism. The results demonstrated high level expression of P2RX7 in DLBCL patients, typically in patients with relapse DLBCL. 2′(3′)-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl) adenosine 5-triphosphate (Bz-ATP), an agonist of P2X7, significantly accelerated the proliferation of DLBCL cells, whereas delayed proliferation was detected when administrated with antagonist A740003. Furthermore, a urea cycle enzyme named CPS1 (carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1), which up-regulated in P2X7-activated DLBCL cells while down-regulated in P2X7-inhibited group, was demonstrated to involve in such process. Our study reveals the role of P2X7 in the proliferation of DLBCL cells and implies that P2X7 may serve as a potential molecular target for the treatment of DLBCL.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that had been used for the findings of this research project are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Chapuy B, Stewart C, Dunford AJ, Kim J, Kamburov A, Redd RA et al (2018) Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat Med 24:679–690. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0016-8
Pasqualucci L, Dalla-Favera R (2014) SnapShot: diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 25:132–132. e131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.12.012
Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, Tolar P, Young RM, Romesser PB et al (2010) Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 463:88–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08638
Lenz G, Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lam L, George TC, Wright GW et al (2008) Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science 319:1676–1679. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1153629
Kaur J, Dora S (2023) Purinergic signaling: diverse effects and therapeutic potential in cancer. Front Oncol 13:1058371. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1058371
Di Virgilio F, Sarti AC, Falzoni S, De Marchi E, Adinolfi E (2018) Extracellular ATP and P2 purinergic signalling in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer 18:601–618. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0037-0
Burnstock G, Di Virgilio F (2013) Purinergic signalling and cancer. Purinergic Signal 9:491–540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-013-9372-5
Mai Y, Guo Z, Yin W, Zhong N, Dicpinigaitis PV, Chen R (2021) P2X receptors: potential therapeutic targets for symptoms Associated with Lung Cancer - A Mini Review. Front Oncol 11:691956. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.691956
Nagel D, Vincendeau M, Eitelhuber AC, Krappmann D (2014) Mechanisms and consequences of constitutive NF-kappaB activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Oncogene 33:5655–5665. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.565
Jelassi B, Chantome A, Alcaraz-Perez F, Baroja-Mazo A, Cayuela ML, Pelegrin P et al (2011) P2X(7) receptor activation enhances SK3 channels- and cystein cathepsin-dependent cancer cells invasiveness. Oncogene 30:2108–2122. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.593
Burnstock G (2016) P2X ion channel receptors and inflammation. Purinergic Signal 12:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-015-9493-0
Burnstock G, Knight GE (2018) The potential of P2X7 receptors as a therapeutic target, including inflammation and tumour progression. Purinergic Signal 14:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-017-9593-0
Feng W, Yang F, Wang R, Yang X, Wang L, Chen C et al (2016) High level P2X7-Mediated signaling impairs function of hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep 12:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-016-9651-y
Feng W, Yang X, Wang L, Wang R, Yang F, Wang H et al (2021) P2X7 promotes the progression of MLL-AF9 induced acute myeloid leukemia by upregulation of Pbx3. Haematologica 106:1278–1289. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.243360
Morgan R, Pandha HS (2020) PBX3 in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020431
Adinolfi E, Melchiorri L, Falzoni S, Chiozzi P, Morelli A, Tieghi A et al (2002) P2X7 receptor expression in evolutive and indolent forms of chronic B lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 99:706–708. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v99.2.706
He X, Wan J, Yang X, Zhang X, Huang D, Li X et al (2021) Bone marrow niche ATP levels determine leukemia-initiating cell activity via P2X7 in leukemic models. J Clin Invest 131. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI140242
Illes P, Muller CE, Jacobson KA, Grutter T, Nicke A, Fountain SJ et al (2021) Update of P2X receptor properties and their pharmacology: IUPHAR Review 30. Br J Pharmacol 178:489–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15299
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ (2012) Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent among samples. Theory Biosci 131:281–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-012-0162-3
Compagno M, Lim WK, Grunn A, Nandula SV, Brahmachary M, Shen Q et al (2009) Mutations of multiple genes cause deregulation of NF-kappaB in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 459:717–721. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07968
Brune V, Tiacci E, Pfeil I, Doring C, Eckerle S, van Noesel CJ et al (2008) Origin and pathogenesis of nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma as revealed by global gene expression analysis. J Exp Med 205:2251–2268. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20080809
Vicente-Duenas C, Fontan L, Gonzalez-Herrero I, Romero-Camarero I, Segura V, Aznar MA et al (2012) Expression of MALT1 oncogene in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells recapitulates the pathogenesis of human lymphoma in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:10534–10539. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1204127109
Gomez-Abad C, Pisonero H, Blanco-Aparicio C, Roncador G, Gonzalez-Menchen A, Martinez-Climent JA et al (2011) PIM2 inhibition as a rational therapeutic approach in B-cell lymphoma. Blood 118:5517–5527. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-03-344374
Juskevicius D, Lorber T, Gsponer J, Perrina V, Ruiz C, Stenner-Liewen F et al (2016) Distinct genetic evolution patterns of relapsing diffuse large B-cell lymphoma revealed by genome-wide copy number aberration and targeted sequencing analysis. Leukemia 30:2385–2395. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.135
Scholtysik R, Kreuz M, Hummel M, Rosolowski M, Szczepanowski M, Klapper W et al (2015) Characterization of genomic imbalances in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by detailed SNP-chip analysis. Int J Cancer 136:1033–1042. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29072
Dybkaer K, Bogsted M, Falgreen S, Bodker JS, Kjeldsen MK, Schmitz A et al (2015) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma classification system that associates normal B-cell subset phenotypes with prognosis. J Clin Oncol 33:1379–1388. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.57.7080
Marques SC, Ranjbar B, Laursen MB, Falgreen S, Bilgrau AE, Bodker JS et al (2016) High miR-34a expression improves response to doxorubicin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Exp Hematol 44:238–246e232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2015.12.007
Barrans SL, Crouch S, Care MA, Worrillow L, Smith A, Patmore R et al (2012) Whole genome expression profiling based on paraffin embedded tissue can be used to classify diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and predict clinical outcome. Br J Haematol 159:441–453. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12045
Tarantelli C, Gaudio E, Arribas AJ, Kwee I, Hillmann P, Rinaldi A et al (2018) PQR309 is a Novel Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor with Preclinical Antitumor Activity in Lymphomas as a single Agent and in combination therapy. Clin Cancer Res 24:120–129. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1041
Petrich AM, Leshchenko V, Kuo PY, Xia B, Thirukonda VK, Ulahannan N et al (2012) Akt inhibitors MK-2206 and nelfinavir overcome mTOR inhibitor resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 18:2534–2544. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1407
Chong JH, Zheng GG, Ma YY, Zhang HY, Nie K, Lin YM et al (2010) The hyposensitive N187D P2X7 mutant promotes malignant progression in nude mice. J Biol Chem 285:36179–36187. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.128488
Summar ML, Dasouki MJ, Schofield PJ, Krishnamani MR, Vnencak-Jones C, Tuchman M et al (1995) Physical and linkage mapping of human carbamyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS1) and reassignment from 2p to 2q35. Cytogenet Cell Genet 71:266–267. https://doi.org/10.1159/000134124
Morris SM Jr (2002) Regulation of enzymes of the urea cycle and arginine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 22:87–105. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.110801.140547
Coiffier B, Sarkozy C (2016) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: R-CHOP failure-what to do? Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2016:366–378. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2016.1.366
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P et al (2007) The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109:1857–1861. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-08-038257
Gisselbrecht C, Glass B, Mounier N, Singh Gill D, Linch DC, Trneny M et al (2010) Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J Clin Oncol 28:4184–4190. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.28.1618
Chen YJ, Abila B, Mostafa Kamel Y (2023) CAR-T: what is next? Cancers. 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030663
Del Toro-Mijares R, Oluwole O, Jayani RV, Kassim AA, Savani BN, Dholaria B (2023) Relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy: current challenges and therapeutic options. Br J Haematol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.18656
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A et al (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/35000501
Chen L, Monti S, Juszczynski P, Ouyang J, Chapuy B, Neuberg D et al (2013) SYK inhibition modulates distinct PI3K/AKT- dependent survival pathways and cholesterol biosynthesis in diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Cancer Cell 23:826–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2013.05.002
Adinolfi E, Cirillo M, Woltersdorf R, Falzoni S, Chiozzi P, Pellegatti P et al (2010) Trophic activity of a naturally occurring truncated isoform of the P2X7 receptor. FASEB J 24:3393–3404. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-153601
Giuliani AL, Colognesi D, Ricco T, Roncato C, Capece M, Amoroso F et al (2014) Trophic activity of human P2X7 receptor isoforms a and B in osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE 9:e107224. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107224
Pegoraro A, Orioli E, De Marchi E, Salvestrini V, Milani A, Di Virgilio F et al (2020) Differential sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells to daunorubicin depends on P2X7A versus P2X7B receptor expression. Cell Death Dis 11:876. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03058-9
Zanoni M, Sarti AC, Zamagni A, Cortesi M, Pignatta S, Arienti C et al (2022) Irradiation causes senescence, ATP release, and P2X7 receptor isoform switch in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis 13:80. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04526-0
He X, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Xie L, Yu Z, Zheng J (2021) Function of the P2X7 receptor in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Exp Hematol 104:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2021.10.001
Bian S, Sun X, Bai A, Zhang C, Li L, Enjyoji K et al (2013) P2X7 integrates PI3K/AKT and AMPK-PRAS40-mTOR signaling pathways to mediate Tumor Cell Death. PLoS ONE 8:e60184. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060184
Butler SL, Dong H, Cardona D, Jia M, Liu C (2008) The antigen for Hep Par 1 antibody is the urea cycle enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1. Lab Invest 88:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.3700699
elikta M, Tanaka I, Tripathi SC, Fahrmann JF, Aguilar-Bonavides C, Villalobos P et al (2017) Role of CPS1 in cell growth, metabolism, and prognosis in LKB1-Inactivated lung adenocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 109:1. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djw231
Funding
This work was supported by grant 2020JQ-546 from the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi; grant 81802862 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); the Personnel Training Specialized Research Foundation RC(XM)202002 from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiao Yang acquired funding, designed and performed experiments, analyzed and interpreted data and wrote the manuscript. Yuanyuan Ji designed experiments, interpreted data. Lin Mei, Wenwen Jing and Xin Yang performed experiments, analyzed and interpreted data. Qianwei Liu analyzed and interpreted data. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no other competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xiao Yang and Yuanyuan Ji contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.



Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Ji, Y., Mei, L. et al. Potential role of the P2X7 receptor in the proliferation of human diffused large B-cell lymphoma. Purinergic Signalling (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-023-09947-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-023-09947-w